Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(y'=x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x+3\left(m-1\right)\)
Hàm đồng biến trên khoảng đã cho khi với mọi \(x>1\) ta luôn có:
\(g\left(x\right)=x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x+3\left(m-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\min\limits_{x>1}g\left(x\right)\ge0\)
Do \(a=1>0;-\dfrac{b}{2a}=m-1\)
TH1: \(m-1\ge1\Rightarrow m\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(x\right)_{min}=f\left(m-1\right)=\left(m-1\right)^2-2\left(m-1\right)^2+3\left(m-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(m-1\right)\left(4-m\right)\ge0\Rightarrow1\le m\le4\Rightarrow2\le m\le4\)
TH2: \(m-1< 1\Rightarrow m< 2\Rightarrow g\left(x\right)_{min}=g\left(1\right)=m\ge0\)
Vậy \(0\le m\le4\)

Hàm bậc 2 có \(a=1>0;-\dfrac{b}{2a}=-\dfrac{m+1}{2}\) nên đồng biến trên \(\left(-\dfrac{m+1}{2};+\infty\right)\)
Để hàm đồng biến trên khoảng đã cho thì \(-\dfrac{m+1}{2}\le-2\Rightarrow m\ge3\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tập đã cho có vô số phần tử
Còn phần tử nguyên thì có \(2021-3=2018\) phần tử

a: \(y=-x^3-3x^2+\left(5-m\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-3\cdot2x+5-m\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-6x+5-m\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-6\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(5-m\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(36+12\left(5-m\right)< =0\)
=>\(36+60-12m< =0\)
=>\(-12m+96< =0\)
=>-12m<=-96
=>m>=8
b: \(y=x^3+\left(2m-2\right)\cdot x^2+mx\)
=>\(y'=3x^2+2\left(2m-2\right)\cdot x+m\)
=>\(y'=3x^2+\left(4m-4\right)x+m\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì y'>=0 với mọi x
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3>0\\\left(4m-4\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot m< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(16m^2-32m+16-12m< =0\)
=>\(16m^2-44m+16< =0\)
=>\(4m^2-11m+4< =0\)
=>\(\dfrac{11-\sqrt{57}}{8}< =m< =\dfrac{11+\sqrt{57}}{8}\)

a: \(y=-x^3+\left(m+2\right)x^2-3x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+2\left(m+2\right)x-3\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+\left(2m+4\right)\cdot x-3\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2m+4\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(-3\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+16m+16-4\cdot9< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+16m-20< =0\)
=>\(m^2+4m-5< =0\)
=>\(\left(m+5\right)\left(m-1\right)< =0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+5>=0\\m-1< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=-5\\m< =1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-5<=m<=1
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+5< =0\\m-1>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=1\\m< =-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
b: \(y=x^3-3x^2+\left(1-m\right)x\)
=>\(y'=3x^2-3\cdot2x+1-m\)
=>\(y'=3x^2-6x+1-m\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên R thì \(y'>=0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3>0\\\left(-6\right)^2-4\cdot3\left(1-m\right)>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(36-12\left(1-m\right)>=0\)
=>\(36-12+12m>=0\)
=>12m+24>=0
=>m+2>=0
=>m>=-2

a: TXĐ: D=R\{-1}
\(y'=\dfrac{\left(x+m\right)'\left(x+1\right)-\left(x+1\right)'\left(x+m\right)}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{x+1-x-m}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{1-m}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên từng khoảng xác định thì \(y'< 0\forall x\)
=>\(\dfrac{1-m}{\left(x+1\right)^2}< 0\)
=>1-m<0
=>m>1
b: TXĐ: D=R\{m}
\(y=\dfrac{2x-3m}{x-m}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(2x-3m\right)'\left(x-m\right)-\left(2x-3m\right)\left(x-m\right)'}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x-m\right)-\left(2x-3m\right)}{\left(x-m\right)^2}=\dfrac{2x-2m-2x+3m}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{m}{\left(x-m\right)^2}\)
Để hàm số đồng biến trên từng khoảng xác định thì \(y'>0\forall x\)
=>\(\dfrac{m}{\left(x-m\right)^2}>0\)
=>m>0
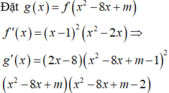
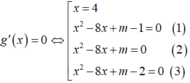



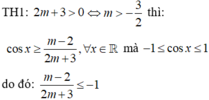
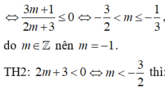
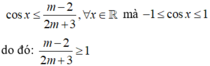
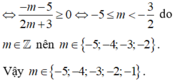

Đáp án đúng : B