Phân tích thành nhân tử: cos 2x + sin 2x + 3sinx +cos x -2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a) Dat sin x = y
y2 - 3y - 4= 0
y = -1 hoac y = 4 (loai)
voi y = -1 thi sin x = -1 => \(x=-\frac{\pi}{2}+2k\pi\)
b) Chia hai ve cho 2 ta co:
\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}sinx+\frac{1}{2}cosx=sin2x\)
\(cos\frac{\pi}{6}sinx+sin\frac{\pi}{6}cosx=sin2x\)
\(sin\left(x+\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=sin2x\)
\(x+\frac{\pi}{6}=2x+2k\pi\) hoac \(x+\frac{\pi}{6}=\pi-2x+2k\pi\)
\(x=\frac{\pi}{6}-2k\pi\) hoac \(x=-\frac{\pi}{18}+2k\pi\)
Ta thực hiện theo các bước sau :
Bước 1 : Biến đổi
\(a_1\sin^2x+b_1\sin x\cos x+c_1\cos^2x=\left(A\sin x+B\cos x\right)\left(a_2\sin x+b_2\cos x\right)+C\left(\sin^2x+\cos^2x\right)\)
Bước 2 : Khi đó :
\(I=\int\frac{\left(A\sin x+B\cos x\right)\left(a_2\sin x+b_2\cos x\right)+C\left(\sin^2x+\cos^2x\right)}{a_2\sin x+b_2\cos x}\)
\(=\int\left(A\sin x+B\cos x\right)+C\int\frac{dx}{a_2\sin x+b_2\cos x}\)
= \(-A\cos x+B\sin x+\sqrt{\frac{C}{a^2_a+b_2^2}}\int\frac{dx}{\sin\left(x+\alpha\right)}\)
=\(-A\cos x+B\sin x+\frac{C}{\sqrt{a_2^2+b^2_2}}\ln\left|\tan\frac{x+\alpha}{2}\right|+C\)
Trong đó :
\(\sin\alpha=\frac{b_2}{\sqrt{a_2^2}+b^{2_{ }}_2};\cos\alpha=\frac{a_2}{\sqrt{a_2^2}+b^{2_{ }}_2}\)

a/ Hàm xác định trên R
\(y\left(-x\right)=sin^2\left(-2x\right)+1=sin^22x+1=y\left(x\right)\)
Hàm chẵn
b/ Hàm xác định trên R
\(y\left(-x\right)=sin^2\left(-x\right)-cos^2\left(-x\right)=sin^2x-cos^2x=y\left(x\right)\)
Hàm chẵn
c/ Hàm xác định trên R
\(y=sin^2x+cos^2x=1\Rightarrow y\left(-x\right)=1=y\left(x\right)\)
Hàm chẵn
d/ ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\)
Miền xác định của hàm là miền đối xứng
\(y\left(-x\right)=tan\left(-x\right)+3sin\left(-x\right)-7\)
\(=-tanx-3sinx-7\)
Hàm ko chẵn ko lẻ

Ta có :
\(I=\int\frac{dx}{\left(3\tan^2x-2\tan x-1\right)\cos^2x}=\int\frac{d\left(\tan x\right)}{3\tan^2x-2\tan x-1}\)
Đặt \(t=\tan x\Rightarrow I=\int\frac{dt}{3t^2-2t-1}=\frac{1}{3}.\frac{1}{t+\frac{1}{3}}\int\left(\frac{1}{t-1}-\frac{1}{t+\frac{1}{3}}\right)dt\)
= \(\frac{1}{4}\ln\left|\frac{t-1}{t+\frac{1}{3}}\right|=\frac{1}{4}\ln\left|\frac{3t-3}{3t +3}\right|+C\)
Thay trả lại :
\(t=\tan x\Rightarrow I=\frac{1}{4}\ln\left|\frac{3\tan x-3}{3\tan x+1}\right|+C\)

a.
Với \(cosx=0\) ko phải nghiệm
Với \(cosx\ne0\) chia 2 vế cho \(cos^2x\)
\(\Rightarrow-3tanx+tan^2x=2+2tan^2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow tan^2x+3tanx+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=-1\\tanx=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=arctan\left(-2\right)+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
Với \(cosx=0\) không phải nghiệm
Với \(cosx\ne0\) chia 2 vế cho \(cos^2x\)
\(\Rightarrow2tan^2x+tanx-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}tanx=1\\tanx=-\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=arctan\left(-\dfrac{3}{2}\right)+k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)

a.
Thực hiện phép biến đổi tương đương:
\(\dfrac{sinx+cosx-1}{1-cosx}=\dfrac{2cosx}{sinx-cosx+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(sinx+cosx-1\right)\left(sinx-cosx+1\right)=2cosx\left(1-cosx\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2x-\left(cosx-1\right)^2=2cosx-2cos^2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2x-cos^2x+2cosx-1=2cosx-2cos^2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-cos^2x-cos^2x-1=-2cos^2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2cos^2x=-2cos^2x\) (luôn đúng)
Vậy đẳng thức đã cho được chứng minh
b.
\(cot^2x-cos^2x=\dfrac{cos^2x}{sin^2x}-cos^2x=cos^2x\left(\dfrac{1}{sin^2x}-1\right)=\dfrac{cos^2x\left(1-sin^2x\right)}{sin^2x}=cot^2x.cos^2x\)

a) Dễ thấy cosx = 0 không thỏa mãn phương trình đã cho nên chiaw phương trình cho cos2x ta được phương trình tương đương 2tan2x + tanx - 3 = 0.
Đặt t = tanx thì phương trình này trở thành
2t2 + t - 3 = 0 ⇔ t ∈ {1 ; ![]() }.
}.
Vậy ![]()
b) Thay 2 = 2(sin2x + cos2x), phương trình đã cho trở thành
3sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 5cos2x = 2sin2x + 2cos2x
⇔ sin2x - 4sinxcosx + 3cos2x = 0
⇔ tan2x - 4tanx + 3 = 0
⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan3 + kπ, k ∈ Z.
c) Thay sin2x = 2sinxcosx ; ![]() =
= ![]() (sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
(sin2x + cos2x) vào phương trình đã cho và rút gọn ta được phương trình tương đương
![]() sin2x + 2sinxcosx -
sin2x + 2sinxcosx - ![]() cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔
cos2x = 0 ⇔ tan2x + 4tanx - 5 = 0 ⇔ ![]()
⇔ x = ![]() + kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
+ kπ ; x = arctan(-5) + kπ, k ∈ Z.
d) 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x - 4sin2x = -4
⇔ 2cos2x - 3√3sin2x + 4 - 4sin2x = 0
⇔ 6cos2x - 6√3sinxcosx = 0 ⇔ cosx(cosx - √3sinx) = 0
⇔ 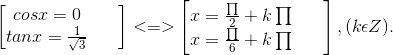

Câu 1 đề sai, chắc chắn 1 trong 2 cái \(cot^2x\) phải có 1 cái là \(cos^2x\)
2.
\(\dfrac{1-sinx}{cosx}-\dfrac{cosx}{1+sinx}=\dfrac{\left(1-sinx\right)\left(1+sinx\right)-cos^2x}{cosx\left(1+sinx\right)}=\dfrac{1-sin^2x-cos^2x}{cosx\left(1+sinx\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1-\left(sin^2x+cos^2x\right)}{cosx\left(1+sinx\right)}=\dfrac{1-1}{cosx\left(1+sinx\right)}=0\)
3.
\(\dfrac{tanx}{sinx}-\dfrac{sinx}{cotx}=\dfrac{tanx.cotx-sin^2x}{sinx.cotx}=\dfrac{1-sin^2x}{sinx.\dfrac{cosx}{sinx}}=\dfrac{cos^2x}{cosx}=cosx\)
4.
\(\dfrac{tanx}{1-tan^2x}.\dfrac{cot^2x-1}{cotx}=\dfrac{tanx}{1-tan^2x}.\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{tan^2x}-1}{\dfrac{1}{tanx}}=\dfrac{tanx}{1-tan^2x}.\dfrac{1-tan^2x}{tanx}=1\)
5.
\(\dfrac{1+sin^2x}{1-sin^2x}=\dfrac{1+sin^2x}{cos^2x}=\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}+tan^2x=\dfrac{sin^2x+cos^2x}{cos^2x}+tan^2x\)
\(=tan^2x+1+tan^2x=1+2tan^2x\)