Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của các phân thức sau
\(B=\dfrac{x^2-2x+2016}{x^2}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1) Xét rằng x > 7 <=> A < 0
Lại xét x < 7 thì mẫu là một số nguyên dương. P/s A có tử và mẫu đều là số dương, mà tử lại bất biến
A(max) <=> mẫu 7 - x nhỏ nhất <=> 7 - x = 1 => x = 7 - 1 = 6 <=> A = 1
Từ những điều trên thì A sẽ có GTLN khi và chỉ khi x = 6

A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
a, A là phân số ⇔ \(x\) + 2 # 0 ⇒ \(x\) # -2
b, Để A là một số nguyên thì 2\(x-1\) ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2\(x\) + 4 - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 2(\(x\) + 2) - 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ 5 ⋮ \(x\) + 2
⇒ \(x\) + 2 \(\in\) { -5; -1; 1; 5}
⇒ \(x\) \(\in\) { -7; -3; -1; 3}
c, A = \(\dfrac{2x-1}{x+2}\)
A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)
Với \(x\) \(\in\) Z và \(x\) < -3 ta có
\(x\) + 2 < - 3 + 2 = -1
⇒ \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > \(\dfrac{5}{-1}\) = -5 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\)< 5
⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 + 5 = 7 ⇒ A < 7 (1)
Với \(x\) > -3; \(x\) # - 2; \(x\in\) Z ⇒ \(x\) ≥ -1 ⇒ \(x\) + 2 ≥ -1 + 2 = 1
\(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) > 0 ⇒ - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 0 ⇒ 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{x+2}\) < 2 (2)
Với \(x=-3\) ⇒ A = 2 - \(\dfrac{5}{-3+2}\) = 7 (3)
Kết hợp (1); (2) và(3) ta có A(max) = 7 ⇔ \(x\) = -3

\(A=2\left(x^2-4x+4\right)-7=2\left(x-2\right)^2-7\ge-7\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=2\)
\(B=\left(x^2+3x+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{1}{4}=\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\ge-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(C=4\left(x^2-2x+1\right)-4=4\left(x-1\right)^2-4\ge-4\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(D=\dfrac{1}{-\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+6}=\dfrac{1}{-\left(x+1\right)^2+6}\ge\dfrac{1}{6}\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
1.
$A=2x^2-8x+1=2(x^2-4x+4)-7=2(x-2)^2-7$
Vì $(x-2)^2\geq 0$ với mọi $x\in\mathbb{R}$
$\Rightarrow A\geq 2.0-7=-7$
Vậy $A_{\min}=-7$ khi $x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=2$
2.
$B=x^2+3x+2=(x^2+3x+1,5^2)-0,25=(x+1,5)^2-0,25\geq 0-0,25=-0,25$
Vậy $B_{\min}=-0,25$ khi $x=-1,5$
3.
$C=4x^2-8x=(4x^2-8x+4)-4=(2x-2)^2-4\geq 0-4=-4$
Vậy $C_{\min}=-4$ khi $2x-2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1$
4. Để $D_{\min}$ thì $5-x^2-2x$ là số thực âm lớn nhất
Mà không tồn tại số thực âm lớn nhất nên không tồn tại $x$ để $D_{\min}$

A\(=2x^2-8x+1\)
=2x(x-4)+1≥1
Min A=1 ⇔x=4
B=\(x^2+3x+2\)
\(=\left(x^2+2.x.\dfrac{3}{2}+\dfrac{9}{4}\right)-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(=\left(x+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\)≥\(-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Min B=-1/4⇔x=-3/2
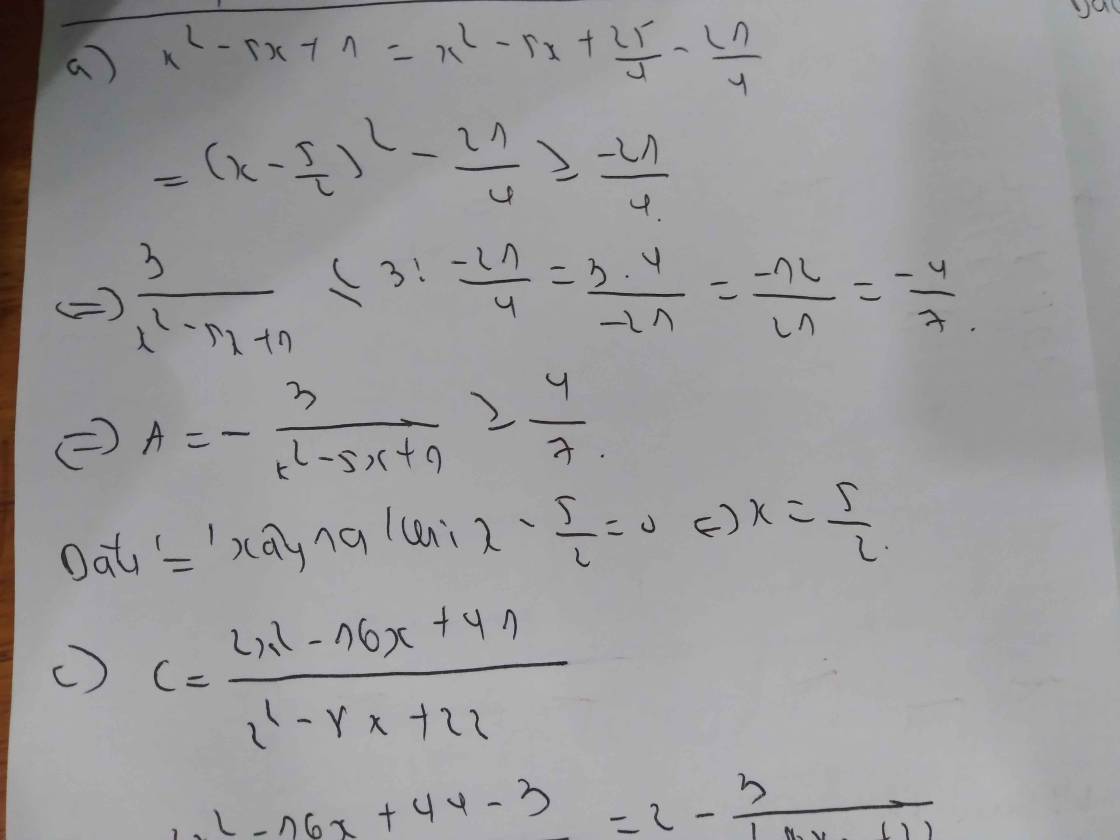
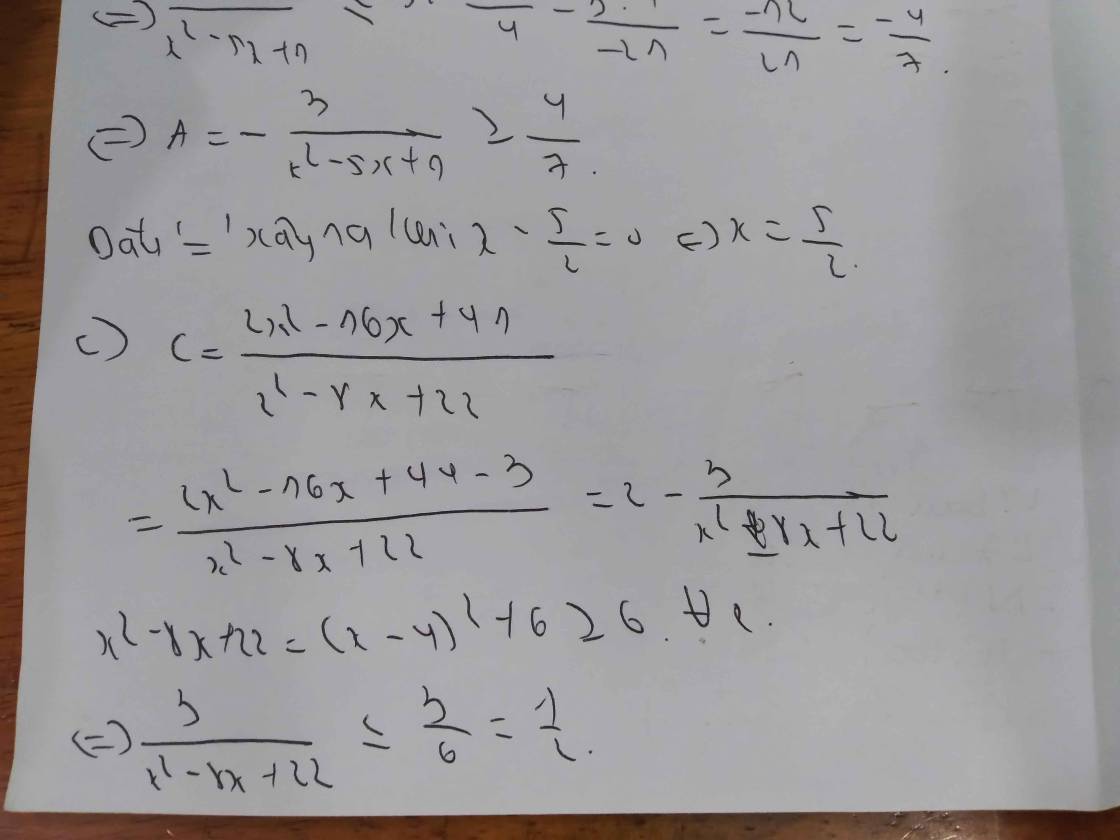
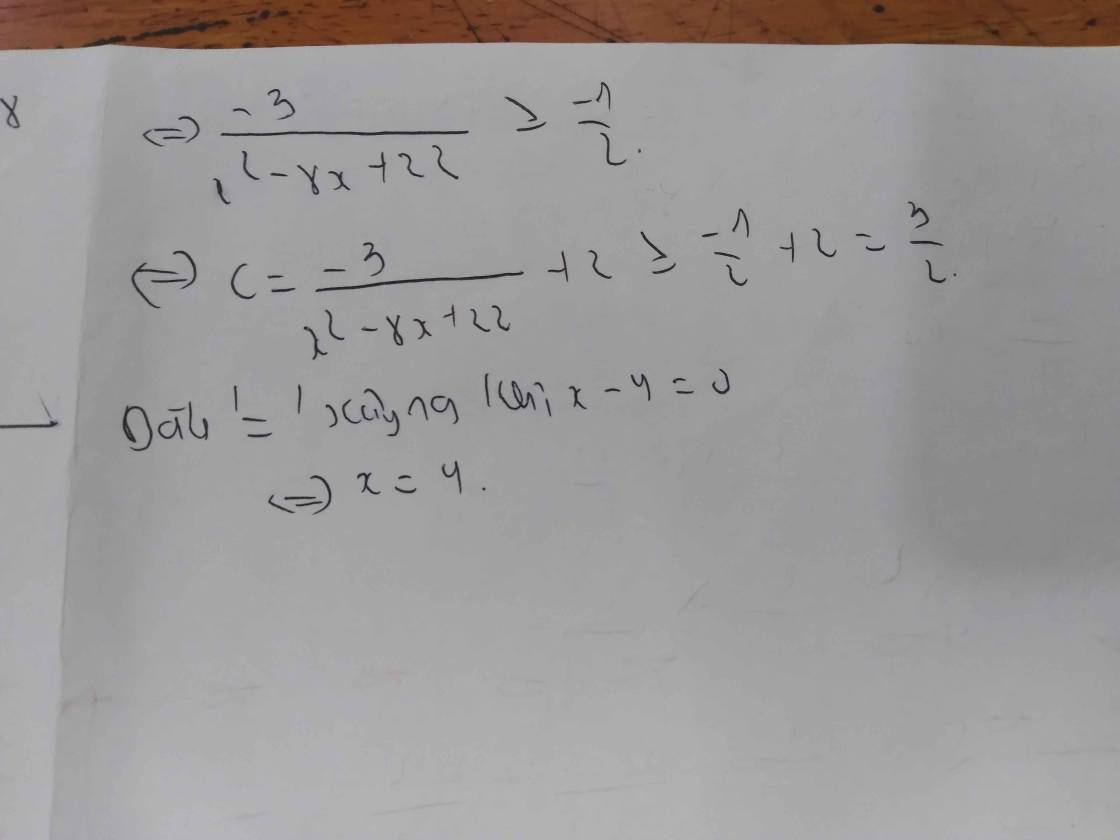
Ta có:
\(B=\dfrac{x^2-2x+2016}{x^2}\left(x\ne0\right)\)
\(B=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2}-\dfrac{2x}{x^2}+\dfrac{2016}{x^2}\)
\(B=1-\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{2016}{x^2}\)
\(B=2016\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2}-\dfrac{1}{2016}\cdot\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)\)
\(B=2016\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2}-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2016}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)\)
\(B=2016\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2}-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2016}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{4064256}+\dfrac{2015}{4064256}\right)\)
\(B=2016\left[\dfrac{1}{x^2}-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2016}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{4064256}\right]+2016\cdot\dfrac{2015}{4064256}\)
\(B=2016\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)^2+\dfrac{2015}{2016}\)
Ta có: \(2016\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow2016\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)^2+\dfrac{2015}{2016}\ge\dfrac{2015}{2016}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi:
\(2016\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)^2+\dfrac{2015}{2016}=\dfrac{2015}{2016}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2016\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2016}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{2016}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{2016}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2016\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy: \(B_{min}=\dfrac{2015}{2016}\Leftrightarrow x=2016\)
Em nghĩ khi càng lớn thì B càn nhỏ ạ vì nếu thay x = 3 vào B thì giá trị của B gần bằng 224 còn nếu x = 10 thì B là 20,96 nên giá trị x = 1 chưa phải là GTNN của B ạ