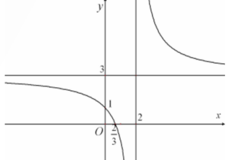
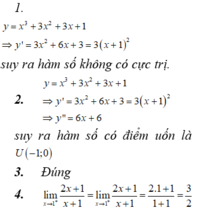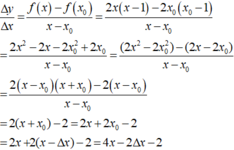2. Số gia của hàm số y = 2x^2 -3x +1 theo x và denta x là? 3. Số gia của hàm số y = ✓2x^2 +1 theo x và denta x là?
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



\(y=x^3-3x^2+2x+2\Rightarrow y'=3x^2-6x+2\)
Vi \(\Delta\perp d:y=x-3\Rightarrow y'=-1\Leftrightarrow3x^2-6x+2=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1\Rightarrow y=1-3+2+2=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta:y=-1\left(x-1\right)+2\)

∆y=f(1+∆x)-f(1)=(1+∆x)2+2(1+∆x)-(1+2)=(∆x)2+4∆x
Đáp án B
Chú ý. Tránh các sai lầm thay trực tiếp ∆x hoặc 1 vào hàm (A,D) hoặc lấy hiệu của f(∆x) và f(1) (C)

a. \(y'=\dfrac{-1}{\left(x-1\right)}\)
b. \(y'=\dfrac{5}{\left(1-3x\right)^2}\)
c. \(y=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2+1}{x+1}=x+1+\dfrac{1}{x+1}\Rightarrow y'=1-\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{4x\left(x^2-2x-3\right)-2x^2\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}=\dfrac{-4x^2-12x}{\left(x^2-2x-3\right)^2}\)
e. \(y'=1+\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
g. \(y'=\dfrac{\left(4x-4\right)\left(2x+1\right)-2\left(2x^2-4x+5\right)}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}=\dfrac{4x^2+4x-14}{\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
2.
a. \(y'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3.\left(x^2+x+1\right)'=4\left(x^2+x+1\right)^3\left(2x+1\right)\)
b. \(y'=5\left(1-2x^2\right)^4.\left(1-2x^2\right)'=-20x\left(1-2x^2\right)^4\)
c. \(y'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)'=3\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x-1}\right)^2.\left(\dfrac{-3}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\right)=\dfrac{-9\left(2x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
d. \(y'=\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)^3-3\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)^6}=\dfrac{-x^2-6x-5}{\left(x-1\right)^4}\)
e. \(y'=-\dfrac{\left[\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^2\right]'}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+5\right)\left(2x-2\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^4}=-\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x^2-2x+5\right)^3}\)
f. \(y'=4\left(3-2x^2\right)^3.\left(3-2x^2\right)'=-16x\left(3-2x^2\right)^3\)

a) \(y = 2x(x - 3) = 2{x^2} - 6\)
Hàm số có lũy thừa bậc cao nhất của x là bậc hai
b) \(y = x({x^2} + 2) - 5 = {x^3} + 2x - 5\)
Hàm số có lũy thừa bậc cao nhất của x là bậc ba
c) \(y = - 5(x + 1)(x - 4) = - 5{x^2} + 15x + 20\)
Hàm số có lũy thừa bậc cao nhất của x là bậc hai

a) Hàm số \(y = - 3{x^2}\) là hàm số bậc hai.
\(y = - 3.{x^2} + 0.x + 0\)
Hệ số \(a = - 3,b = 0,c = 0\).
b) Hàm số \(y = 2x\left( {{x^2} - 6x + 1} \right)\)\( \Leftrightarrow y = 2{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 2x\) có số mũ cao nhất là 3 nên không là hàm số bậc hai.
c) Hàm số \(y = 4x\left( {2x - 5} \right)\)\( \Leftrightarrow y = 8{x^2} - 20x\) có số mũ cao nhất là 2 nên là hàm số bậc hai.
Hệ số \(a = 8,b = - 20,c = 0\)

\(c,y=2x+2-2x=2\\ d,y=3x-3-x=2x-3\\ f,y=x+\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{x^2+1}{x}\)
Hs bậc nhất là a,b,d,e
\(a,-2< 0\Rightarrow\text{nghịch biến}\\ b,\sqrt{2}>0\Rightarrow\text{đồng biến}\\ d,2>0\Rightarrow\text{đồng biến}\\ e,-\dfrac{2}{3}< 0\Rightarrow\text{nghịch biến}\)