Tìm tất cả các nghiệm nguyên của phương trình:
x.(x2 + 2x + 4) = y3 - 3
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Để pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\)
\(\Rightarrow m^2-4.1.\left(-2\right)>0\\ \Rightarrow m^2+8>0\left(luôn.đúng\right)\)
Vậy pt luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng định lý Vi-ét ta có:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-m\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x^2_1x_2+x_1x^2_2=2021\\ \Leftrightarrow x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)=2021\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(-m\right)\left(-2\right)=2021\\ \Leftrightarrow2m=2021\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{2021}{2}\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì
\(\Delta>0\\ \Rightarrow m^2-4.1.\left(-2\right)>0\\ \Rightarrow m^2+8>0.đúng.\forall.m\)
Vậy pt luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng đlí Viét ta có
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=-m\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Lại có
\(x_1x_2+x_1x_2=2021\\ \Rightarrow x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)< 2021\\ \Rightarrow-2\left(-m\right)=2021\Rightarrow2m=2021\\ \Rightarrow m=\dfrac{2021}{2}\)

+, Nếu x = 0 => ko tồn tại y thuộc Z
+, Nếu x khác 0 => x^2 >= 1 => x^2-1 >= 0
Có : y^3 = x^3+2x^2+3x+2 > x^3 ( vì 2x^2+3x+2 > 0 )
Lại có : y^3 = (x^3+3x^3+3x+1)-(x^2-1) = (x+1)^3 - (x^2-1) < = (x+1)^3
=> x^3 < y^3 < = (x+1)^3
=> y^3 = (x+1)^3
=> x^2-1 = 0
=> x=-1 hoặc x=1
+, Với x=-1 thì y = 0
+, Với x=1 thì y = 2
Vậy .............
Tk mk nha
Ta có: \(x^3+2x^2+3x+2=y^3\) (1)
Xét \(2x^2+3x+2=2\left(x^2+\frac{3}{2}x\right)+2=2\left(x^2+\frac{3}{2}x+\frac{9}{16}\right)+2-2.\frac{9}{16}\)
\(=2\left(x+\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+\frac{7}{8}\) Vì \(\left(x+\frac{3}{4}\right)^2\ge0\Rightarrow2\left(x+\frac{3}{4}\right)^2+\frac{7}{8}\ge\frac{7}{8}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow y^3>x^3\Rightarrow y^3\ge\left(x+1\right)^3\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3+2x^2+3x+2\ge\left(x+1\right)^3\) \(\Rightarrow x^3+2x^2+3x+2\ge x^3+3x^2+3x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3+3x^2+3x+1-x^3-2x^2-3x-2\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-1\le0\Rightarrow x^2\le1\) Vì \(x\in Z\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x^2=1\\x^2=0\end{cases}}\)
+ TH1: x2 = 0 => x =0 Thay vào pt (1) ta được y3 = 2 (loại) vì y nguyên
+ TH2 : x2 = 1 => \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
Thay x=1 vào pt (1) ta đc: 1+2+3+2 = 8 = y3 => y = 2
Thay x= -1 vào pt (1) ta đc: -1 + 2 -3 +2 = 0 =y3 => y = 0
Vậy cặp (x;y) là (1;2) ; (-1;0).


Phương trình đã cho tương đương m = x 2 - 2 x - 3
Đặt y = f x = x 2 - 2 x - 3
Ta có đồ thị hàm số y = f(x) như sau:
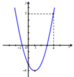
Dựa vào đồ thị, để phương trình y = f x = x 2 - 2 x - 3 = m có nghiệm x ∈ [0; 4] thì - 4 ≤ m ≤ 5
Đáp án cần chọn là: C


\(\dfrac{2x}{x^2+1}\ge1\Leftrightarrow2x\ge x^2+1\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2\le0\)
Mà \(\left(x-1\right)^2\ge0\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(A=\left\{1\right\}\)
Để \(x^2-2bx+4=0\Leftrightarrow\Delta=4b^2-4\cdot4< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b^2-4< 0\Leftrightarrow\left(b-2\right)\left(b+2\right)< 0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\le-2;x\ge2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow B=\left\{x\in R|x\le-2;x\ge2\right\}\)
Vậy \(A\cap B=\varnothing\)

TH1: m=-1/2
BPT sẽ là -2x-3/2-3>0
=>-2x>9/2
=>x<-9/4
=>Loại
TH2: m<>-1/2
Δ=(-2)^2-4(2m+1)(3m-3)
=4-4(6m^2-6m+3m-3)
=4-4(6m^2-3m-3)
=4-24m^2+12m+12
=-24m^2+12m+16
Để BPT vô nghiệm thì -24m^2+12m+16<=0 và 2m+1<0
=>m<-1/2 và \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m< =\dfrac{3-\sqrt{105}}{2}\\m>=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{105}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m< =\dfrac{3-\sqrt{105}}{2}\)
*Sử dụng phương pháp chặn (hai đầu):
\(x\left(x^2+2x+4\right)=y^3-3\left(1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+4x+3=y^3-x^3\)
Ta có \(2x^2+4x+3=2\left(x+1\right)^2+1>0\)
\(\Rightarrow y^3-x^3>0\Rightarrow y^3>x^3\left(2\right)\)
Lại có: \(\left(x+2\right)^3-y^3=\left(x^3+6x^2+12x+8\right)-\left(x^3+2x^2+4x+3\right)=4x^2+8x+5=4\left(x+1\right)^2+1>0\)
\(\Rightarrow y^3< \left(x+2\right)^3\left(3\right)\)
Từ (2), (3) suy ra \(x^3< y^3< \left(x+2\right)^3\Rightarrow y^3=\left(x+1\right)^3\).
Thay vào (1) ta được:
\(x^3+2x^2+4x=\left(x+1\right)^3-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+2x^2+4x=x^3+3x^2+3x+1-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(x=2\Rightarrow y=3\)
Với \(x=-1\Rightarrow y=0\)
Vậy các nghiệm nguyên của pt (1) là \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(2;3\right),\left(-1;0\right)\)