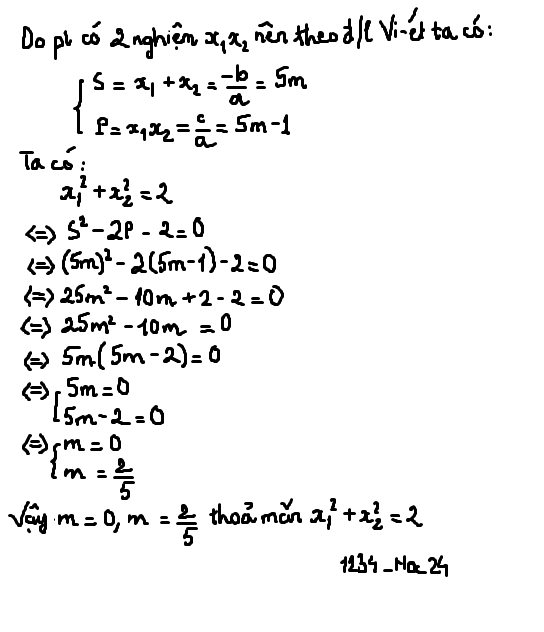Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(2x^2-\left(4m+3x\right)x+2m^2-1=0\)
\(-x^2-4mx+2m^2-1=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(4m\right)^2+4\left(2m^2-1\right)=24m^2-4\)
Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\Leftrightarrow24m^2-4>0\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{6}}\)
Vì phương trình có 2 nghiệm phân biệt, Áp dụng hệ thức Vi ét, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-4m\\x_1.x_2=1-2m^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_2^2=6\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2\left(x_1.x_2\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16m^2-2\left(1-2m^2\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20m^2=8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2=\dfrac{2}{5}\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{5}}\left(TM\right)\\m=-\sqrt{\dfrac{2}{5}}\left(\text{Loại vì m}>\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{6}}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...

Do pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\) nên theo đ/l Vi-ét , ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=3m\\P=x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=3m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có :
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow S^2+2P-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3m\right)^2+2\left(3m-1\right)-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9m^2+6m-2-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9m^2+6m-8=0\)
\(\Delta=b^2-4ac=6^2-4.9.\left(-8\right)=324>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Pt có 2 nghiệm \(m_1,m_2\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{-b+\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-6+18}{18}=\dfrac{2}{3}\\m_2=\dfrac{-b-\sqrt{\Delta}}{2a}=\dfrac{-6-18}{18}=-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(m=\dfrac{2}{3};m=-\dfrac{4}{3}\) thì thỏa mãn \(x_1^2+x_2^2=6\)

\(\Delta=\left(-3m\right)^2-4\left(3m-1\right)\)
\(=9m^2-12m+4=\left(3m-1\right)^2+3>0\)
=> pt luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Theo hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=3m\\x_1.x_2=3m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1.x_2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3m\right)^2-2\left(3m-1\right)=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9m^2-6m+2=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9m^2-6m-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{5}}{3}\\x=\dfrac{1+\sqrt{5}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Do phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1, x2
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}S=x_1+x_2=5m\\P=x_1.x_2=5m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=2\)
\(\left(x_1^2+2x_1x_2+x_2^2\right)-2x_1x_2=2\)
\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-2=0\)
\(\left(5m^2\right)-2\left(5m-1\right)-2=0\)
\(25m^2-10m+2-2=0\)
\(25m^2-10m=0\)
\(5m\left(5m-2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=0\\m=\dfrac{2}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...

x1+x2=2m+2; x1x2=m^2+4
x1^2+2(m+1)x2<=2m^2+20
=>x1^2+x2(x1+x2)<=2m^2+20
=>x1^2+x2x1+x2^2<=2m^2+20
=>(x1+x2)^2-x1x2<=2m^2+20
=>(2m+2)^2-(m^2+4)<=2m^2+20
=>4m^2+8m+4-m^2-4-2m^2-20<=0
=>m^2-8m-20<=0
=>m<=-10 hoặc m>2
\(x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+m^2+4=0\left(1\right)\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\Delta'>0\) hay \(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-m^2-4=m^2+2m+1-m^2-4=2m-4>0\Leftrightarrow m>2\)
Theo hệ thức Viét ta có : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1.x_2=m^2+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vì \(x_1^2\) là nghiệm của phương trình (1) nên ta có : \(x_1^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+m^2+4=0\Leftrightarrow x_1^2=2\left(m+1\right)x_1-m^2-4\)
Ta lại có : \(x_1^2+2\left(m+1\right)x_2\le2m^2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(m+1\right)x_1-m^2-4+2\left(m+1\right)x_2\le2m^2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(m+1\right)\left(x_1+x_2\right)-m^2-4\le2m^2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m+1\right)^2-m^2\le2m^2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m^2+2m+1\right)-m^2\le2m^2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+8m-16\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-10\le m\le2\)
Kết hợp điều kiện....