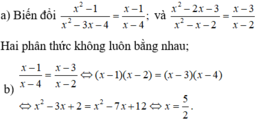Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) ĐKXĐ: \(^{x^3+2x^2+x+2}\)khác 0
=> x^2(x+2)+(x+2) Khác 0
=> (x^2+1)(x+2) khác 0
=> x^2 khác -1(vô lý) và x khác -2
Vậy x khác -2 thì biểu thức A được xác định
b)\(A=\frac{3x^3+6x^2}{x^3+2x^2+x+2}=\frac{3x^2\left(x+2\right)}{x^2\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{3x^2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{3x^2}{x^2+1}\)
Để A=2 thì \(\frac{3x^2}{x+2}=2\)=>\(3x^2=2\left(x^2+1\right)=>3x^2=2x^2+2\)
\(=>x^2=2=>x=\sqrt{2}\)(Thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định)

\(\dfrac{x^3-x^2-x+1}{x^4-2x^2+1}=\dfrac{x^2\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\cdot\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2\cdot\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\cdot\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{x+1}\)
\(\dfrac{5x^3+10x^2+5x}{x^3+3x^2+3x+1}=\dfrac{5x\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)^3}=\dfrac{5x}{x+1}\)

EM MỚI LỚP 3 LÊN EM KO BIẾT GÌ HẾT
CHẮC CHỊ HOẶC ANH NÊN TRA GOOGLE

Ta có:
\(\dfrac{x^2-4}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x+1}\)
Và:
\(\dfrac{x+2}{2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{2x\left(x-2\right)}\)
Vậy ta đã biến đổi hai phân thức đó để chúng bằng phân thức cũ và có tủ bằng nhau

bài1 A=\(\left(\frac{3-x}{x+3}\cdot\frac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\frac{x}{x+3}\right):\frac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(\left(-\frac{x-3\cdot\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)^2\cdot\left(x-3\right)}+\frac{x}{x+3}\right):\frac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(-\frac{x}{x+3}\cdot\frac{x+3}{3x^2}=\frac{-1}{3x}\)
b) thế \(x=-\frac{1}{2}\)vào biểu thức A
\(-\frac{1}{3\cdot\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)}=\frac{2}{3}\)
c) A=\(-\frac{1}{3x}< 0\)
VÌ (-1) <0 nên 3x>0
x >0

\(a,Đkxđ:x\ne\pm2\)
\(A=\frac{1}{x-2}+\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{x^2+1}{x^2-4}\)
\(=\frac{x+2+x-2+x^2+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2+2x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2-4}\)
b, Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)< 0;\forall-2< 2< 2;x\ne-1\)
Mà: \(\left(x+1\right)^2>0\left(\forall x\ne-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}< 0;\forall-2< x< 2;x\ne-1\)
Vậy ............

Đặt phân thức đã cho là A
\(ĐKXĐ:x^2-x\ne0\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\ne0\)\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x-1\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne1\end{cases}}\)
a) \(A=\frac{2x-2}{x^2-x}=\frac{2\left(x-1\right)}{x\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{2}{x}\)
Với \(x=3\)( thoả mãn ĐKXĐ ) \(\Rightarrow A=\frac{2}{3}\)
Với \(x=0\)( không khoả mãn ĐKXĐ ) \(\Rightarrow\)Không tìm được giá trị của A
b) \(A=2\)\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{x}=2\)\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)( không thoả mãn ĐKXĐ )
Vậy không tìm được giá trị của x để \(A=2\)
c) A có giá trị nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{x}\inℤ\)\(\Leftrightarrow2⋮x\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
So sánh với ĐKXĐ \(\Rightarrow x=1\)không thoả mãn
Vậy A nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2;-1;2\right\}\)
ĐKXĐ:
----------->x khác 0
---------->(x-1) khác 0 ----------> x khác 1
VẠY ĐKXĐ LÀ X khác 0 và 1.
Bạn tự rút gọn nha
a, 2x-2\ x^2-x= 2\x
Thay x=3 vào biểu thức có:
-----> = 2\3
Vậy nếu thay x=3 vào biểu thức thì = 2\3
thay x=0 vào biểu thức có
------> = 0 vì 2\0=0
VẬY nếu thay x=0 thì biểu thức thì =0
b,
theo đề bài ta có
2\x=2
-----> 2:x=2
Vậy x=1
Câu c mik ko chắc nên bn tự làm nha
mik rất sorry:(((((((