Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(n_{FeO}=\dfrac{0,36}{72}=0,005\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=2n_{FeO}=0,01\left(mol\right)\\ \Rightarrow m_{ddH_2SO_4}=\dfrac{0,01.98}{98\%}=1\left(g\right)\\ n_{Fe_2\left(SO_4\right)_3}=\dfrac{1}{2}n_{FeO}=0,0025\left(mol\right)\\ \Rightarrow m_{Fe_2\left(SO_4\right)_3}=0,0025.400=1\left(g\right)\)

\(n_{Fe} = \dfrac{11,2}{56} = 0,2(mol)\\ \Rightarrow n_{Fe_2(SO_4)_3} = \dfrac{1}{2}n_{Fe} = 0,1(mol)\\ \Rightarrow m_{Fe_2(SO_4)_3} = 0,1.400 = 40(gam) \)
\(m_{O_2}=14.4-11.2=3.2\left(g\right)\)
\(n_{O_2}=\dfrac{3.2}{32}=0.1\left(mol\right)\)
\(O_2+4e\rightarrow2O^{2-}\)
\(0.1....0.4\)
\(S^{+6}+2e\rightarrow S^{+4}\)
\(.......0.4.....0.2\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=2\cdot0.2=0.4\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H_2O}=\dfrac{1}{2}n_{H_2SO_4}=\dfrac{0.4}{2}=0.2\left(mol\right)\)
\(BTKL:\)
\(m_{Muối}=14.4+0.4\cdot98-0.2\cdot64-0.2\cdot18=37.2\left(g\right)\)

Đáp án B
Vì H2SO4 đặc nóng dư nên khí A sinh ra là SO2.
Muối khan thu được là
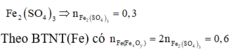
Vì dung dịch NaOH dư nên khỉ dẫn SO2 vào đung dịch NaOH chỉ xảy ra một phản ứng:
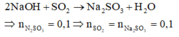
Coi oxit FexOy ban đầu là hỗn hợp của Fe và O.
Gọi nO = a.
Áp dụng định luật bảo toàn moi electron, ta có:


$n_{SO_2} = 0,01(mol)$
Bảo toàn nguyên tố với S :
$n_{H_2SO_4} = 3n_{Fe_2(SO_4)_3} + n_{SO_2}$
$\Rightarrow n_{Fe_2(SO_4)_3} = \dfrac{0,1 - 0,01}{3} = 0,03(mol)$
$z = 0,03.400 = 12(gam)$
$n_{Fe} = 2n_{Fe_2(SO_4)_3} = 0,06(mol)$
Bảo toàn e : $3n_{Fe} = 2n_O + 2n_{SO_2} \Rightarrow n_O = \dfrac{0,06.3 - 0,01.2}{2} = 0,08(mol)$
$n_{Fe} : n_O = 0,06 : 0,08 = 3 : 4$
Vậy oxit là $Fe_3O_4$
$m + z = \dfrac{0,06}{3}.232 + 12 = 16,64$

công thức oxit của sắt : Fe2Oy
nSO2=0,075 mol
2FexOy + (6x-2y)H2SO4 ---> xFe2(SO4)3 + (3x-2y)SO2 + (6x-2y)H2O
0,25 mol..........................................0,075 mol
theo pt trên ta có
\(\frac{0,25.2}{6x-2y}=\frac{0,075.2}{3x-2y}\)
<=> 0,75x-0,5y=0,45x-0,15y
<=>0,3x=0,35y<=> \(\frac{x}{y}=\frac{0,35}{0,3}=\frac{7}{6}\)
=> oxit sắt là Fe7O6
sao bạn lại để đấp án oxit fe như vậy làm j có công thức oxit fe đó

Coi hỗn hợp X gồm : Fe , O
\(n_{Fe}=a\left(mol\right),n_O=b\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_X=56a+16b=30\left(g\right)\left(1\right)\)
\(n_{SO_2}=\dfrac{11.2}{22.4}=0.5\left(mol\right)\)
\(\text{Bảo toàn e : }\)
\(3n_{Fe}=2n_O+2n_{SO_2}\)
\(\Rightarrow3a=2b+1\left(2\right)\)
\(\left(1\right),\left(2\right):a=0.475,b=0.2125\)
\(n_{Fe_2\left(SO_4\right)_3}=\dfrac{0.475}{2}=0.2375\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_{Fe_2\left(SO_4\right)_3}=0.2375\cdot400=95\left(g\right)\)
Coi X gồm Fe(a mol) ; O(b mol)
=> 56a + 16b = 30(1)
n SO2 = 11,2/22,4 = 0,5(mol)
Bảo toàn e : 3n Fe = 2n O + 2n SO2
<=> 3a - 2b = 1(2)
Từ (1)(2) suy ra a = 0,475 ; b = 0,2125
n Fe2(SO4)3 = 0,5a = 0,2375(mol)
=> m = 0,2375.400 = 95(gam)
Thí nghiệm 2 :
Gọi n FeSO4 = y(mol) ; n Fe2(SO4)3 = x(mol)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố Fe : x + y = 0,475
Bảo toàn e : 2x.3 + 2y = 0,2125.2
=> x = -0,13125 <0
(Sai đề)




