Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Giải:
+ Xét hạng tử thứ nhất là: 5\(x^3\) vậy hạng tử này có bậc là 3
+ Xét hạng tử thứ hai là: \(xy^2z^3\)
\(x\) có bậc là 1
y2 có bậc là 2
z3 có bậc là 3
Vậy hạng tử \(xy^2z^3\) có bậc là: 1 + 2 + 3 = 6
+ Bậc của hạng tử \(xy^2z^3\) lớn hơn bậc của hạng tử - 5\(x^3\) nên đó là bậc của đa thức vì vậy bậc của đa thức là 6

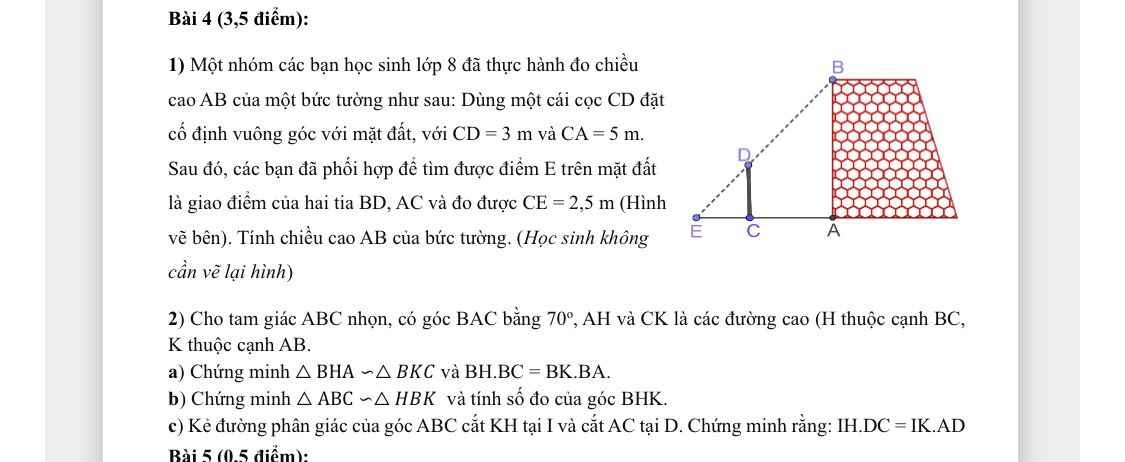
2:
a: Xét ΔBHA vuông tại H và ΔBKC vuông tại K có
\(\widehat{HBA}\) chung
Do đó: ΔBHA~ΔBKC
=>\(\dfrac{BH}{BK}=\dfrac{BA}{BC}\)(2)
=>\(\dfrac{BH}{BA}=\dfrac{BK}{BC}\)
=>\(BH\cdot BC=BK\cdot BA\)
b: Xét ΔBHK và ΔBAC có
\(\dfrac{BH}{BA}=\dfrac{BK}{BC}\)
\(\widehat{HBK}\) chung
Do đó: ΔBHK~ΔBAC
=>\(\widehat{BHK}=\widehat{BAC}=70^0\)
c: Xét ΔBKH có BI là phân giác
nên \(\dfrac{IH}{IK}=\dfrac{BH}{BK}\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔBAC có BD là phân giác
nên \(\dfrac{DA}{DC}=\dfrac{BA}{BC}\left(3\right)\)
Từ (1),(2),(3) suy ra \(\dfrac{IH}{IK}=\dfrac{DA}{DC}\)
=>\(IH\cdot DC=DA\cdot IK\)

a: ΔABC cân tại A
mà AD là đường cao
nên D là trung điểm của BC
ΔADB vuông tại D
=>\(DA^2+DB^2=AB^2\)
=>\(DB=\sqrt{5^2-4^2}=3\left(cm\right)\)
b: Xét ΔHDB vuông tại D và ΔHEA vuông tại E có
\(\widehat{DHB}=\widehat{EHA}\)(hai góc đối đỉnh)
Do đó: ΔHDB~ΔHEA
=>\(\dfrac{HD}{HE}=\dfrac{HB}{HA}\)
=>\(HD\cdot HA=HB\cdot HE\)

a) $-(2x-4)(x+2)+(x+2)^2+(x-2)^2-4x^2-1-4x=-3$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2-2(x-2)(x+2)+(x+2)^2-4x^2-4x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2+x+2)^2-4x^2-4x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x)^2-4x^2-4x=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow -4x=-2$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac12$
b) $(4x-1)^2-16(x+1)(x+3)=25$
$\Leftrightarrow (4x)^2-2.4x.1+1^2-16(x^2+4x+3)=25$
$\Leftrightarrow 16x^2-8x+1-16x^2-64x-48=25$
$\Leftrightarrow -72x-47=25$
$\Leftrightarrow -72x=72$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-1$
c) $(3x-7)^2=9(3x-7)(x+5)+694$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x)^2-2.3x.7+7^2=9(3x^2+8x-35)+694$
$\Leftrightarrow 9x^2-42x+49=27x^2+72x-315+694$
$\Leftrightarrow 18x^2+114x+330=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 9x^2+57x+165=0$
$\Leftrightarrow 9\left(x+\frac{19}{6}\right)^2+\frac{299}{4}=0$ (vô lí)
=> Pt vô nghiệm
d) $(2x-1)^2+(x+3)^2=5(x+7)(x-7)-3x$
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2-4x+1+x^2+6x+9=5(x^2-49)-3x$
$\Leftrightarrow 5x^2+2x+10=5x^2-3x-245$
$\Leftrightarrow 5x=-255$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-51$
#$\mathtt{Toru}$

a: Ta có: \(AK=KB=\dfrac{AB}{2}\)
\(DI=IC=\dfrac{DC}{2}\)
mà AB=CD
nên AK=KB=DI=IC
Xét tứ giác AKCI có
AK//CI
AK=CI
Do đó: AKCI là hình bình hành
=>AI//CK và AI=CK
b: Xét ΔDNC có
I là trung điểm của DC
IM//NC
Do đó: M là trung điểm của DN
=>DM=MN
Xét ΔBAM có
K là trung điểm của BA
KN//AM
Do đó: N là trung điểm của BM
=>BN=NM
=>BN=NM=DM
c: Xét tứ giác BKDI có
BK//DI
BK=DI
Do đó: BKDI là hình bình hành
=>DK//BI
=>EK//FI
ta có: AI//CK
=>IE//KF
Xét tứ giác EKFI có
EK//FI
EI//KF
Do đó: EKFI là hình bình hành


a: Xét ΔABH vuông tại H và ΔCBA vuông tại A có
\(\widehat{ABH}\) chung
Do đó: ΔABH~ΔCBA
b: ΔABC vuông tại A
=>\(AB^2+AC^2=BC^2\)
=>\(BC=\sqrt{6^2+8^2}=10\left(cm\right)\)
Xét ΔABC có BD là phân giác
nên \(\dfrac{AD}{AB}=\dfrac{CD}{BC}\)
=>\(\dfrac{AD}{6}=\dfrac{CD}{10}\)
=>\(\dfrac{AD}{3}=\dfrac{CD}{5}\)
mà AD+CD=AC=8cm
nên Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{AD}{3}=\dfrac{CD}{5}=\dfrac{AD+CD}{3+5}=\dfrac{8}{8}=1\)
=>\(AD=3\cdot1=3\left(cm\right);CD=5\cdot1=5\left(cm\right)\)
c:
ΔBAD vuông tại A
=>\(S_{BAD}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot BA\cdot AD=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot6\cdot3=9\left(cm^2\right)\)
ΔBHA~ΔBAC
=>\(\dfrac{BH}{BA}=\dfrac{BA}{BC}=\dfrac{6}{10}=\dfrac{3}{5}\)
Xét ΔBAD vuông tại A và ΔBHI vuông tại H có
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{HBI}\)
Do đó: ΔBAD~ΔBHI
=>\(\dfrac{S_{BAD}}{S_{BHI}}=\left(\dfrac{BA}{BH}\right)^2=\left(\dfrac{5}{3}\right)^2=\dfrac{25}{9}\)
=>\(S_{BHI}=S_{BAD}\cdot\dfrac{9}{25}=\dfrac{81}{25}\left(cm^2\right)\)



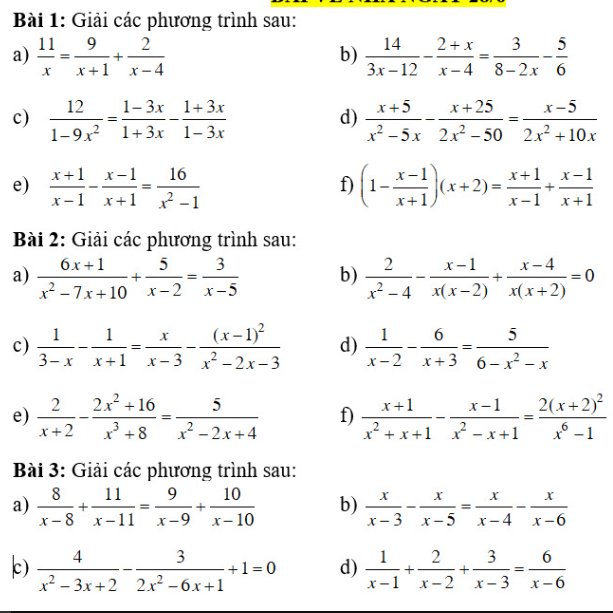
Bài 1:
e: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{16}{x^2-1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{16}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=16\)
=>\(\left(x+1+x-1\right)\left(x+1-x+1\right)=16\)
=>4x=16
=>x=4(nhận)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1-1\right\}\)
\(\left(1-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\right)\left(x+2\right)=\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}+\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+1-x+1}{\left(x+1\right)}\left(x+2\right)=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2+\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>\(2\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=2\left(x^2+1\right)\)
=>\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=x^2+1\)
=>\(x^2+x-2=x^2+1\)
=>x-2=1
=>x=3(nhận)
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-1;4\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{11}{x}=\dfrac{9}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x-4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{11}{x}=\dfrac{9\left(x-4\right)+2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{11}{x}=\dfrac{11x-34}{x^2-3x-4}\)
=>\(11\left(x^2-3x-4\right)=x\left(11x-34\right)\)
=>\(11x^2-33x-44=11x^2-34x\)
=>-33x-44=-34x
=>-33x+34x=44
=>x=44(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne4\)
\(\dfrac{14}{3x-12}-\dfrac{2+x}{x-4}=\dfrac{3}{8-2x}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-4}=\dfrac{-3}{2\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{28}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{6\left(x+2\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{-9}{6\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5\left(x-4\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}\)
=>28-6(x+2)=-9-5(x-4)
=>28-6x-12=-9-5x+20
=>-6x+16=-5x+11
=>-6x+5x=11-16
=>-x=-5
=>x=5(nhận)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{\dfrac{1}{3};-\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{12}{1-9x^2}=\dfrac{1-3x}{1+3x}-\dfrac{1+3x}{1-3x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{12}{\left(1-3x\right)\left(1+3x\right)}=\dfrac{\left(1-3x\right)^2-\left(1+3x\right)^2}{\left(1+3x\right)\left(1-3x\right)}\)
=>\(\left(1-3x\right)^2-\left(1+3x\right)^2=12\)
=>\(9x^2-6x+1-9x^2-6x-1=12\)
=>-12x=12
=>x=-1(nhận)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;5;-5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+5}{x^2-5x}-\dfrac{x+25}{2x^2-50}=\dfrac{x-5}{2x^2+10x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5}{x\left(x-5\right)}-\dfrac{x+25}{2\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-5}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x+5\right)^2}{2x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x+25\right)}{2x\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-5\right)^2}{2x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
=>\(2\left(x+5\right)^2-x\left(x+25\right)=\left(x-5\right)^2\)
=>\(2x^2+20x+50-x^2-25x=x^2-10x+25\)
=>-5x+50=-10x+25
=>5x=-25
=>x=-5(loại)
Bài 2:
a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;5\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{6x+1}{x^2-7x+10}+\dfrac{5}{x-2}=\dfrac{3}{x-5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6x+1}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}+\dfrac{5\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-5\right)}\)
=>6x+1+5x-25=3x-6
=>11x-24=3x-6
=>8x=18
=>x=9/4(nhận)
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;2;-2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{x-1}{x\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x-4}{x\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=0\)
=>2x-(x-1)(x+2)+(x-4)(x-2)=0
=>\(2x-\left(x^2+x-2\right)+x^2-6x+8=0\)
=>\(x^2-4x+8-x^2-x+2=0\)
=>-5x+10=0
=>x=2(loại)
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{x^2-2x-3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-1}{x-3}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{x}{x-3}+\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(-1-x\right)\left(x+1\right)-x+3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>-(x+1)^2-x+3+(x-1)2=0
=>\(-x^2-2x-1-x+3+x^2-2x+1=0\)
=>-5x+3=0
=>\(x=\dfrac{3}{5}\left(nhận\right)\)
d: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;-3\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x-2}-\dfrac{6}{x+3}=\dfrac{5}{6-x^2-x}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+3-6\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{-5}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>x+3-6(x-2)=-5
=>x+3-6x+12+5=0
=>-5x+20=0
=>x=4(nhận)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>-2
\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{x^3+8}=\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x^2+16}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)-2x^2-16-5x-10}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=0\)
=>\(2x^2-4x+8-2x^2-5x-26=0\)
=>-9x-18=0
=>x=-2(loại)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{x^2+x+1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x^2-x+1}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{x^6-1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x+2\right)^2}{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}\)
=>2(x^2-1)=2(x+2)^2
=>\(x^2-1=\left(x+2\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+4x+4-x^2+1=0\)
=>4x+5=0
=>\(x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\left(nhận\right)\)
Bài 3:
c:
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-1}+\dfrac{x}{x-2}+\dfrac{x}{x-3}=\dfrac{3x-12}{x-6}\)
=>
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;2;\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt{7}}{2}\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{4}{x^2-3x+2}-\dfrac{3}{2x^2-6x+1}+1=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{4\left(2x^2-6x+1\right)-3\left(x^2-3x+2\right)}{\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left(2x^2-6x+1\right)}=-1\)
=>\(8x^2-24x+4-3x^2+9x-6=-\left(x^2-3x+2\right)\left[2\cdot\left(x^2-3x\right)+1\right]\)
=>\(5x^2-15x-2=-\left[2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+2\right]\)
=>\(5\left(x^2-3x\right)-2+2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+2=0\)
=>\(2\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+10\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)=0\)
=>\(\left(x^2-3x\right)\left(x^2-3x+5\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-3x+5=\left(x-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{11}{4}>=\dfrac{11}{4}>0\forall x\)
nên x(x-3)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=3\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
a:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{8;9;10;11\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{8}{x-8}+\dfrac{11}{x-11}=\dfrac{9}{x-9}+\dfrac{10}{x-10}\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{8}{x-8}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{11}{x-11}+1\right)=\left(\dfrac{9}{x-9}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{10}{x-10}+1\right)\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{x-8}+\dfrac{x}{x-11}-\dfrac{x}{x-9}-\dfrac{x}{x-10}=0\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{1}{x-8}+\dfrac{1}{x-11}-\dfrac{1}{x-9}-\dfrac{1}{x-10}\right)=0\)
=>x=0(nhận)
b:
ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;4;5;6\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x}{x-3}-\dfrac{x}{x-5}=\dfrac{x}{x-4}-\dfrac{x}{x-6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x\left(x-5\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{x\left(x-6\right)-x\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-2x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}=\dfrac{-2x}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\)
=>\(x\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}-\dfrac{1}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}\right)=0\)
=>\(x\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)-\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x-6\right)}=0\)
=>\(x\left(x^2-10x+24-x^2+8x-15\right)=0\)
=>x(-2x+9)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=\dfrac{9}{2}\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)