Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Mình có công thức tham khảo cho bạn đây:
Giả sử hợp chất AxBy:
Ta có: x . hóa trị A = y . hóa trị B
\(\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{y}= \dfrac{hóa trị B}{hóa trị A}= \dfrac{b'}{a'}\). Chú ý: \(\dfrac{b'}{a'} \) là tỉ số tối giản nhé
\(\Rightarrow \begin{cases} x= hóa trị B=b'\\ y= hóa trị A= a'(2) \end{cases} \)
Ví dụ: Fe (III) và O:
Gọi CTHH là FexOy
Có: \(\dfrac{x}{y}= \dfrac{hóa trị O}{hóa trị Fe}= \dfrac{2}{3}\) \(\Rightarrow\)\(Fe_2O_3\)
Tương tự Cu và O
CTHH: Cu1O1 nhưng do chỉ số 1 không cần ghi nên CTHH là CuO
Tương tự bạn cũng có thể coi B trong AxBy là 1 nhóm như -(OH) ; =SO4;...
Cách 2) Bạn lấy Bội chung nhỏ nhất của hóa trị A và B trong AxBy.
x= BCNN : hóa trị A
y= BCNN : hóa trị B
Ví dụ: Al và O
Gọi CTHH là AlxOy
BCNN của hóa trị Al (III) và O(II) là 6
x= 6:3=2
y= 6:2 = 3
CTHH: Al2O3
Bạn đọc lại phần lập CTHH khi biết hóa trị nhé
C2) Theo thứ tự nhé:
\(P_2O_3 ; NH_3; FeO; Cu(OH)_2; Ca(NO_3)_2\)
\(Ag_2SO_4; Ba_3(PO_4)_2; Fe_2(SO_4)_3; Al_2(SO_4)_3; NH_4NO_3\)
C3) Theo thứ tự:
a) \(Na_2O\)
Ở CTHH trên, có 2 nguyên tử Na kết hợp với 1 nguyên tử O nên:
\(M_{Na_2O}= 2 . M_{Na} + 1. M_O=2 . 23 + 1 . 16=62 (g/mol)\)
b)
\(ZnCl_2; M_{ZnCl_2}=136 (g/mol)\)
c)\(Cu(OH)_2 \)
Ở đây, bạn thấy 1 nguyên tử Cu kết hợp với 2 nhóm OH nên ta có:
\(M_{Cu(OH)_2}= 1 . M_{Cu} + 2 . M_{nhóm -OH}= 1 . 64 + 2 . 17=98 (g/mol)\)
d)\(Fe(NO_3)_3; M_{Fe(NO_3)_3}=242 (g/mol)\)
e)\(AlPO_4; M= 122 (g/mol)\)
f)\(CaSO_4; M_{CaSO_4}= 136 (g/mol)\)

Nếu đã có sản phẩm là KNO2 và O2 thì có lẽ OaNbKc là KNO3 bạn nhé.

a) \(n_{Al}=\dfrac{5,4}{27}=0,2\left(mol\right);n_{H_2SO_4}=0,1.0,5=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: \(2Al+3H_2SO_4\rightarrow Al_2\left(SO_4\right)_3+3H_2\)
Theo đề:0,2......0,05
Lập tỉ lệ: \(\dfrac{0,2}{2}>\dfrac{0,05}{3}\)=> Al dư, H2SO4 hết
=> \(V_{H_2}=0,05.22,4=1,12\left(l\right)\)
=> Chọn C
b) \(n_{Al_2\left(SO_4\right)_3}=\dfrac{1}{3}n_{H_2SO_4}=\dfrac{0,05}{3}=\dfrac{1}{60}\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(C_{M\left(Al_2\left(SO_4\right)_3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{60}{0,1}}==0,17M\)
=> Chọn A

Science and technology has become a debated topic in the society. On one hand, it is necessary for the modern life where other countries are continuously developing in the field of science and technology. It becomes very necessary for other countries too to grow in the same way to be strong and well developed other countries for the future safety and security. It is science and technology which helps other weak countries to develop and be strong. We have to take support of science and technology forever to improve the way of life for the betterment of mankind. If we do not take the help of technologies such as computer, internet, electricity, etc we cannot be economically strong in the future and would be backward forever even we cannot survive in such a competitive and technological world.
Advancement in the field of medical, agriculture, education, economy, sports, games, jobs, tourism, etc are the examples of science and technology. All such advancements show us that how both are equally beneficial for our life. We can see a clear difference in our life style while matching the ancient and modern way of life. High level of scientific and technological advancement in the field of medicine has made easy the treatment of various lethal diseases which was earlier not possible. It has helped a lot to the doctors to find effective ways to cure diseases through medicine or operations as well as research vaccines to cure diseases such as cancer, AIDS, diabetes, Alzheimer’s, Leukemia, etc.

nguyễn thị hương giang
em nghĩ thế, GP tuần này của cj ấy cao quá!

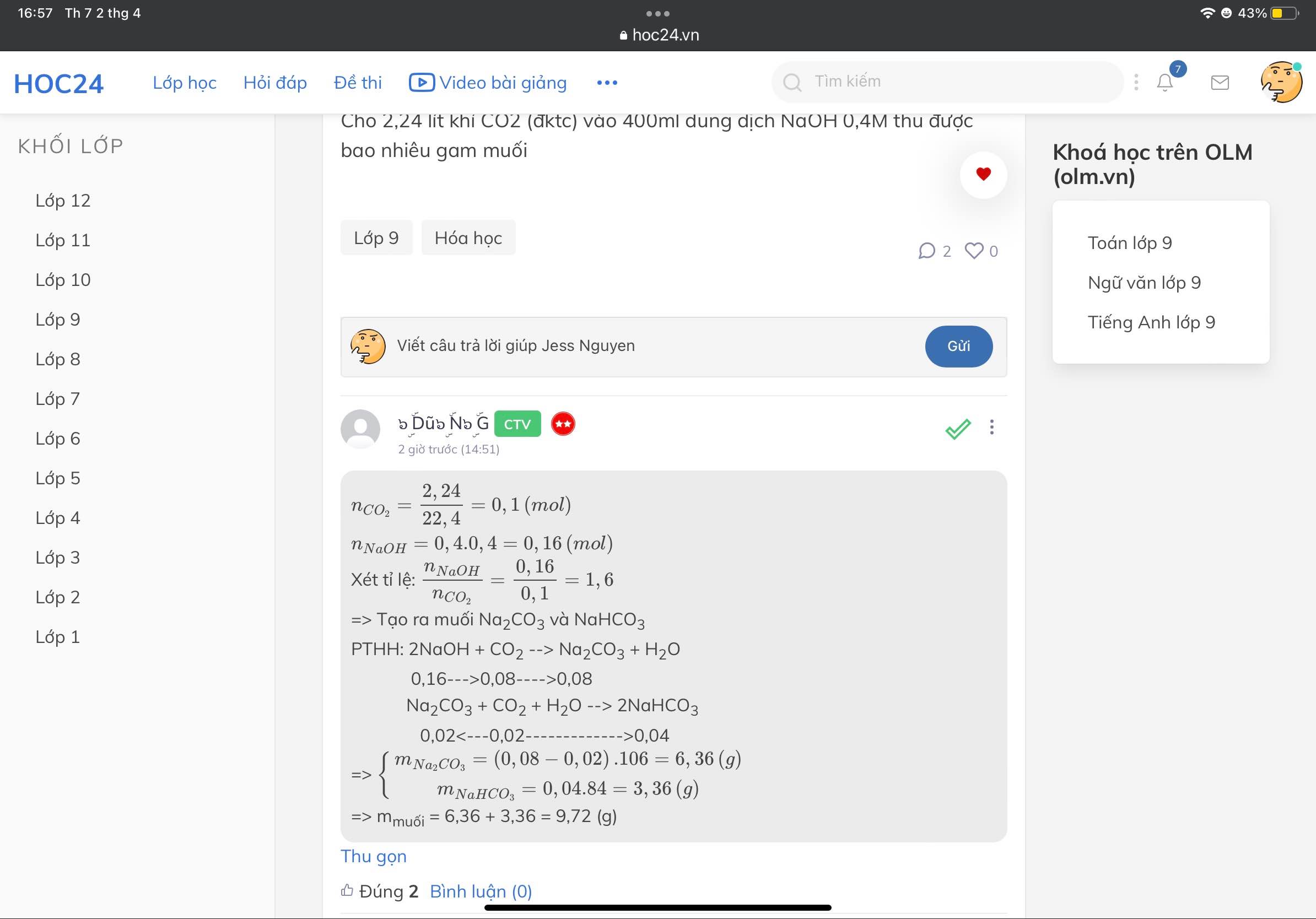
"mọi người cho em hỏi là cái phần xét tỉ lệ để ra 2 muối dưới đây nó có nghĩa là gì, để làm gì thế"
=> Để tìm số muối tạo ra bn nhé :)
PTHH: NaOH + CO2 --> Na2CO3 + H2O (1)
NaOH + CO2 --> NaHCO3 (2)
Bn xét tỉ lệ \(T=\dfrac{n_{NaOH}}{n_{CO_2}}\)
Xảy ra 3 TH
+ Nếu T \(\le1\) => Ra NaHCO3 (Xảy ra pư (2) và tính số mol theo NaOH)
+ Nếu T \(\ge2\) => Ra Na2CO3 (Xảy ra pư (1) và tính số mol theo CO2)
+ Nếu 1 < T < 2 => Ra 2 muối Na2CO3, NaHCO3 (Xảy ra đồng thời (1), (2))
* Nếu nó tạo ra 2 muối thì bn có thể lm 2 cách
+ đặt ẩn, giải hệ phương trình (giống bn Kudo)
+ viết phương trình tạo muối trung hòa trước (tính số mol theo NaOH), sau đó CO2 tác dụng với muối trung hòa tạo ra muối axit (tính số mol theo CO2 còn lại)
PTHH: 2NaOH + CO2 --> Na2CO3 + H2O
Na2CO3 + CO2 + H2O --> 2NaHCO3
Còn nếu bn không thích dùng tỉ lệ thì bn cứ viết phương trình tạo muối trung hòa trước, sau đó CO2 tác dụng với muối trung hòa tạo ra muối axit thôi (đúng với mọi TH :D)





Bài 6:
PTHH: \(Fe+2HCl\rightarrow FeCl_2+H_2\uparrow\)
a_____2a______a_____a (mol)
\(2Al+6HCl\rightarrow2AlCl_3+3H_2\uparrow\)
b______3b______b_____\(\dfrac{3}{2}\)b (mol)
Ta lập được HPT: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}56a+27b=22,2\\a+\dfrac{3}{2}b=\dfrac{13,44}{22,4}=0,6\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=0,3\\b=0,2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\%m_{Fe}=\dfrac{0,3\cdot56}{22,2}\cdot100\%\approx75,68\%\\\%m_{Al}=24,32\%\end{matrix}\right.\)