Tìm min, max của P = x2 + y2 với x, y là các số thực không âm và x + y + xy = 15
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có: \(\left(x-y\right)\left(1-xy\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4}\left(x-y+1-xy\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(x+1\right)^2\left(1-y\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow P\le\dfrac{\left(1+x\right)^2\left(1-y\right)^2}{4\left(1+x\right)^2\left(1+y\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{y^2-2y+1}{y^2+2y+1}\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(1-\dfrac{4y}{y^2+2y+1}\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(P_{max}=\dfrac{1}{4}\) khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;0\right)\)
Lại có:
\(\left(y-x\right)\left(1-xy\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4}\left(y-x+1-xy\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(1+y\right)^2\left(1-x\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow-P\le\dfrac{\left(1+y\right)^2\left(1-x\right)^2}{4\left(1+y\right)^2\left(1+x\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{1-2x+x^2}{1+2x+x^2}\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(1-\dfrac{4x}{x^2+2x+1}\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow-P\le\dfrac{1}{4}\Rightarrow P\ge-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(P_{min}=-\dfrac{1}{4}\) khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;1\right)\)
(Do \(y\ge0\Rightarrow\dfrac{4y}{y^2+2y+1}\ge0\Rightarrow1-\dfrac{4y}{y^2+2y+1}\le1\Rightarrow...\))

Đáp án C.
Ta có
1 = x + y ≥ 2 x y ⇒ x y ≤ 1 2 ⇒ 0 ≤ x y ≤ 1 4
⇒ P = x 2 + x + y 2 + y x y + x + y + 1 = x + y 2 − 2 x y + 1 x y + 1 + 1 = 2 − 2 x y x y + 2
Đặt t = x y ⇒ t ∈ 0 ; 1 4 ⇒ P = 2 − 2 t t + 2 = f t
Bảng biến thiên:
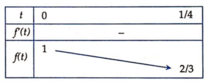
=> M + m = 5 3

1) Áp dụng bất đẳng thức AM - GM và bất đẳng thức Schwarz:
\(P=\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{ab}}\ge\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{a+b}{2}}\ge\dfrac{4}{a+\dfrac{a+b}{2}}=\dfrac{8}{3a+b}\ge8\).
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi a = b = \(\dfrac{1}{4}\).
2.
\(4=a^2+b^2\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\left(a+b\right)^2\Rightarrow a+b\le2\sqrt{2}\)
Đồng thời \(\left(a+b\right)^2\ge a^2+b^2\Rightarrow a+b\ge2\)
\(M\le\dfrac{\left(a+b\right)^2}{4\left(a+b+2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2}{4\left(x+2\right)}\) (với \(x=a+b\Rightarrow2\le x\le2\sqrt{2}\) )
\(M\le\dfrac{x^2}{4\left(x+2\right)}-\sqrt{2}+1+\sqrt{2}-1\)
\(M\le\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{2}-x\right)\left(x+4-2\sqrt{2}\right)}{4\left(x+2\right)}+\sqrt{2}-1\le\sqrt{2}-1\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=2\sqrt{2}\) hay \(a=b=\sqrt{2}\)
3. Chia 2 vế giả thiết cho \(x^2y^2\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{y^2}-\dfrac{1}{xy}\ge\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow0\le\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\le4\)
\(A=\left(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2}+\dfrac{1}{y^2}-\dfrac{1}{xy}\right)=\left(\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)^2\le16\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(x=y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)



\(\left(x^2+9\right)+\left(y^2+9\right)+3\left(x^2+y^2\right)\ge6x+6y+6xy=90\)
\(\Rightarrow4\left(x^2+y^2\right)+18\ge90\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2\ge18\)
\(P_{min}=18\) khi \(x=y=3\)
\(x+y+xy=15\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le15\\y\le15\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\left(x-15\right)\le0\\y\left(y-15\right)\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2\le15x+15y\) (1)
Cũng từ đó ta có: \(\left(x-15\right)\left(y-15\right)\ge0\Rightarrow xy\ge15x+15y-225\)
\(\Rightarrow16x+16y-225\le x+y+xy=15\)
\(\Rightarrow x+y\le15\) (2)
(1);(2) \(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2\le15.15=225\)
\(P_{max}=225\) khi \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(0;15\right);\left(15;0\right)\)