
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

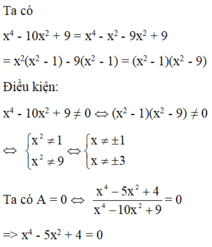
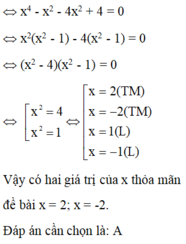

Bài 1:
a: Để B có nghĩa thì \(x^4-10x^2+9< >0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)< >0\)
hay \(x\notin\left\{3;1;-3;-1\right\}\)
b: \(B=0\) khi \(x^4-5x^2+4=0\)
=>(x-2)(x+2)=0
hay \(x\in\left\{2;-2\right\}\)

Lời giải:
a. ĐKXĐ: $x\neq \pm 1; \pm 3$
$A=\frac{x^4-5x^2+4}{x^4-10x^2+9}=\frac{(x-1)(x+1)(x-2)(x+2)}{(x-1)(x+1)(x-3)(x+3)}$
$=\frac{(x-2)(x+2)}{(x-3)(x+3)}=\frac{x^2-4}{x^2-9}$
b.
Để $A=0$ thì $x^2-4=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\pm 2$ (thỏa mãn)
c.
$|2x-1|=7$
$\Rightarrow 2x-1=7$ hoặc $2x-1=-7$
$\Rightarrow x=4$ hoặc $x=-3$.
Mà $x\neq \pm 1; \pm 3$ nên $x=4$
Khi đó:
$A=\frac{4^2-4}{4^2-9}=\frac{12}{7}$

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\)
Ta có: \(B=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x^2+10x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50-5x+50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+5x-x-5}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)-\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
b) Để B=0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\)
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: Để B=0 thì x=1
Để \(B=\dfrac{1}{4}\) thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)(nhận)
Vậy: Để \(B=\dfrac{1}{4}\) thì \(x=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
c) Thay x=3 vào biểu thức \(B=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\), ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{3-1}{2}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\)
Vậy: Khi x=3 thì B=1
d) Để B<0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Để B<0 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x\notin\left\{0;-5\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để B>0 thì \(\dfrac{x-1}{2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1>0\)
hay x>1
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: x>1
Vậy: Để B>0 thì x>1

\(A=\frac{4}{x+2}+\frac{2}{x-2}+\frac{6-5x}{x^2-4}\)
a) ĐKXĐ : x ≠ ±2
\(=\frac{4\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{6-5x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{4x-8+2x+4+6-5x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{1}{x-2}\)
b) Để A = 1 => \(\frac{1}{x-2}=1\)=> x - 2 = 1 => x = 3 ( tm )
c) Để A > 1 => \(\frac{1}{x-2}>1\)
=> \(\frac{1}{x-2}-1>0\)
=> \(\frac{1}{x-2}-\frac{x-2}{x-2}>0\)
=> \(\frac{1-x+2}{x-2}>0\)
=> \(\frac{-x+3}{x-2}>0\)
Xét hai trường hợp
1. \(\hept{\begin{cases}-x+3>0\\x-2>0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}-x>-3\\x>2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x< 3\\x>2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow2< x< 3\)
2. \(\hept{\begin{cases}-x+3< 0\\x-2< 0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}-x< -3\\x< 2\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x>3\\x< 2\end{cases}}\)( loại )
Vậy với 2 < x < 3 thì A > 1
d) Để A nguyên => \(\frac{1}{x-2}\)nguyên
=> 1 ⋮ x - 2
=> x - 2 ∈ Ư(1) = { ±1 }
=> x ∈ { 1 ; 3 } thì A nguyên

a) \(ĐKXĐ:x\ne\pm2\)
\(A=\dfrac{4}{x+2}+\dfrac{2}{x-2}+\dfrac{6-5x}{x^2-4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{4\left(x-2\right)+2\left(x+2\right)+6-5x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{4x-8+2x+4+6-5x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{x+2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\dfrac{1}{x-2}\)
b) Để A = 1
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-2}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\) (tm)
Vậy ...
c) Để A > 1
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-2}>1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-2}-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1-x+2}{x-2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-x+3}{x-2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3-x\right)\left(x-2\right)>0\)
Trường hợp \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-x>0\\x-2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 3\\x>2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2< x< 3\) (tm)
Trường hợp \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3-x< 0\\x-2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>3\\x< 2\end{matrix}\right.\) (ktm)
Vậy ...
d) Để A nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x-2}\in Z\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2\inƯ\left(1\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{1;3;0;4\right\}\)
Vậy ...

a) \(\dfrac{x^4+x^3+x+1}{x^4-x^3+2x^2-x+1}\)
= \(\dfrac{x^3\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)}{x^3\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)+2x^2}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3-1\right)+2x^2}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)+2x^2}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2.\left(x^2-x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x^2+x+1\right)+2x^2}\)
Ta thấy mẫu thức của phân thức vốn đã lớn hơn 0 với mọi x, vậy để p/t trên có giá trị bằng 0 thì tử thức phải bằng 0
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy x = -1
b) \(\dfrac{x^4-5x^2+4}{x^4-10x^2+9}\)
= \(\dfrac{x^4-x^3+x^3-x^2-4x^2+4}{x^4-x^3+x^3-x^2-9x^2+9}\)
= \(\dfrac{x^3\left(x-1\right)+x^2\left(x-1\right)-4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^3\left(x-1\right)+x^2\left(x-1\right)-9\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+x^2-4x-4\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+x^2-9x-9\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{x^3+x^2-4x-4}{x^3+x^2-9x-9}\)
= \(\dfrac{x^2\left(x+1\right)-4\left(x+1\right)}{x^2\left(x+1\right)-9\left(x+1\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\) ( ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne\pm3\) )
Để phân thức trên có giá trị bằng 0 thì tử thức phải bằng 0
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) ( thoả mãn điều kiện xác định )
Vậy x = 2 hoặc x = -2

a/ \(\dfrac{x^4+x^3+x+1}{x^4-x^3+2x^2-x+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^3\left(x+1\right)+\left(x+1\right)}{x^4-x^3+x^2+x^2-x+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^3+1\right)}{x^2\left(x^2-x+1\right)+\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2\left(x^2-x+1\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2+1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy ...
b/ \(\dfrac{x^4-5x^2+4}{x^4-10x^2+9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^4-x^2-4x^2+4}{x^4-x^2-9x^2+9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)-4\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)-9\left(x^2-1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2-4\right)}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2-9\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x^2-9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy..