Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(a,PTHH:2Cu+O_2\xrightarrow{t^o}2CuO\\ n_{Cu}=\dfrac{11,52}{64}=0,18(mol)\\ b,n_{CuO}=n_{Cu}=0,18(mol)\\ \Rightarrow m_{CuO}=0,18.80=14,4(g)\\ c,n_{O_2}=0,5.n_{Cu}=0,09(mol)\\ \Rightarrow V_{O_2}=0,09.22,4=2,016(l)\\ \Rightarrow V_{kk}=2,016.5=10,08(l)\)

a, \(4Al+3O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}2Al_2O_3\)
b, \(n_{Al_2O_3}=\dfrac{20,4}{102}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Theo PT: \(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{3}{2}n_{Al_2O_3}=0,3\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow V_{O_2}=0,3.22,4=6,72\left(l\right)\)
c, \(V_{kk}=\dfrac{V_{O_2}}{20\%}=33,6\left(l\right)\)

bài tập 2
3Fe + 2O2 -\(-^{t^o}->\) Fe3O4 (1)
ADCT n= m/M
\(n_{fe_3O_4}\)= 11,6/ 232= 0,05 mol
Theo pt(1) có
\(\dfrac{n_{O2}}{n_{Fe3O4}}\)=\(\dfrac{2}{1}\)
-> \(n_{O2}\)= 2/1 x \(n_{fe3o4}\)
= 0,1 mol
ADCT V= n x 22,4
Vo2= 0,1 x 22,4
= 2,24 (l)
bài tập 4
OXIT AXIT:
- CO2: Cacbon đi oxit
- N2O: đi ni tơ oxit
- SO3: Lưu huỳnh tri oxit
- CO: cacbon oxit
P2O5: đi photpho penta oxit
NO2: Nitơ đi oxit
OXIT BA ZƠ
- HgO: thủy ngân (II) oxit
- MgO: Magie oxit
- FeO: sắt (II) oxit
- Li2O: liti oxit
-CaO: canxi oxit
- BaO: bari oxit
- Na2O: natri oxit
- Al2O3 : Nhôm oxit
ZnO: kẽm oxit

nSO2 = 12,8 : 64=0,2 (mol)
pthh : S+ O2 -t->SO2
0,2<--0,2<------0,2(mol)
=> mS= 0,2.32=6,4 (g)
=> VO2= 0,2.22,4=4,48 (l)
ta có
VO2 = 1/5 Vkk <=> Vkk = VO2 : 1/5 = 4,48:1/5 = 22.4 (l)
S + O2 to→to→ SO2
nS=12,832=0,4(mol)
a) Theo PT: nSO2=nS=0,4(mol)
⇒VSO2=0,4×22,4=8,96(l)
b) Theo PT: nO2=nS=0,4(mol)
⇒VO2=0,4×22,4=8,96(l)
⇒VKK=5VO2=5×8,96=44,8(l)

a, Theo giả thiết ta có: \(n_P=\dfrac{3,1}{31}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
\(4P+5O_2--t^o->2P_2O_5\)
Ta có: \(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{5}{4}.n_P=0,125\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow V_{O_2\left(đktc\right)}=0,125.22,4=2,8\left(l\right)\)
b, Theo giả thiết ta có: \(n_{CH_4}=\dfrac{1,12}{22,4}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(CH_4+2O_2--t^o->CO_2+2H_2O\)
Ta có: \(n_{O_2}=2.n_{CH_4}=0,1\left(mol\right)\Rightarrow V_{O_2\left(đktc\right)}=2,24\left(l\right)\)
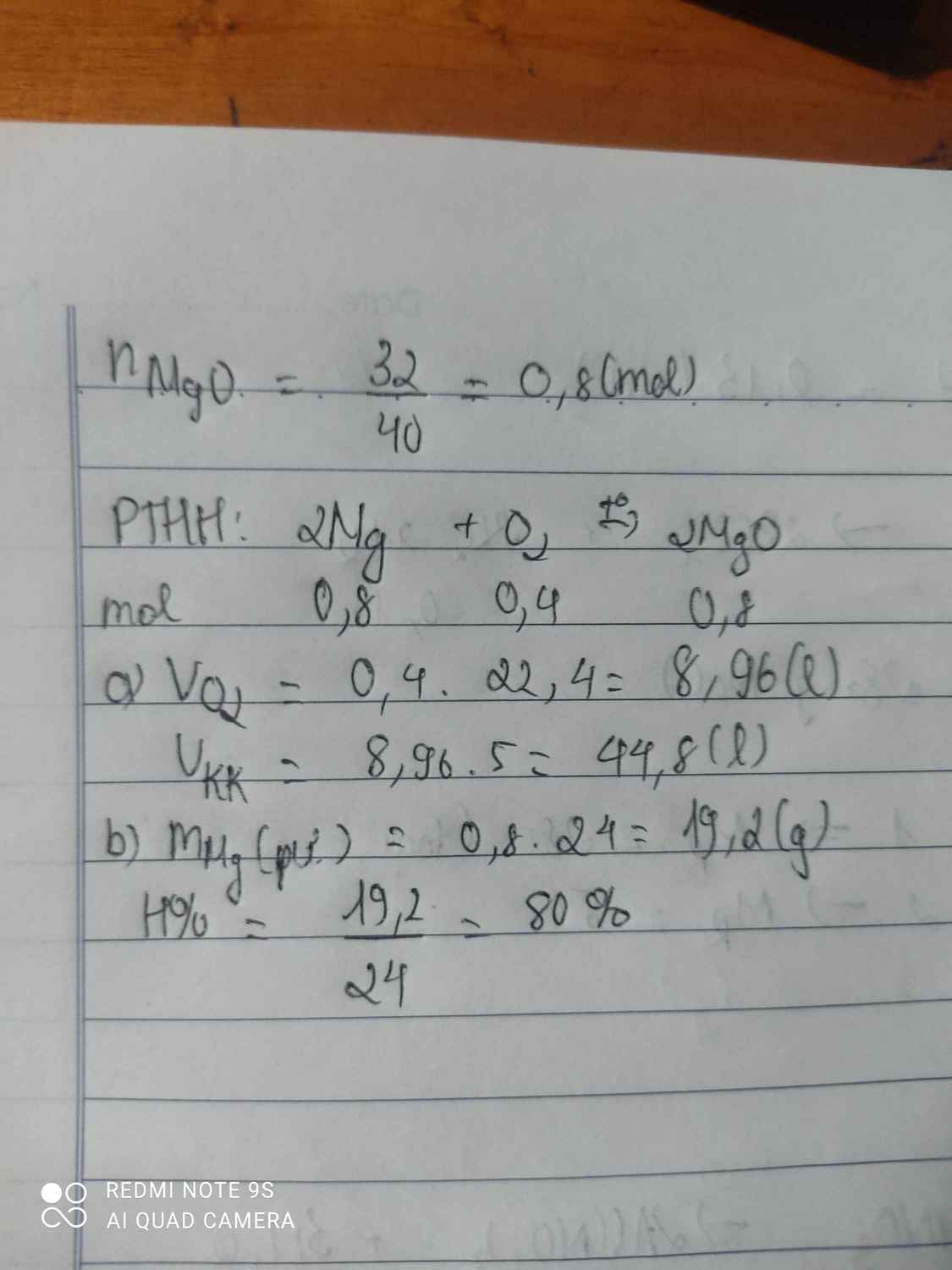
PTHH: \(2Cu+O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}2CuO\)
Ta có: \(n_{CuO}=\dfrac{12}{80}=0,15\left(mol\right)=n_{Cu\left(p/ư\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{Cu\left(dư\right)}=\dfrac{12,8}{64}-0,15=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{O_2\left(cầnthêm\right)}=0,025mol\) \(\Rightarrow V_{O_2\left(thêm\right)}=0,025\cdot22,4=0,56\left(l\right)\)
\(n_{Cu} = \dfrac{12,8}{64} = 0,2(mol)\\ n_{CuO} = \dfrac{12}{80} = 0,15(mol)\\ 2Cu + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CuO\)
Ta thấy : nCu = 0,2 > nCuO = 0,15 nên Cu dư.
Theo PTHH : \(n_{O_2\ } = \dfrac{1}{2}n_{CuO} = 0,075(mol)\)
Nếu đốt cháy hết lượng Cu ban đầu thì cần \(n_{O_2} = \dfrac{1}{2}n_{Cu} = 0,1(mol)\)
Suy ra :
\(n_{O_2\ cần\ thêm} = 0,1 - 0,075 = 0,025(mol)\\ \Rightarrow V_{O_2} = 0,025.22,4 = 0,56(lít)\)