Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Câu 1: Lời giải:
a, Đặt \(A=\dfrac{3x+7}{x-1}\).
Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{3x+7}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x-3+10}{x-1}=\dfrac{3x-3}{x-1}+\dfrac{10}{x-1}=3+\dfrac{10}{x-1}\)
Để \(A\in Z\) thì \(\dfrac{10}{x-1}\in Z\Rightarrow10⋮x-1\Leftrightarrow x-1\in U\left(10\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm5;\pm10\right\}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
| \(x-1\) | \(1\) | \(-1\) | \(2\) | \(-2\) | \(5\) | \(-5\) | \(10\) | \(-10\) |
| \(x\) | \(2\) | \(0\) | \(3\) | \(-1\) | \(6\) | \(-4\) | \(11\) | \(-9\) |
Vậy, với \(x\in\left\{-9;-4;-1;0;2;3;6;11\right\}\)thì \(A=\dfrac{3x+7}{x-1}\in Z\).
Câu 3:
a, Ta có: \(-\left(x+1\right)^{2008}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow P=2010-\left(x+1\right)^{2008}\le2010\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left(x+1\right)^{2008}=0\Rightarrow x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy \(MAX_P=2010\) khi x = -1
b, Ta có: \(-\left|3-x\right|\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow Q=1010-\left|3-x\right|\le1010\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left|3-x\right|=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(MAX_Q=1010\) khi x = 3
c, Vì \(\left(x-3\right)^2+1\ge0\) nên để C lớn nhất thì \(\left(x-3\right)^2+1\) nhỏ nhất
Ta có: \(\left(x-3\right)^2\ge0\Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2+1\ge1\)
\(\Rightarrow C=\dfrac{5}{\left(x-3\right)^2+1}\le\dfrac{5}{1}=5\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left(x-3\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy \(MAX_C=5\) khi x = 3
d, Do \(\left|x-2\right|+2\ge0\) nên để D lớn nhất thì \(\left|x-2\right|+2\) nhỏ nhất
Ta có: \(\left|x-2\right|\ge0\Rightarrow\left|x-2\right|+2\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow D=\dfrac{4}{\left|x-2\right|+2}\le\dfrac{4}{2}=2\)
Dấu " = " khi \(\left|x-2\right|=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy \(MAX_D=2\) khi x = 2

\(A=-1,6:\left(1+\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{-16}{10}:\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(A=\dfrac{-8}{5}.\dfrac{3}{5}\)
\(A=\dfrac{-24}{25}\)
\(B=1,4.\dfrac{15}{49}-\left(\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{2}{3}\right):2\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{14}{10}.\dfrac{15}{49}-\left(\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{2}{3}\right):\dfrac{11}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{14}{10}.\dfrac{15}{49}-\dfrac{22}{15}:\dfrac{11}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{3}{7}-\dfrac{22}{15}:\dfrac{11}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{3}{7}-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(B=\dfrac{-5}{21}\)
\(A=-1,6:\left(1+\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{-8}{5}:\left(1+\dfrac{2}{3}\right)\)
\(A=\dfrac{-8}{5}:\dfrac{5}{3}\)
\(A=\dfrac{-24}{25}\)
\(B=1,4.\dfrac{15}{49}-\left(\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{2}{3}\right):2\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{7}{5}.\dfrac{15}{49}-\left(\dfrac{4}{5}+\dfrac{2}{3}\right):\dfrac{11}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{7}{5}.\dfrac{15}{49}-\dfrac{22}{15}:\dfrac{11}{5}\)
\(B=\dfrac{3}{7}-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(B=\dfrac{-5}{21}\)

\(A=11\dfrac{3}{13}-\left(2\dfrac{4}{7}+5\dfrac{3}{13}\right)\)
\(A=11\dfrac{3}{13}-5\dfrac{3}{13}-2\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(A=6-2\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(A=5\dfrac{7}{7}-2\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(A=3\dfrac{3}{7}\)
\(B=\left(6\dfrac{4}{9}+3\dfrac{7}{11}\right)-4\dfrac{4}{9}\)
\(B=\left(6\dfrac{4}{9}-4\dfrac{4}{9}\right)+3\dfrac{7}{11}\)
\(B=2+3\dfrac{7}{11}\)
\(B=5\dfrac{7}{11}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}.\dfrac{2}{11}+\dfrac{-5}{7}-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}.\left(\dfrac{2}{11}+1\right)-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}.\dfrac{13}{11}-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-65}{77}-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{4}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{160}{11}\)
\(D=0,7.2\dfrac{2}{3}.20.0,375.\dfrac{5}{28}\)
\(D=\dfrac{7}{10}.\dfrac{8}{3}.20.\dfrac{375}{1000}.\dfrac{5}{28}\)
\(D=\dfrac{7}{28}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-0,25-\dfrac{1}{12}\right)\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{12}\right)\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{12}\right)\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right).0\)
\(\Rightarrow E=0\)

Câu 3:
a: \(A=-\left|x-10\right|+2018< =2018\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=10
\(B=-\left(x+2\right)^2+1999< =1999\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=-2
b: \(A=\left(2x-8\right)^2+3>=3\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=4
\(B=\left|x^2-25\right|-2017>=-2017\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=5 hoặc x=-5

a: =>-3/2+x-7=5-1/3x+4/15
=>4/3x=413/30
hay x=413/40
b: \(\Leftrightarrow5-\dfrac{3}{2}x=-\dfrac{22}{3}\cdot\dfrac{-11}{8}=\dfrac{121}{12}\)
=>3/2x=-61/12
hay x=-61/18
c: (3x+2)2+|3x+2y|=0
=>3x+2=0 và 3x=-2y
=>x=-2/3 và -2y=-2
=>(x,y)=(-2/3;1)

ính giá trị của các biểu thức sau:
A=827−(349+427)A=827−(349+427)
B=(1029+235)−629B=(1029+235)−629
Giải:
A=827−(349+427)A=827−(349+427)
=587−(319+307)=58−307−319=4−319=587−(319+307)=58−307−319=4−319
= 36−319=5936−319=59
B=(1029+235)−629B=(1029+235)−629
=1029−629+235=4+235=635
ính giá trị của các biểu thức sau:
A
=
8
2
7
−
(
3
4
9
+
4
2
7
)
A=827−(349+427)
B
=
(
10
2
9
+
2
3
5
)
−
6
2
9
B=(1029+235)−629
Giải:
A
=
8
2
7
−
(
3
4
9
+
4
2
7
)
A=827−(349+427)
=
58
7
−
(
31
9
+
30
7
)
=
58
−
30
7
−
31
9
=
4
−
31
9
=587−(319+307)=58−307−319=4−319
=
36
−
31
9
=
5
9
36−319=59
B
=
(
10
2
9
+
2
3
5
)
−
6
2
9
B=(1029+235)−629
=
10
2
9
−
6
2
9
+
2
3
5
=
4
+
2
3
5
=
6
3
5
Xem thêm tại: http://loigiaihay.com/bai-100-trang-47-sgk-toan-6-tap-2-c41a24737.html#ixzz4eUGN0ooE

a)<=>\(\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right).2}{6}-\dfrac{3.3}{6}=\dfrac{5-2x}{6}-\dfrac{1.3}{6}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{4x-6}{6}-\dfrac{9}{6}=\dfrac{5-2x}{6}-\dfrac{3}{6}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{4x-6}{6}-\dfrac{9}{6}-\dfrac{5-2x}{6}+\dfrac{3}{6}=0\)
<=>\(\dfrac{4x-6-9-5+2x+3}{6}=\dfrac{4x-17}{6}=0\)
<=>\(4x-17=0\)
<=>\(4x=17\)<=>\(x=\dfrac{17}{4}\)
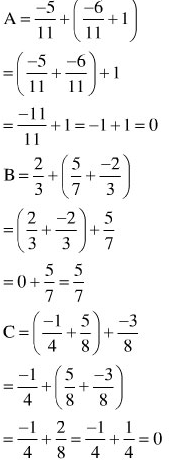
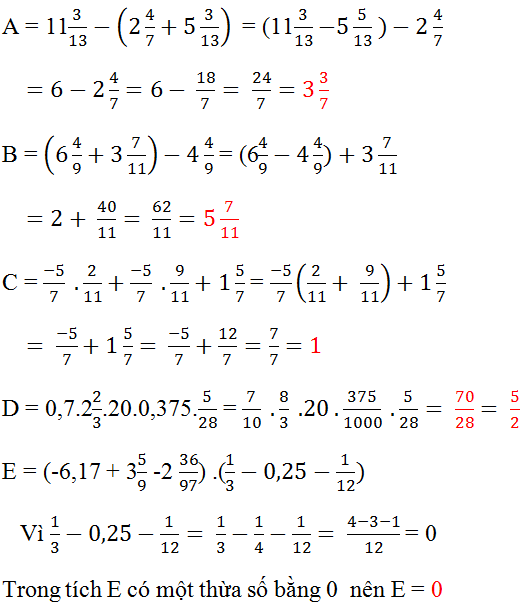

Giải:
Ta có:
|x+1/3|=2/3
⇒x+1/3=2/3 hoặc x+1/3=-2/3
x=1/3 hoặc x=-1
+)TH1: (nếu như có ngoặc)
Khi x=1/3:
A=(1/3)2-3.(1/3)+1
A=1/9
Khi x=-1
A=(-1)2-3.(-1)+1
A=5
+)TH2: (nếu x ko có ngoặc)
Khi x=-1
A=-12-3.-1+1
A=3
Trường hợp này chỉ có -1 vì 1/3 2 =1/9 ; còn ko có ngoặc hay có ngoặc còn tùy thuộc vào đề bài và cách suy nghĩ của bạn nhé!
Chúc bạn học tốt!