
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Vẽ đồ thị hàm số
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y = 0,5 x 2 | 2 | 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 2 |
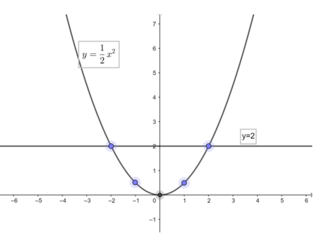
Dựa vào đồ thị ta thấy:
Khi -2 < x < 2 thì 0 ≤ y ≤ 2

Vẽ đồ thị hàm số
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y = 0,5 x 2 | 2 | 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 2 |
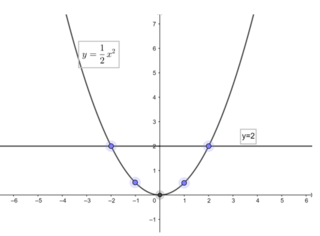
Dựa vào đồ thị ta thấy:
Khi x ≤ 0 thì y ≥ 0

Vẽ đồ thị hàm số
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y = 0,5 x 2 | 2 | 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 2 |
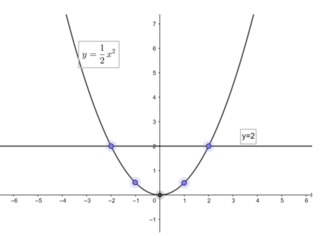
Dựa vào đồ thị ta thấy:
Để giá trị y < 2 thì -2 < x < 2

Vẽ đồ thị hàm số
| x | -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| y = 0,5 x 2 | 2 | 0,5 | 0 | 0,5 | 2 |
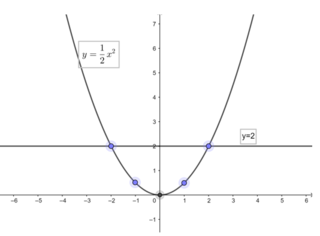
Dựa vào đồ thị ta thấy:
Để giá trị y > 2 thì x > 2 hoặc x < -2

a, Vì \(5-3\sqrt{2}>0\) nên hs đồng biến trên R
b, \(x=5+3\sqrt{2}\Leftrightarrow y=25-18+\sqrt{2}-1=6+\sqrt{2}\)
c, \(y=0\Leftrightarrow\left(5-3\sqrt{2}\right)x+\sqrt{2}-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1-\sqrt{2}}{5-3\sqrt{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\left(1-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(5+3\sqrt{2}\right)}{7}=\dfrac{-2\sqrt{2}-1}{7}\)

a: f(5)=75/2
=>\(a\cdot5^2=\dfrac{75}{2}\)
=>\(a=\dfrac{75}{2}:25=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: \(y=f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}x^2\)
Khi x=-3 thì \(y=\dfrac{3}{2}\left(-3\right)^2=\dfrac{3}{2}\cdot9=\dfrac{27}{2}\)
b: y=15
=>\(\dfrac{3}{2}x^2=15\)
=>\(x^2=10\)
=>\(x=\pm\sqrt{10}\)

Bài 1:
Hàm số y=(m-3)x+4 đồng biến trên R khi m-3>0
=>m>3
Hàm số y=(m-3)x+4 nghịch biến trên R khi m-3<0
=>m<3
Bài 4:
a: Vì \(a=3-\sqrt{2}>0\)
nên hàm số \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)x+1\) đồng biến trên R
b: Khi x=0 thì \(y=0\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)+1=1\)
Khi x=1 thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\cdot1+1=3-\sqrt{2}+1=4-\sqrt{2}\)
Khi \(x=\sqrt{2}\) thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\cdot\sqrt{2}+1=3\sqrt{2}-2+1=3\sqrt{2}-1\)
Khi \(x=3+\sqrt{2}\) thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(3+\sqrt{2}\right)-1\)
=9-4-1
=9-5
=4
Khi \(x=3-\sqrt{2}\) thì \(y=\left(3-\sqrt{2}\right)^2-1\)
\(=11-6\sqrt{2}-1=10-6\sqrt{2}\)
Vẽ đồ thị hàm số
Dựa vào đồ thị ta thấy:
Khi x ≤ 2 thì y ≥ 0