
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


25.
\(R=\dfrac{BC}{2}\)
\(r=\dfrac{BC}{2}.tan\left(\dfrac{45^0}{2}\right)=\dfrac{BC\left(\sqrt{2}-1\right)}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{R}{r}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}-1}=1+\sqrt{2}\)
26.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2R.sinA\\b=2RsinB\\c=2RsinC\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2R.sinA+2R.sinB=2.2R.sinC\)
\(\Rightarrow sinA+sinB=2sinC\)
27.
\(p=\dfrac{13+14+15}{2}=21\)
\(S=\sqrt{p\left(p-13\right)\left(p-14\right)\left(p-15\right)}=84\)
28.
\(AM=\sqrt{\dfrac{2\left(AB^2+AC^2\right)-BC^2}{4}}=7,5\left(cm\right)\)

24.
Đường thẳng có 1 vtcp là \(\overrightarrow{u}=\left(2;-5\right)\)
25.
\(a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc.cosA\)
26.
A là mệnh đề sai, công thức đúng: \(S=\dfrac{1}{2}ab.sinC\)
27.
\(BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2-2AB.AC.cosA}=\sqrt{3^2+4^2-2.3.4.cos60^0}=\sqrt{13}\)
28.
\(\widehat{A}=180^0-\left(35^030'+45^0\right)=99^030'\)
Áp dụng định lý hàm sin:
\(\dfrac{a}{sinA}=\dfrac{b}{sinB}\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a.sinB}{sinA}=\dfrac{12,5.sin\left(35^030'\right)}{sin\left(99^030'\right)}=7,36\left(m\right)\)

a: \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-4;3\right)AC;=\left(-2;0\right)\)
Vì -2/-4<>0/3
nên A,B,C không thẳng hàng
=>A,B,C là ba đỉnh của một tam giác
b: A là trung điểm của EC
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_E+1=2\cdot3=6\\y_E-1=2\cdot\left(-1\right)=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow E\left(5;-1\right)\)
c: A là trọng tâm của tam giác BCG
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1+1+x_G=3\cdot3=9\\2-1+y_G=3\cdot\left(-1\right)=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow G\left(9;-4\right)\)
d: ADBC là hình bình hành
=>vecto AD=vecto CB
vecto CB=(-2;3)
vecto AD=(x-3;y+1)
Do đó, ta có:
x-3=-2 và y+1=3
=>x=1 và y=2
=>D(1;2)
f: Tọa độ H là;
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3-1+1}{3}=1\\y=\dfrac{-1+2-1}{3}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)


17.
\(f\left(x\right)>0;\forall x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=1>0\left(luôn-đúng\right)\\\Delta'=\left(2m-1\right)^2-\left(3m^2-2m+4\right)< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m-3< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1< m< 3\)
\(\Rightarrow m=\left\{0;1;2\right\}\)
18.
\(\pi< x< \dfrac{3\pi}{2}\Rightarrow cosx< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow cosx=-\sqrt{1-sin^2x}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{5}}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow tanx=\dfrac{sinx}{cosx}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}\)
\(tan\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=\dfrac{tanx+tan\dfrac{\pi}{4}}{1-tanx.tan\dfrac{\pi}{4}}=\dfrac{\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}+1}{1-\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}}{5}.1}=9+4\sqrt{5}\)
19.
\(a^2=b^2+c^2+bc\Rightarrow b^2+c^2-a^2=-bc\)
\(\Rightarrow cosA=\dfrac{b^2+c^2-a^2}{2bc}=\dfrac{-bc}{2bc}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=120^0\)
20.
Đường tròn (C) tâm \(I\left(2;-1\right)\) bán kính \(R=2\)
\(d\left(I;\Delta\right)=\dfrac{\left|2-1-3\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+1^2}}=\sqrt{2}\)
Gọi H là trung điểm AB \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}IH=d\left(I;\Delta\right)\\AH=\dfrac{1}{2}AB\end{matrix}\right.\)
Áp dụng định lý Pitago trong tam giác vuông IAH:
\(IA^2=IH^2+AH^2\Leftrightarrow R^2=IH^2+AH^2\)
\(\Rightarrow AH=\sqrt{2}\Rightarrow AB=2AH=2\sqrt{2}\)

15.
\(\Delta'=m^2+m-2>0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m>1\\m< -2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đáp án B
16.
\(\dfrac{\pi}{2}< a< \pi\Rightarrow\dfrac{\pi}{4}< \dfrac{a}{2}< \dfrac{\pi}{2}\Rightarrow\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}< sin\dfrac{a}{2}< 1\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}< sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}< 1\)
\(sina=\dfrac{3}{5}\Leftrightarrow sin^2a=\dfrac{9}{25}\Leftrightarrow4sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}.cos^2\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{9}{25}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}\left(1-sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}\right)=\dfrac{9}{100}\Leftrightarrow sin^4\dfrac{a}{2}-sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}+\dfrac{9}{100}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{1}{10}< \dfrac{1}{2}\left(loại\right)\\sin^2\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{9}{10}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow sin\dfrac{a}{2}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{10}}{10}\)
17.
Áp dụng công thức trung tuyến:
\(AM=\dfrac{\sqrt{2\left(AB^2+AC^2\right)-BC^2}}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{201}}{2}\)
18.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+4>m^2+2m\) ; \(\forall x\in\left[-2;1\right]\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m< \min\limits_{\left[-2;1\right]}\left(x^2+2x+4\right)\)
Xét \(f\left(x\right)=x^2+2x+4\) trên \(\left[-2;1\right]\)
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=-1\in\left[-2;1\right]\) ; \(f\left(-2\right)=4\) ; \(f\left(-1\right)=3\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=7\)
\(\Rightarrow\min\limits_{\left[-2;1\right]}\left(x^2+2x+4\right)=f\left(1\right)=3\)
\(\Rightarrow m^2+2m< 3\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m-3< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow-3< m< 1\Rightarrow m=\left\{-2;-1;0\right\}\)
Đáp án C
 giúp em mấy câu này với ạ
giúp em mấy câu này với ạ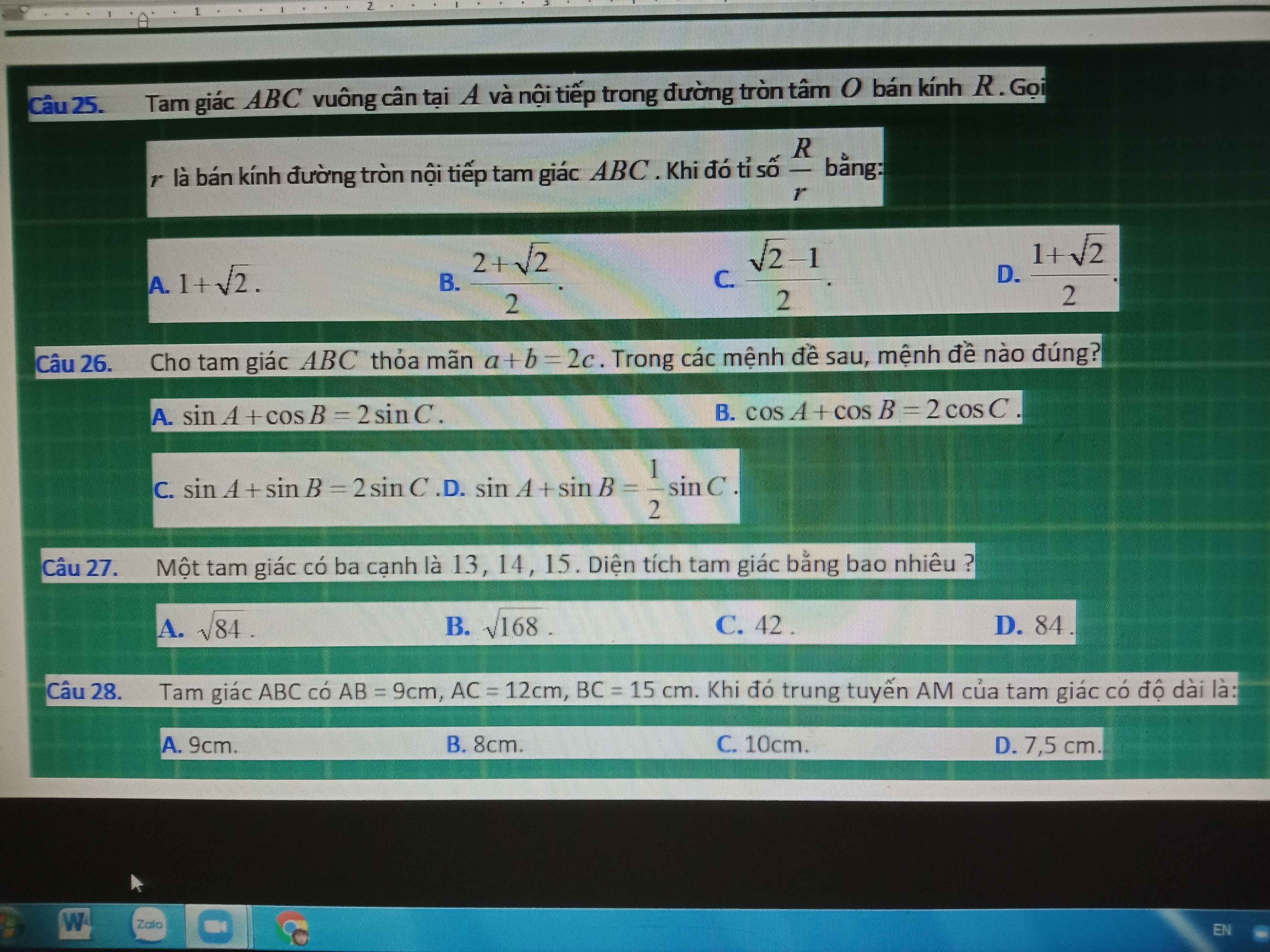







 giúp mình mấy câu này với mình cảm ơn nhìu ạ
giúp mình mấy câu này với mình cảm ơn nhìu ạ

7D
8C
9D
10B
11C