
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Chọn B.
Ta có: f(x + 1) = log2(x + 1) và g(x + 2) = log2(2 - x)
![]()
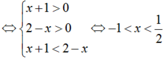

Đáp án: B.
Các phương trình còn lại có nhiều hơn một nghiệm:
(x - 5)( x 2 - x - 12) = 0 có các nghiệm x = 5, 4, -3.
sin 2 x - 5sinx + 4 = 0 ⇔ sinx = 1, có vô số nghiệm
sinx - cosx + 1 = 0 có các nghiệm x = 0, x = 3 π /2

Đáp án: B.
Các phương trình còn lại có nhiều hơn một nghiệm:
(x - 5)( x 2 - x - 12) = 0 có các nghiệm x = 5, 4, -3.
sin 2 x - 5sinx + 4 = 0 ⇔ sinx = 1, có vô số nghiệm
sinx - cosx + 1 = 0 có các nghiệm x = 0, x = 3π/2.

ĐKXĐ: \(-1< x< 2\)
Khi đó:
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)-2log_2\left(m-\frac{x}{2}+4\left(\sqrt{2-x}+\sqrt{2x+2}\right)\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2\frac{\sqrt{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)}}{m-\frac{x}{2}+4\left(\sqrt{2-x}+\sqrt{2x+2}\right)}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{\sqrt{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)}}{m-\frac{x}{2}+4\left(\sqrt{2-x}+\sqrt{2x+2}\right)}\le1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)}\le m-\frac{x}{2}+4\left(\sqrt{2-x}+\sqrt{2x+2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)}+\frac{x}{2}-4\left(\sqrt{2-x}+\sqrt{2x+2}\right)\le m\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2-x}+\sqrt{2x+2}=t\Rightarrow\sqrt{3}\le t\le3\)
\(t^2=x+4+2\sqrt{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)}\Rightarrow\sqrt{\left(2-x\right)\left(2x+2\right)}+\frac{x}{2}=\frac{t^2}{2}-2\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{t^2}{2}-4t-2\le m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=\frac{t^2}{2}-4t-2\) trên \(\left[\sqrt{3};3\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)_{min}=f\left(3\right)=-\frac{19}{2}\Rightarrow m_{min}=-\frac{19}{2}\)