
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\( x^4-2x^2-400x-9999=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\( x^4+11x^3+ 119x^2+909x-11.(x^3+11x^2 +119x+909)=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \((x-11).(x^3+11x^3 +119x+909)=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\((x-11).(x^3+2x^2+ 101x+9x^2+ 18x+909)=0 \)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \((x-11).(x+9).(x^2+ 2x+101)=0 \)
Vậy nghiệm của pt là \(11\) và \(-9\)

\(\frac{x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}+\frac{x+1}{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)}=\frac{2x+5}{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\)
\(\frac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+4\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\frac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{\left(2x+5\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(2x-1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+x-12+x^2-x-2=2x^2+x-10\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)
\(\frac{x+4}{2x^2-5x+2}+\frac{x+1}{2x^2-7x+3}=\frac{2x+5}{2x^2-7x+3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x+4}{2x^2-5x+2}=\frac{2x-5}{2x^2-7x+3}-\frac{x+1}{2x^2-7x+3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x+4}{2x^2-5x+2}=\frac{x+4}{2x^2-7x+3}\)
TH1:\(x+4\ne0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x^2-5x+2=2x^2-7x+3\)
\(\Rightarrow-5x+2=-7x+3\)
\(\Rightarrow2x=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\)
TH2:\(x+4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-4\)

X^4-2x^2-400x-9999 <=>x^4+11x^3-11x^3+119x^2-121x^2+909x-1309x-9999=0 <=>x^4+11x^3+119x^2+909x-11(x^3+11x^2+119x+9999)<=>(x-11)(x^3+11x^2+119x+909) . Phân tích tiếp ta được (x-11)(x+9)(x^2+2x+101)

(x + 2)( x 2 – 3x + 5) = (x + 2) x 2
⇔ (x + 2)( x 2 – 3x + 5) – (x + 2) x 2 = 0
⇔ (x + 2)[( x 2 – 3x + 5) – x 2 ] = 0
⇔ (x + 2)( x 2 – 3x + 5 – x 2 ) = 0
⇔ (x + 2)(5 – 3x) = 0
⇔ x + 2 = 0 hoặc 5 – 3x = 0
x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = -2
5 – 3x = 0 ⇔ x = 5/3
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = -2 hoặc x = 5/3

Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ ±2.
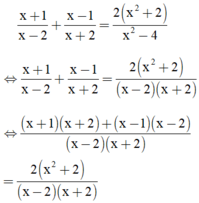
⇒ (x + 1)(x + 2) + (x – 1)(x – 2) = 2(x2 + 2)
⇔ x2 + x + 2x + 2 + x2 – x – 2x + 2 = 2x2 + 4
⇔ 2x2 + 4 = 2x2 + 4
⇔ 0x = 0.
Vậy phương trình nghiệm đúng với mọi x ≠ ±2.

Ta có:Giá trị tuyệt đối của một đa thức luôn luôn >=0
Mặt khác, ta có -2x2-2=-2(x2+1) luôn luôn <0(vì x2+1 >=1>0),(-2>0)
-->không thể có giá trị của x phù hợp
Ta có: \(\left|2x^2-5x+3\right|=-2x^2-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x^2-5x+3\right|=-\left(2x^2+2\right)\)
mà \(\left|2x^2-5x+3\right|\ge0\forall x\)
và \(-\left(2x^2+2\right)< 0\forall x\)
nên \(x\in\varnothing\)
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)

Nếu đặt u = x 2 − 1 thì x 2 = u + 1 nên phương trình có dạng
( 2 + 2)u = 2(u + 1) − 2 (1)
Ta giải phương trình (1):
(1) ⇔ 2 u + 2u = 2u + 2 − 2
⇔ 2 u = 2 − 2
⇔ 2 u = 2 ( 2 − 1) ⇔ u = 2 − 1
⇔ x 2 − 1 = 2 − 1
⇔ x 2 = 2
⇔ x = 1

\(x^4-2x^2=400x+9999=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+11x^3+119x^2+909x-11\left(x^3+11x^3+119x+909\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-11\right)\left(x^3+11x^2+119x+909\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-11\right)\left(x^3+2x^2+101x+9x^2+18x+909\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-11\right)\left(x+9\right)\left(x^2+2x+101\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}11\\-9\end{cases}}\)