Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(-1\right)=-2;f\left(0\right)=2;f\left(2\right)=-2\)
\(\Rightarrow M=2;m=-2\Rightarrow P=6\)
Cả 4 đáp án đều sai (kiểm tra lại đề bài, có đúng là \(f\left(x\right)=x^3-3x^2+2\) hay không?)

\(g\left(x\right)=x^4-4x^3+4x^2+a\)
\(g'\left(x\right)=4x^3-12x^2+8x=0\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(0\right)=f\left(2\right)=\left|a\right|\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=\left|a+1\right|\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}M=\left|a\right|\\m=\left|a+1\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|a\right|\ge\left|a+1\right|\\\left|a\right|\le2\left|a+1\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{2}{3}\le a\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\\a\le-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a=\left\{-3;-2\right\}\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}M=\left|a+1\right|\\m=\left|a\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|a+1\right|\ge\left|a\right|\\\left|a+1\right|\le2\left|a\right|\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{1}{2}\le a\le-\dfrac{1}{3}\\a\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a=\left\{1;2;3\right\}\)

1/ \(f'\left(x\right)=\frac{3\sqrt{x^2+1}-\frac{x\left(3x+1\right)}{\sqrt{x^2+1}}}{x^2+1}=\frac{3\left(x^2+1\right)-3x^2-x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}}=\frac{3-x}{\left(x^2+1\right)\sqrt{x^2+1}}\)
Hàm số đồng biến trên \(\left(-\infty;3\right)\) nghịch biến trên \(\left(3;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đạt GTLN tại \(x=3\)
\(f\left(x\right)_{max}=f\left(3\right)=\frac{10}{\sqrt{10}}=\sqrt{10}\)
2/ \(y'=\frac{\sqrt{x^2+2}-\frac{\left(x-1\right)x}{\sqrt{x^2+2}}}{x^2+2}=\frac{x^2+2-x^2+x}{\left(x^2+2\right)\sqrt{x^2+2}}=\frac{x+2}{\left(x^2+2\right)\sqrt{x^2+2}}\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow x=-2\in\left[-3;0\right]\)
\(y\left(-3\right)=-\frac{4\sqrt{11}}{11}\) ; \(y\left(-2\right)=-\frac{\sqrt{6}}{2}\) ; \(y\left(0\right)=-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}M=-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\\N=-\frac{\sqrt{6}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow MN=\frac{\sqrt{12}}{4}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Tất cả các đáp án đều sai
3/ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left|x-3\right|\ge0\\\sqrt{x+1}>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge0\) \(\forall x\Rightarrow N=0\) khi \(x=3\)
- Với \(0\le x< 3\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(3-x\right)\sqrt{x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=-\sqrt{x+1}+\frac{\left(3-x\right)}{2\sqrt{x+1}}=\frac{-2\left(x+1\right)+3-x}{2\sqrt{x+1}}=\frac{-3x+1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=0\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{3}\)
- Với \(3< x\le4\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-3\right)\sqrt{x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x+1}+\frac{x-3}{2\sqrt{x+1}}=\frac{2\left(x+1\right)+x-3}{2\sqrt{x+1}}=\frac{3x-1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}>0\) \(\forall x>3\)
Ta có: \(f\left(0\right)=3\) ; \(f\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)=\frac{16\sqrt{3}}{9}\) ; \(f\left(4\right)=\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow M=\frac{16\sqrt{3}}{9}\Rightarrow M+2N=\frac{16\sqrt{3}}{9}\)
Câu 2 hình như câu B mà người ta nói đạt GTLN . GTNN tại M , N nên là 0 x -2 =0

a) 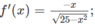
f′(x) > 0 trên khoảng (-4; 0) và f’(x) < 0 trên khoảng (0; 4).
Hàm số đạt cực đại tại x = 0 và f C Đ = 5
Mặt khác, ta có f(-4) = f(4) = 3
Vậy 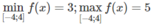
d) f(x) = | x 2 − 3x + 2| trên đoạn [-10; 10]
Khảo sát sự biến thiên và vẽ đồ thị của hàm số g(x) = x 2 – 3x + 2.
Ta có:
g′(x) = 2x − 3; g′(x) = 0 ⇔ x = 3/2
Bảng biến thiên:
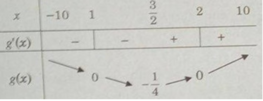
Vì
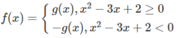
nên ta có đồ thị f(x) như sau:
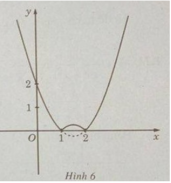
Từ đồ thị suy ra: min f(x) = f(1) = f(2) = 0; max = f(x) = f(−10) = 132
e) 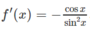
f′(x) < 0 nên và f’(x) > 0 trên (π/2; 5π/6] nên hàm số đạt cực tiểu tại x = π/2 và f C T = f(π/2) = 1
Mặt khác, f(π/3) = 2√3, f(5π/6) = 2
Vậy min f(x) = 1; max f(x) = 2
g) f(x) = 2sinx + sin2x trên đoạn [0; 3π/2]
f′(x) = 2cosx + 2cos2x = 4cos(x/2).cos3(x/2)
f′(x) = 0
⇔ 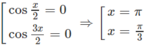
Ta có: f(0) = 0,
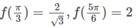
Từ đó ta có: min f(x) = −2 ; max f(x) = 3√3/2

3.
\(y'=-3x^2-6x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(y\left(-1\right)=m-2\) ; \(y\left(1\right)=m-4\)
\(\Rightarrow y_{min}=y\left(1\right)=m-4\)
\(\Rightarrow m-4=0\Rightarrow m=4\)
4.
Hàm đã cho bậc nhất trên bậc nhất nên đơn điệu trên mọi khoảng xác định
\(\Rightarrow y_{min}+y_{max}=y\left(1\right)+y\left(2\right)=\frac{m+1}{2}+\frac{m+2}{3}=8\)
\(\Rightarrow m=\frac{41}{5}\)
Đáp án B
1.
\(y'=\frac{1}{\left(sinx+1\right)^2}.cosx>0\Rightarrow y\) đồng biến
\(m=y_{min}=y\left(0\right)=2\)
\(M=y_{max}=y\left(1\right)=\frac{5}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow M^2+m^2=\frac{41}{4}\)
2.
Hàm xác định trên \(\left[-2;2\right]\)
\(y'=1-\frac{x}{\sqrt{4-x^2}}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\)
\(y\left(-2\right)=-2\) ; \(y\left(\sqrt{2}\right)=2\sqrt{2}\) ; \(y\left(2\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow N=-2;M=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow M+2N=2\sqrt{2}-4\)

Chọn B.
P =
2
(
x
3
+
y
3
)
-
3
x
y
![]()
![]() (do
x
2
+
y
2
=
2
)
(do
x
2
+
y
2
=
2
)
Đặt x + y = t. Ta có
x
2
+
y
2
=
2
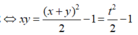
Từ ![]()
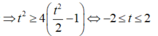
P = f(t) 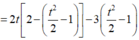
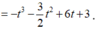
Xét f(t) trên [-2;2].
Ta có ![]()
Bảng biến thiên
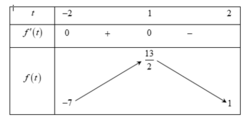
Từ bảng biến thiên ta có max P = max f(t) = 13 2 ; min P = min f(t) = -7
Lời bình: Có thể thay bbt thay bằng
Ta có ![]()
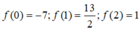
Suy ra kết luận.

Chọn C
Gọi A (d; e; f) thì A thuộc mặt cầu (S1): (x - 1)2 + (y - 2)2 + (z- 3)2 = 1 có tâm I1 = (1; 2; 3), bán kính R1 = 1
B (a; b; c) thì B thuộc mặt cầu (S2): (x - 3)2 + (y - 2)2 + z2 = 9 có tâm I2 = (-3; 2; 0), bán kính R2 = 3
Ta có I1I2 = 5 > R1 + R2 => (S1) và (S2) không cắt nhau và ở ngoài nhau.
Dễ thấy F = AB, AB max khi A ≡ A1; B ≡ B1
=> Giá trị lớn nhất bằng I1I2 + R1 + R2 = 9.
AB min khi A ≡ A2; B ≡ B2
=> Giá trị nhỏ nhất bằng I1I2 - R1 - R2 = 1.
Vậy M - m =8