Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Câu 1:
Để ý rằng \((2-\sqrt{3})(2+\sqrt{3})=1\) nên nếu đặt
\(\sqrt{2+\sqrt{3}}=a\Rightarrow \sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{a}\)
PT đã cho tương đương với:
\(ma^x+\frac{1}{a^x}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ma^{2x}-4a^x+1=0\) (*)
Để pt có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\) thì pt trên phải có dạng pt bậc 2, tức m khác 0
\(\Delta'=4-m>0\Leftrightarrow m< 4\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Viete, với $x_1,x_2$ là hai nghiệm của pt (*)
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} a^{x_1}+a^{x_2}=\frac{4}{m}\\ a^{x_1}.a^{x_2}=\frac{1}{m}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} a^{x_2}(a^{x_1-x_2}+1)=\frac{4}{m}\\ a^{x_1+x_2}=\frac{1}{m}(1)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(x_1-x_2=\log_{2+\sqrt{3}}3=\log_{a^2}3\) :
\(\Rightarrow a^{x_2}(a^{\log_{a^2}3}+1)=\frac{4}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^{x_2}(\sqrt{3}+1)=\frac{4}{m}\Rightarrow a^{x_2}=\frac{4}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}\) (2)
\(a^{x_1}=a^{\log_{a^2}3+x_2}=a^{x_2}.a^{\log_{a^2}3}=a^{x_2}.\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow a^{x_1}=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}\) (3)
Từ \((1),(2),(3)\Rightarrow \frac{4}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}.\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}=\frac{1}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{16\sqrt{3}}{m^2(\sqrt{3}+1)^2}=\frac{1}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{16\sqrt{3}}{(\sqrt{3}+1)^2}=-24+16\sqrt{3}\) (thỏa mãn)
Câu 2:
Nếu \(1> x>0\)
\(2017^{x^3}>2017^0\Leftrightarrow 2017^{x^3}>1\)
\(0< x< 1\Rightarrow \frac{1}{x^5}>1\)
\(\Rightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}> 2017^1\Leftrightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}>2017\)
\(\Rightarrow 2017^{x^3}+2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}> 1+2017=2018\) (đpcm)
Nếu \(x>1\)
\(2017^{x^3}> 2017^{1}\Leftrightarrow 2017^{x^3}>2017 \)
\(\frac{1}{x^5}>0\Rightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}>2017^0\Leftrightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{5}}>1\)
\(\Rightarrow 2017^{x^3}+2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}>2018\) (đpcm)

Điều kiện x>1
Từ (1) ta có \(\log_{\sqrt{3}}\frac{x+1}{x-1}>\log_34\) \(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x+1}{x-1}>2\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) 1<x<3
Đặt \(t=\log_2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)\)
Tìm điều kiện của t :
- Xét hàm số \(f\left(x\right)=\log_2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)\) với mọi x thuộc (1;3)
- Đạo hàm : \(f\left(x\right)=\frac{2x-2}{\ln2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)}>\) mọi \(x\in\left(1,3\right)\)
Hàm số đồng biến nên ta có \(f\left(1\right)\) <\(f\left(x\right)\) <\(f\left(3\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow\)2<2<3
- Ta có \(x^2-2x+5=2'\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(x-1\right)^2=2'-4\)
Suy ra ứng với mõi giá trị \(t\in\left(2,3\right)\) ta luôn có 1 giá trị \(x\in\left(1,3\right)\)
Lúc đó (2) suy ra : \(t-\frac{m}{t}=5\Leftrightarrow t^2-5t=m\)
Xét hàm số : \(f\left(t\right)=t^2-5t\) với mọi \(t\in\left(2,3\right)\)
- Đạo hàm : \(f'\left(t\right)=2t-5=0\Leftrightarrow t=\frac{5}{2}\)
- Bảng biến thiên :
| x | 2 \(\frac{5}{2}\) 3 |
| y' | + 0 - |
| y | -6 -6 -\(\frac{25}{4}\) |
Để hệ có 2 cặp nghiệm phân biệt \(\Leftrightarrow-6>-m>-\frac{25}{4}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\frac{25}{4}\) <m<6

a) Đặt t = 13x > 0 ta được phương trình:
13t2 – t – 12 = 0 ⇔ (t – 1)(13t + 12) = 0
⇔ t = 1 ⇔ 13x = 1 ⇔ x = 0
b)
Chia cả hai vế phương trình cho 9x ta được phương trình tương đương
(1+(23)x)(1+3.(23)x)=8.(23)x(1+(23)x)(1+3.(23)x)=8.(23)x
Đặt t=(23)xt=(23)x (t > 0) , ta được phương trình:
(1 + t)(1 + 3t) = 8t ⇔ 3t2 – 4t + 1 = 0 ⇔ t∈{13,1}t∈{13,1}
Với t=13t=13 ta được nghiệm x=log2313x=log2313
Với t = 1 ta được nghiệm x = 0
c) Điều kiện: x > 2
Vì nên phương trình đã cho tương đương với:
[log3(x−2)=0log5x=1⇔[x=3x=5[log3(x−2)=0log5x=1⇔[x=3x=5
d) Điều kiện: x > 0
log22x – 5log2x + 6 = 0
⇔(log2x – 2)(log2x – 3) = 0
⇔ x ∈ {4, 8}





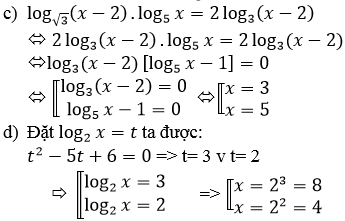
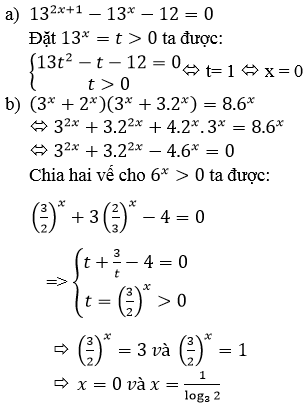


1/ ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log_{5x}5-log_{5x}x+log_5^2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{log_55x}-\dfrac{1}{log_x5x}+log_5^2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{1+log_5x}-\dfrac{1}{1+log_x5}+log_5^2x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{1+log_5x}-\dfrac{log_5x}{1+log_5x}+\left(log_5x-1\right)\left(log_5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1-log_5x}{1+log_5x}-\left(1-log_5x\right)\left(1+log_5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-log_5x\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{1+log_5x}-\left(1+log_5x\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-log_5x=0\\\dfrac{1}{1+log_5x}=1+log_5x\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1-log_5x=0\\1+log_5x=1\\1+log_5x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{25}\end{matrix}\right.\)
2/ ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log_5\left(5^x-1\right).log_{25}\left(5^{x+1}-5\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_5\left(5^x-1\right).log_{5^2}5\left(5^x-1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_5\left(5^x-1\right)\left(1+log_5\left(5^x-1\right)\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_5^2\left(5^x-1\right)+log_5\left(5^x-1\right)-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_5\left(5^x-1\right)=1\\log_5\left(5^x-1\right)=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5^x-1=5\\5^x-1=\dfrac{1}{25}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5^x=6\\5^x=\dfrac{26}{25}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=log_56\\x=log_5\dfrac{26}{25}\end{matrix}\right.\)
3/ ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(2log_3^2x-log_3x.log_3\left(\sqrt{2x+1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_3x\left(2log_3x-log_3\left(\sqrt{2x+1}-1\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_3x=0\Rightarrow x=1\\2log_3x-log_3\left(\sqrt{2x+1}-1\right)=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1): \(log_3x^2=log_3\left(\sqrt{2x+1}-1\right)\Leftrightarrow x^2=\sqrt{2x+1}-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+1=\sqrt{2x+1}\Leftrightarrow x^4+2x^2+1=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+2x^2-2x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^3+2x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(l\right)\\x^3+2x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\) ????
Pt bậc 3 kia có nghiệm rất xấu, chỉ giải được bằng công thức Cardano mà bậc phổ thông không học, nên bạn có chép đề sai không vậy?