
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: \(\left(x,y\right)\in\left\{\left(1;2\right);\left(-1;-2\right);\left(2;1\right);\left(-2;-1\right)\right\}\)

a) Nhân 7 với 0; 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; … ta được các bội của 7 là: 0; 7; 14; 21; 28; 35; 42; 49; 56; 63; 70;…
Ta được B(7) = {0; 7; 14; 21; 28; 35; 42; 49; 56; 63; 70;…}. Mà x ∈ B(7) và x < 70
Vậy x ∈ {0; 7; 14; 21; 28; 35; 42; 49; 56; 63}.
b) Chia 50 cho các số từ 1 đến 50, ta thấy 50 chia hết cho 1; 2; 5; 10; 25; 50 nên
Ư(50) = {1; 2; 5; 10; 25; 50}. Mà y ∈ Ư(50) và y > 5
Vậy y ∈ {10; 25; 50}.


Bài 10:
a: 2x-3 là bội của x+1
=>\(2x-3⋮x+1\)
=>\(2x+2-5⋮x+1\)
=>\(-5⋮x+1\)
=>\(x+1\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{0;-2;4;-6\right\}\)
b: x-2 là ước của 3x-2
=>\(3x-2⋮x-2\)
=>\(3x-6+4⋮x-2\)
=>\(4⋮x-2\)
=>\(x-2\inƯ\left(4\right)\)
=>\(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{3;1;4;0;6;-2\right\}\)
Bài 14:
a: \(4n-5⋮2n-1\)
=>\(4n-2-3⋮2n-1\)
=>\(-3⋮2n-1\)
=>\(2n-1\inƯ\left(-3\right)\)
=>\(2n-1\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
=>\(2n\in\left\{2;0;4;-2\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{1;0;2;-1\right\}\)
mà n>=0
nên \(n\in\left\{1;0;2\right\}\)
b: \(n^2+3n+1⋮n+1\)
=>\(n^2+n+2n+2-1⋮n+1\)
=>\(n\left(n+1\right)+2\left(n+1\right)-1⋮n+1\)
=>\(-1⋮n+1\)
=>\(n+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)
mà n là số tự nhiên
nên n=0

\(x\in\left\{0;4;8;12;16;20;24;28;32;36;40;44;48\right\}\)
\(y\in\left\{1;2;4;13;26;52\right\}\)

a) Ta có: (x-3)(y+2)=5
nên (x-3) và (y+2) là ước của 5
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3;y+2\in\left\{1;-5;-1;5\right\}\)
Trường hợp 1:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=1\\y+2=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\y=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 2:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=5\\y+2=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=8\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 3:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=-1\\y+2=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 4:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3=-5\\y+2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(\left(x,y\right)\in\left\{\left(4;3\right);\left(8;-1\right);\left(2;-7\right);\left(-2;-3\right)\right\}\)
b) Ta có: (x-2)(y+1)=5
nên x-2 và y+1 là các ước của 5
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2;y+1\in\left\{1;-1;5;-5\right\}\)
Trường hợp 1:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=1\\y+1=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 2:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=5\\y+1=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=7\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 3:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=-1\\y+1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
Trường hợp 4:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2=-5\\y+1=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(\left(x,y\right)\in\left\{\left(3;4\right);\left(7;0\right);\left(1;-6\right);\left(-3;-2\right)\right\}\)
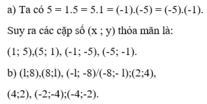

a) Ta có 5 = 1.5 = 5.1 = (-1).(-5) = (-5).(-1).
Suy ra các cặp số (x ; y) thỏa mãn là:
(1; 5),(5; 1), (-1; -5), (-5; -1).
b) (l;8),(8;l), (-l; -8)/(-8;- l);(2;4), (4;2), (-2;-4);(-4;-2).