Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) -5x2 + 3x + 2 = 0 (a = -5; b = 3; c = 2)
\(\Delta=3^2-4\cdot\left(-5\right)+2=31\)
=> Phương trình có nghiệm
Ta có a + b + c = -5 +3 +2 = 0
Nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm:
x1= 1; x2 = \(\dfrac{c}{a}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{-5}\) = \(\dfrac{-2}{5}\)
b) 7x2 + 6x - 13 = 0 (a = 7; b = 6; c = -13)
\(\Delta=6^2-4\cdot7\cdot\left(-13\right)=400\)
Nên phương trình có nghiệm
Ta có a + b + c = 7 + 6 +(-13) = 0
Nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm:
x1= 1; x2 = \(\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{-13}{7}\)
c) x2 - 7x + 12 = 0 (a = 1; b = -7; c = 12)
\(\Delta\) = (-7)2 - 4 * 1 * 12= 1
Nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(x_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-7\right)+\sqrt{1}}{2\cdot1}=4\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-\left(-7\right)-\sqrt{1}}{2\cdot1}=3\)
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1=4 và x2=3
d)-0,4x2 +0,3x +0,7 =0 (a = -0,4; b= 0,3; c= 0,7)
\(\Delta=\left(0,3\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-0,4\right)\cdot0,3=0,57\)
Nên phương trình có nghiệm
Ta có a - b + c = (-0,4) - 0,3 + 0,7 = 0
Nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1 = -1; \(x_2=\dfrac{-c}{a}=\dfrac{-0,7}{-0,4}=\dfrac{7}{4}\)
e)3x2+(3-2m)x-2m =0(a= 3;b=3-2m;c= -2m)
\(\Delta=\left(3-2m\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot\left(-2m\right)\)
= 9 - 12m + 4m +24m = 9 + 16m
Do \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}9>0\\16m\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)nên phương trình có nghiệm
Ta có a - b + c = 3- (3-2m) +( -2m)
= 3 -3 + 2m - 2m = 0
Nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm
x1= - 1; x2=\(\dfrac{-c}{a}=\dfrac{-\left(-2m\right)}{3}=\dfrac{2m}{3}\)
f) 3x2 - \(\sqrt{3}\)x - ( 3+\(\sqrt{3}\))=0
(a= 3; b= \(-\sqrt{3}\); c=\(-\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)\))
\(\Delta=\left(-\sqrt{3}\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot\left(-\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)\right)\)
= 39+12\(\sqrt{3}\)
Nên phương trình có nghiệm
Ta có a - b +c = 3 - (\(-\sqrt{3}\)) + (-(3+\(\sqrt{3}\))) = 0
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1= -1;
x2=\(\dfrac{-c}{a}=\dfrac{-\left(-\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)\right)}{3}=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{3}}{3}\)

Đang làm dở dang mà tự nhiên máy thoát ra. Chép lại oải ghê.
Câu 1: Mình làm mẫu câu a thôi nhé.
a/ \(x^2-2\sqrt{3}x-6=0\)
( a = 1 ; b = -2\(\sqrt{3}\); c = -6 )
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(=\left(-2\sqrt{3}\right)^2-4.1.\left(-6\right)\)
\(=36>0\)
\(\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{36}=6\)
Pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(x_1=\frac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{2\sqrt{3}-6}{2.1}=-3+\sqrt{3}\)
\(x_2=\frac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{2\sqrt{3}+6}{2.1}=3+\sqrt{3}\)
Vậy:..
Câu 2: \(x^2-2\left(2m+1\right)x+4m^2+2=0\)
( a = 1; b = -2(2m+1); c = 4m^2 + 2 )
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(=\left[-2\left(2m+1\right)\right]^2-4.1.\left(4m^2+2\right)\)
\(=4\left(4m^2+4m+1\right)-16m^2-8\)
\(=16m^2+16m+4-16m^2-8\)
\(=16m-4\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\Leftrightarrow16m-4>0\Leftrightarrow m>\frac{1}{4}\)

a, x2 - 18 = 0
⇒ x2 = 18
⇒ \(\sqrt{x}\) = \(\sqrt{18}\)
⇒ x =3 \(\sqrt{2}\)

Câu c;d giải \(\Delta\)
Các câu còn lại là phương trình trùng phương, mình chỉ làm 1 câu thôi. Các câu sau tương tự
a/ \(x^4-2x^2-8=0\left(1\right)\)
Đặt: \(x^2=t\left(t\ge0\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\Rightarrow t^2-2t-8=0\)
( a = 1; b = -2; c = -8 )
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac\)
\(=\left(-2\right)^2-4.1.\left(-8\right)\)
\(=36>0\)
\(\sqrt{\Delta}=\sqrt{36}=6\)
Pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt:
\(t_1=\frac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{2-6}{2.1}=-2\left(l\right)\)
\(t_2=\frac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\frac{2+6}{2.1}=4\left(n\right)\Rightarrow x^2=4\Leftrightarrow x=2hayx=-2\)
Vậy: S = {-2;2}

a, \(1,2x^3-x^2-0,2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^3-10x^2-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^3-5x^2-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(6x^2-5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\6x^2-5x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=-\dfrac{1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt đã cho là \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{6};0;1\right\}\)
b, \(5x^3-x^2-5x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(5x-1\right)-\left(5x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(5x-1\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-1=0\\5x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm1\\x=\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho là \(S=\left\{-1;\dfrac{1}{5};1\right\}\)
\(a,1,2x^3-x^2-0,2x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(1,2x^2-x-0,2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\1,2x^2-x-0,2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=\dfrac{-1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,5x^3-x^2-5x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(5x-1\right)-\left(5x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(5x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{5}\\x=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-8\right)\left(x-10\right)=72x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-4\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-8\right)\left(x-10\right)-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-14x+40\right)\left(x^2-13x+40\right)-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40-0,5x\right)\left(x^2-13,5x+40+0,5x\right)-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40\right)^2-\left(0,5x\right)^2-72x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40\right)^2-72,25x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-13,5x+40+8,5x\right)\left(x^2-13,5x+40-8,5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-5x+40\right)\left(x^2-22x+40\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-5x+40=0\left(VN\right)\\x^2-22x+40=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=20\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Câu a,c xem lại đề, cách làm giống câu b, còn câu e giống câu d
b) \(2x^4+5x^3+x^2+5x+2=0\)
Ta nhận thấy x=0 không phải là 1 nghiệm của phương trình, chia cả 2 vế của phương trình cho \(x^2\ne0\), ta được:
\(2x^2+5x+1+\dfrac{5}{x}+\dfrac{2}{x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)+5\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+1=0\)
Đặt \(y=x+\dfrac{1}{x}\Rightarrow x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}=y^2-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(y^2-2\right)+5y+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2y^2+5y-3=0\)
PT đơn giản, tự giải nha, ta được nghiệm y=1/2 và y=-3
Với y=1/2 thì không tìm được x
Với y=-3 thì tìm được 2 nghiệm, tự giải

a: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-5\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot8=25-96< 0\)
Do đó: Phươbg trình vô nghiệm
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot15\cdot5=9-300< 0\)
Do đó: Phương trình vô nghiệm
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+4-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3\)
hay \(x\in\left\{2+\sqrt{3};2-\sqrt{3}\right\}\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+6x+x+2=0\)
=>(x+2)(3x+1)=0
=>x=-2 hoặc x=-1/3

a, Ta có:
2x2-5x+2=0
<=> 2x2-4x-x+2=0
<=> 2x(x-2)-(x-2)=0
<=> (x-2)(2x-1)=0
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\frac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là : \(S=\left\{2;\frac{1}{2}\right\}\)
b. \(\frac{1}{2}x^2-2\sqrt{2}x-4=0\)
<=> \(x^2-4\sqrt{2}x-8=0\)
Xét : \(\Delta'=\left(-2\sqrt{2}\right)^2-1.\left(-8\right)\)
=8+8
=16
Vì \(\Delta'>0\) nên phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{16}\\x=2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{16}\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\sqrt{2}+4\\x=2\sqrt{2}-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là: \(S=\left\{2\sqrt{2}+4;2\sqrt{2}-4\right\}\)
a) x2 – 8 = 0 ⇔ x2 = 8 ⇔ x = ±√8 ⇔ x = ±2√2
b) 5x2 – 20 = 0 ⇔ 5x2 = 20 ⇔ x2 = 4 ⇔ x = ±2
c) 0,4x2 + 1 = 0 ⇔ 0,4x2 = -1 ⇔ x2 = -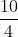 : Vô nghiệm
: Vô nghiệm
d) 2x2 + √2x = 0 ⇔ x(2x + √2) = 0 ⇔ √2x(√2x + 1) = 0
⇔ x1 = 0 hoặc √2x + 1 = 0
Từ √2x + 1 = 0 => x2 =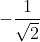
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm
x1 = 0, x2 =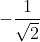
e) -0,4x2 + 1,2x = 0 ⇔ -4x2 + 12x = 0 ⇔ -4x(x – 3) = 0
⇔ x1 = 0,
hoặc x2 - 3 = 0 => x2 = 3
Vậy phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1 = 0, x2 = 3