Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \(4x-7>0\Leftrightarrow4x>7\)\(\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{7}{4}\)
b) \(-5x+8>0\Leftrightarrow5x<8\Leftrightarrow x<\frac{8}{5}\)
c)\(9x-10\le0\Leftrightarrow9x\le10\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{10}{9}\)
d) \(\left(x+1\right)^2+4\le x^2+3x+10\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+4\le x^2+3x+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x\ge-5\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1\)
a,
4x - 7 > 0
↔ 4x > 7
↔ x > \(\dfrac{7}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / x>\(\dfrac{7}{4}\) }
b,
-5x + 8 > 0
↔ 8 > 5x
↔ \(\dfrac{8}{5}\) > x
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / \(\dfrac{8}{5}\) > x }
c,
9x - 10 ≤ 0
↔ 9x ≤ 10
↔ x ≤ \(\dfrac{10}{9}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / x ≤ \(\dfrac{10}{9}\) }
d,
( x - 1 )\(^2\) + 4 ≤ x\(^2\) + 3x + 10
↔ x\(^2\) - 2x +1 +4 ≤ x\(^2\) + 3x + 10
↔ 1 + 4 - 10 ≤ x \(^2\) - x\(^2\) + 3x + 2x
↔ -5 ≤ 5x
↔ -1 ≤ x
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / -1 ≤ x}

\(a,\)\(xy+3x+2y=6\)
\(\Rightarrow xy+3x+2y+6=6+6\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(y+3\right)+2\left(y+3\right)=12\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(y+3\right)\left(y+2\right)=12\)
\(TH1\):\(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=1\\x+2=12\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-2\\x=10\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH2\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=-1\\x+2=-12\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-4\\x=-14\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH3\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=12\\x+2=1\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=9\\x=-1\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH4\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=-12\\x+2=-1\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-15\\x=-3\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH5\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=2\\x+2=6\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-1\\x=4\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH6\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=6\\x+2=2\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=0\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH7\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=-2\\x+2=-6\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-5\\x=-8\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH8\)\(:\)\(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=-6\\x+2=-2\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-9\\x=-4\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH9\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=3\\x+2=4\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=0\\x=2\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH10\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=4\\x+2=3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=1\\x=1\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH11\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=-3\\x+2=-4\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-6\\x=-6\end{cases}}}\)
\(TH12\): \(\orbr{\begin{cases}y+3=-4\\x+2=-3\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}y=-7\\x=-5\end{cases}}}\)
KL...
chưa thấy bạn nào làm bài 3 , thì em làm ạ :))
Giả sử x, y là các số nguyên thoă mãn phương trình đã cho .
\(4x+5y=2012\Leftrightarrow5y=2012-4y\Leftrightarrow5y=4\left(503-y\right).\)(1)
Dễ thấy vế phải của (1) chia hết cho 4 \(\Rightarrow5y⋮4\)mà (5;4)=1 nên y chia hết cho 4.
Đặt \(y=4t\left(t\in Z\right)\)thế vào phương trình đầu ta được : \(4x+20t=2012\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=503-5t\\y=4t\end{cases}.}\)(*)
Thử thay vào các biểu thức của x, y ở (*) ta thấy thỏa mãn
Vậy phương trình có vô số nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(503-5t;4t\right)\forall t\in Z.\)

ta có \(\left(log^b_a+log^a_b+2\right)\left(log^b_a-log_{ab}^b\right).log_b^a-1=\left(log^b_a+log^a_b+2\right)\left(log^b_a.log_b^a-log_{ab}^b.log_b^a\right)-1=\left(log^b_a+log^a_b+2\right)\left(1-\frac{1}{log_b^{ba}}log_b^a\right)-1=\left(log^b_a+log^a_b+2\right)\left(1-\frac{1}{1+log^a_b}log^a_b\right)-1=\left(log^b_a+log^a_b+2\right)\frac{1}{1+log^a_b}-1=\left(log^a_b+\frac{1}{log^a_b}+2\right)\frac{1}{1+log^a_b}-1=\frac{\left(1+log^a_b\right)^2}{log^a_b}\frac{1}{1+log^a}-1=\frac{1+log^a_b}{log_b^a}-1=\frac{1}{log_b^a}\)
ta có:
\(\left(log^b_a+\frac{1}{log^b_a}+2\right)\left(log^b_a-\frac{1}{log^{ab}_a}\right)log^a_b-1\)\(=\frac{\left(log^b_a+1\right)^2}{log^b_a}\left(log^b_a-\frac{1}{1+log^b_a}\right)log^a_b-1\)\(=\frac{\left(log^b_a+1\right)^2}{log^b_a}\left(1-\frac{log^a_b}{1+log^b_a}\right)-1\)\(==\frac{\left(log^b_a+1\right)^2}{log^b_a}\left(\frac{1}{1+log^b_a}\right)-1=\frac{1+log^b_a}{log^b_a}-1=\frac{1}{log^b_a}\)
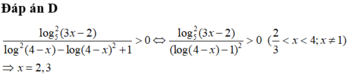

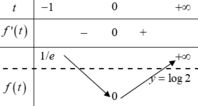



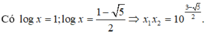
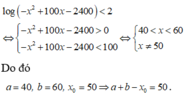
Ta có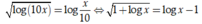
Chọn B.