Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 1:
nếu x1<x2=>2018.x1-3<2018.x2
=>f(x1)<f(x2)
Bài 2:
nếu x dương=>100x2+2 dương
nếu x âm=>100x2+2 dương vì x2 luôn dương
=>f(x)=f(-x)
Bài 3:
nếu x1<x2=>-2019x1+1<2019x2+1
=>f(x1)<f(x2)

\(\text{1)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=-2,\text{ ta có: }f\left(-2\right)-5f\left(-2\right)=\left(-2\right)^2\Rightarrow f\left(-2\right)=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=x^2+5f\left(-2\right)=x^2-5\)
\(f\left(3\right)=3^2-5\)
\(\text{2)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=1,\text{ ta có: }f\left(1\right)+f\left(1\right)+f\left(1\right)=6\Rightarrow f\left(1\right)=2\)
\(\text{Thay }x=-1,\text{ ta có: }f\left(-1\right)+f\left(-1\right)+2=6\Rightarrow f\left(-1\right)=2\)
\(\text{3)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=2,\text{ ta có: }f\left(2\right)+3f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)=2^2\text{ (1)}\)
\(\text{Thay }x=\frac{1}{2},\text{ ta có: }f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)+3f\left(2\right)=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^2\text{ (2)}\)
\(\text{(1) - 3}\times\text{(2) }\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)+3f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)-3f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)-9f\left(2\right)=4-\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow-8f\left(2\right)=\frac{15}{4}\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=-\frac{15}{32}\)

Đồ thị hàm số đi qua O (0; 0)
Cho x = 2 ⇒ y = 1,5. 2 = 3
Ta có: A(2; 3)
Vẽ đường thẳng OA ta có đồ thị hàm số.
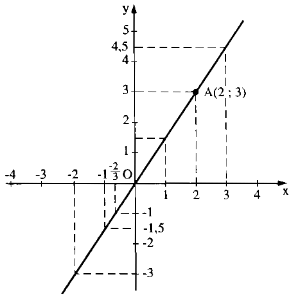
a) f(1) = 1,5. 1 = 1,5
f(-1) = 1,5. (-1) = -1,5
f(-2) = 1,5. (-2) = -3
f(2) = 1,5. 2 = 3
f(0) =0
b)\(y=-1\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-1}{1,5}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(y=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{0}{1,5}=0\)
\(y=4,5\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{4,5}{1,5}=3\)
c) y > 0 ⇒1,5x > 0 ⇒x > 0
y < 0 ⇒ 1,5x < 0 ⇒ x < 0
Đồ thị hàm số đi qua O (0; 0)
Cho x = 2 ⇒⇒ y = 1,5. 2 = 3
Ta có: A(2; 3)
Vẽ đường thẳng OA ta có đồ thị hàm số.

a) f(1) = 1,5. 1 = 1,5
f(-1) = 1,5. (-1) = -1,5
f(-2) = 1,5. (-2) = -3
f(2) = 1,5. 2 = 3
f(0) = 0
b)y=−1⇒x=\(\dfrac{-1}{1,5}=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)
b)y=0⇒x==\(\dfrac{0}{1,5}=0\)
y=4,5⇒x=\(\dfrac{4,5}{1,5}=3\)
c) y > 0 ⇒1,5x > 0 ⇒x > 0
y < 0 ⇒ 1,5x < 0 ⇒ x < 0

a)Với x1 = x2 = 1
\( \implies\) \(f\left(1\right)=f\left(1.1\right)\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(1\right)=f\left(1\right).f\left(1\right)\)
\( \implies\)\(f\left(1\right).f\left(1\right)-f\left(1\right)=0\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(1\right).\left[f\left(1\right)-1\right]=0\)
\( \implies\) \(\orbr{\begin{cases}f\left(1\right)=0\\f\left(1\right)-1=0\end{cases}}\)
Mà \(f\left(x\right)\) khác \(0\) ( với mọi \(x\) \(\in\) \(R\) ; \(x\) khác \(0\) )
\( \implies\) \(f\left(1\right)\) khác \(0\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(1\right)-1=0\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(1\right)=1\)
b)Ta có : \(f\left(\frac{1}{x}\right).f\left(x\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{x}.x\right)\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(\frac{1}{x}\right).f\left(x\right)=f\left(1\right)=1\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(\frac{1}{x}\right).f\left(x\right)=1\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)=\frac{1}{f\left(x\right)}\)
\( \implies\) \(f\left(x^{-1}\right)=\left[f\left(x\right)\right]^{-1}\)

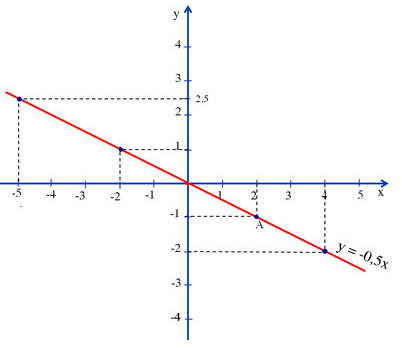
Cho x =2 được y =-2 =>A(2 ;-1) thuộc đồ thị. Vẽ đồ thị
a) Trên đồ thị ta thấy
f(2)=-1
f(-2) =1
f(4)=-2
f(0)=0;
b) Trên đồ thị ta thấy
y=-1 => x=2
y=0 => x=0
y=2,5 => x=-5
c) Khi y dương y > 0 ứng với phần đồ thị nằm trên trục hoành và bên trái trục tung nên x < 0.
Khi y âm : y < 0 ứng với phần đồ thị nằm trên trục hoành và bên phải trục tung nên x > 0

Ta có: y=f(x)=x2−2y=f(x)=x2−2
Thay f(2); f(1); f(0); f(-1); f(-2) vào hàm số:
f(2)=22−2=4−2=2f(2)=22−2=4−2=2
f(1)=12−2=1−2=−1f(1)=12−2=1−2=−1
f(0)=02−2=−2f(0)=02−2=−2
f(−1)=(−1)2−2=1−2=−1f(−1)=(−1)2−2=1−2=−1
f(−2)=(−2)2−2=4−2=2
\(y=f\left(-2\right)=2\left(-2\right)^2-1=7\)