Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) (d) // (d') khi m - 3 = 1
m = 1 + 3
m = 4
Vậy m = 4 thì (d) // (d')
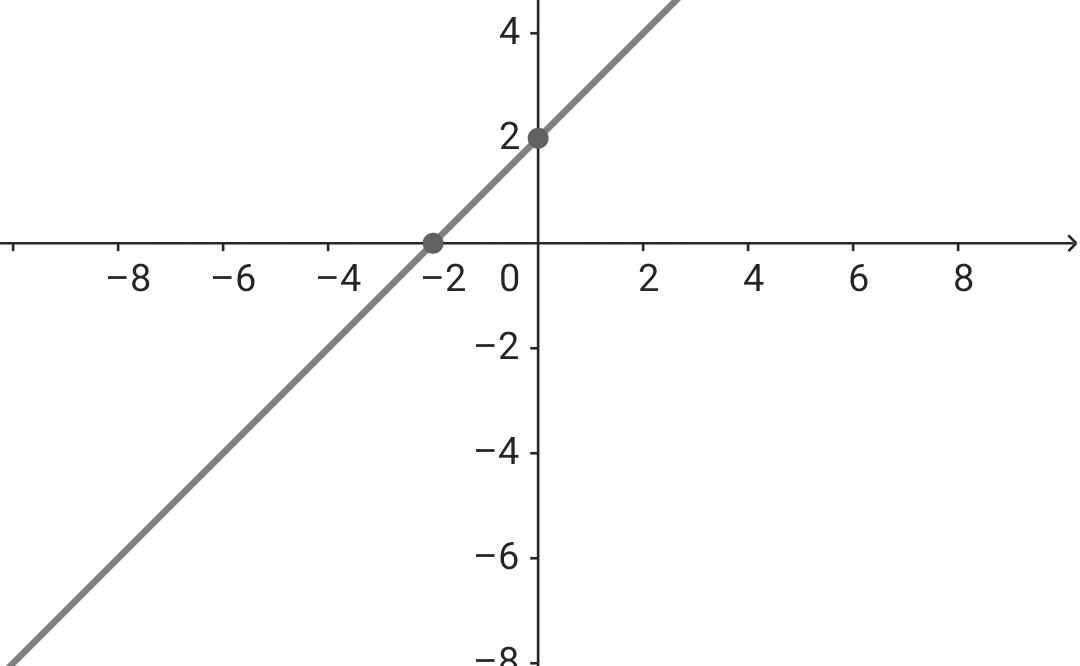
b) Với m = 4 ⇒ (d): y = x + 2
Đồ thị:

a) (d) // (d') khi m - 3 = 1
m = 1 + 3
m = 4
Vậy m = 4 thì (d) // (d')
b) Với m = 4 ⇒ (d): y = x + 2
Đồ thị:


Theo Cô si 4x+\frac{1}{4x}\ge24x+4x1≥2 , đẳng thức xảy ra khi và chỉ khi 4x=\frac{1}{4x}=1\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{4}4x=4x1=1⇔x=41). Do đó
A\ge2-\frac{4\sqrt{x}+3}{x+1}+2016A≥2−x+14x+3+2016
A\ge4-\frac{4\sqrt{x}+3}{x+1}+2014A≥4−x+14x+3+2014
A\ge\frac{4x-4\sqrt{x}+1}{x+1}+2014=\frac{\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{x+1}+2014\ge2014A≥x+14x−4x+1+2014=x+1(2x−1)2+2014≥2014
Hơn nữa A=2014A=2014 khi và chỉ khi \left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{4}\\2\sqrt{x}-1=0\end{matrix}\right.{x=412x−1=0 \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{4}⇔x=41 .
Vậy GTNN = 2014

Bài 3:
Đặt \(a=m^2-4\)
\(a)\) Đồ thị hàm số \(y=\left(m^2-4\right)x-5\)nghịch biến
\(\Leftrightarrow a< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-4< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2< 4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\sqrt{4}< m< \sqrt{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2< m< 2\)
Vậy với \(-2< m< 2\)thì hàm số nghịch biến
\(b)\) Đồ thị hàm số \(y=\left(m^2-4\right)x-5\)đồng biến \(\forall x>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2>4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}m>2\\m< -2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy với \(\orbr{\begin{cases}m>2\\m< -2\end{cases}}\)thì hàm số đồng biến \(\forall x>0\)
1: Để (d)//(d') thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\2\ne-5\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m-3=1
=>m=4
Thay m=4 vào (d), ta được:
\(y=\left(4-3\right)x+2=x+2\)
Vẽ đồ thị:
2: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\\left(m-3\right)x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x\left(m-3\right)=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\\y=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(A\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3};0\right)\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\y=\left(m-3\right)\cdot x+2=0\left(m-3\right)+2=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy: B(0;2)
\(OA=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}-0\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{2}{m-3}\right)^2+0^2}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
\(OB=\sqrt{\left(0-0\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\)
Vì Ox\(\perp\)Oy
nên OA\(\perp\)OB
=>ΔOAB vuông tại O
=>\(S_{OBA}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}\)
Để \(S_{OAB}=2\) thì \(\dfrac{2}{\left|m-3\right|}=2\)
=>|m-3|=1
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m-3=1\\m-3=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=2\end{matrix}\right.\)