(m^2-1)x^2 +mx+1=0 tìmm để thành pt bậc nhất 1 ẩn
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta nhận thấy
\(-x^2+2x-2=-\left[\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+1\right]\)
Ta có
\(x^2-2x+1\ge0\Rightarrow\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+1\ge1\)
\(\Rightarrow-\left[\left(x^2-2x+1\right)+1\right]\le-1\)
\(\Rightarrow PT\Leftrightarrow8x-4=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\left(8x-4\right)\left(-x^2+2x-2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(8x-4\right)\left(x^2-2x+2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}8x-4=0\\x^2-2x+2=0\left(loai\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
do \(x^2-2x+2=x^2-2x+1+1=\left(x-1\right)^2+1>0\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x+3y=1\\\dfrac{1}{3}x-\dfrac{1}{2}y=-\dfrac{1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{2}{3}x+y=\dfrac{1}{3}\\\dfrac{2}{3}x-y=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{2}{3}x+y+\dfrac{2}{3}x-y=\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{3}\\y=\dfrac{2}{3}x+\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0x=0\\y=\dfrac{2}{3}x+\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\in R\\y=\dfrac{2x+1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x+3y=1\\\dfrac{1}{3}x-\dfrac{1}{2}y=-\dfrac{1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x+3y=1\\2x-3y=-1\end{matrix}\right.=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0x=0\\-2x+3y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy có vô số nghiệm

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0,2x+0,5y=0,7\\4x+10y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+10y=3,5\\4x+10y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0x=5,5\left(ko\exists\right)\\4x+2y=3,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0,2x+0,5y=0,7\\4x+10y=9\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x+10y=14\\4x+10y=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> Hpt vô nghiệm

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=8\\\dfrac{1}{2}x-y=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=8\\x-2y=36\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=44\\x+2y=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=22\\y=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=8\\\dfrac{1}{2}x-y=18\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=8\\x-2y=36\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=44\\x-2y=36\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=22\\2y=x-36=22-36=-14\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=22\\x=-\dfrac{14}{2}=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: ...

Gọi H là giao điểm của AG với BC
Xét ΔABC có
G là trọng tâm
H là giao điểm của AG với BC
Do đó: H là trung điểm của BC và \(AG=2GH;GH=\dfrac{1}{3}HA\)
Xét ΔHAB có GD//AB
nên \(\dfrac{HD}{HB}=\dfrac{HG}{HA}\)
=>\(\dfrac{HD}{HB}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{HD}{DB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
=>\(\dfrac{BD}{BH}=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
=>\(BD=\dfrac{2}{3}BH=\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot BC=\dfrac{1}{3}BC\)

a: Xét ΔBAC vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(BH^2=AH\cdot HC=9\cdot16=144=12^2\)
=>BH=12(cm)
ΔBHA vuông tại H
=>\(BH^2+HA^2=BA^2\)
=>\(BA=\sqrt{12^2+9^2}=15\left(cm\right)\)
ΔBHC vuông tại H
=>\(HB^2+HC^2=BC^2\)
=>\(BC=\sqrt{12^2+16^2}=20\left(cm\right)\)
b: Xét ΔBHC vuông tại H có HE là đường cao
nên \(BE\cdot BC=BH^2\left(1\right)\)
Xét ΔBAC vuông tại B có BH là đường cao
nên \(BH^2=HC\cdot HA\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1),(2) suy ra \(BE\cdot BC=HA\cdot HC\)
c: Xét ΔABC có BD là phân giác
nên \(BD=\dfrac{2\cdot BA\cdot BC}{BA+BC}\cdot cos\left(\dfrac{ABC}{2}\right)=\dfrac{2\cdot BA\cdot BC}{BA+BC}\cdot cos45\)
=>\(BD=\dfrac{2\cdot BA\cdot BC}{BA+BC}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}\cdot BA\cdot BC}{BA+BC}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{BD}=\dfrac{BA+BC}{\sqrt{2}\cdot BA\cdot BC}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{BD}=\dfrac{BA+BC}{BA\cdot BC}=\dfrac{1}{BC}+\dfrac{1}{BA}\)


Ta có:
\(\dfrac{3-x}{3+x}=\dfrac{-x+3}{x+3}=\dfrac{-\left(x+3\right)+6}{x+3}=-1+\dfrac{6}{x+3}\)
Để biểu thức nhận giá trị nguyên thì: 6 ⋮ x + 3
=> x + 3 ∈ Ư(6) = {1; -1; 2; -2; 3; -3; 6; -6}
=> x ∈ {-2; -4; -1; -5; 0; -6; 3; -9}

\(a)\dfrac{5}{x+7}=\dfrac{-14}{x-5}\left(x\ne-7;x\ne5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-14\left(x+7\right)=5\left(x-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-14x-98=5x-25\\ \Leftrightarrow5x+14x=-98+25\\ \Leftrightarrow19x=-73\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{73}{19}\left(tm\right)\\ b)\dfrac{3}{3x-2}=\dfrac{1}{x+1}\left(x\ne\dfrac{2}{3};x\ne-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x+1\right)=3x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow3x+3=3x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow3=-2\)
=> Pt vô nghiệm
\(c)\dfrac{x}{x-2}=\dfrac{1}{x+1}+1\left(x\ne2;x\ne-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{x-2}=\dfrac{x+2}{x+1}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x=x^2-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-4\left(tm\right)\)
\(d)\dfrac{x+6}{x+5}+\dfrac{3}{2}=2\left(x\ne-5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x+6\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{3\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(x+6\right)+3\left(x+5\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x+12+3x+15=4\left(x+5\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow5x+27=4x+20\\ \Leftrightarrow5x-4x=20-27\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-7\left(tm\right)\)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>3
\(\dfrac{x+5}{x-3}+2=\dfrac{2}{x-3}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x+5+2x-6}{x-3}=\dfrac{2}{x-3}\)
=>3x-1=2
=>3x=3
=>x=1(nhận)
f: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{0;-1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{3x+5}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x}=3\)
=>\(\dfrac{3x+3+2}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x}=3\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x}=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x+2x+2}{x\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
=>4x+2=0
=>4x=-2
=>\(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(loại\right)\)
g: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;2\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}+\dfrac{x+2}{x-3}=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)+\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{x^2-9+x^2-4}{x^2-5x+6}=2\)
=>\(2\left(x^2-5x+6\right)=2x^2-13\)
=>-10x+12=-13
=>-10x=-25
=>\(x=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(nhận\right)\)
h: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;3\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{2}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{x-3}=\dfrac{3x-20}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2\left(x-3\right)-3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{3x-20}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
=>\(2x-6-3x+6=3x-20\)
=>3x-20=-x
=>4x=20
=>x=5(nhận)
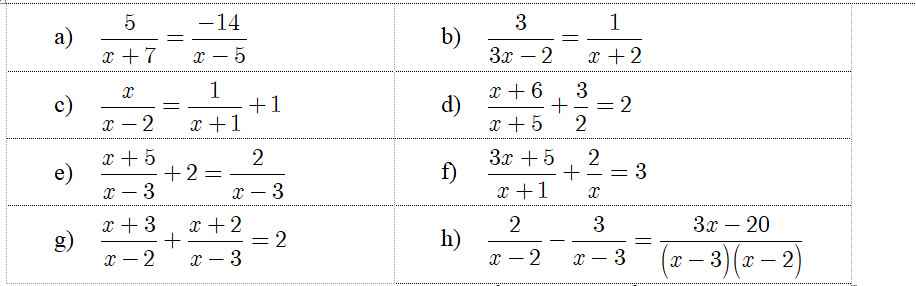
Để đây là phương trình bậc nhất một ẩn thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2-1=0\\m\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2=1\\m\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)