(d1): y=2x
(d2): y=-x+15
tim 2tọa độ giao điểm của (d1) và (d2)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a, PTHDGD: \(x+1=2x+5\Leftrightarrow x=-4\Leftrightarrow y=-3\Leftrightarrow A\left(-4;-3\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-4;-3\right)\) là giao 2 đths
b, PTHDGD: \(5-3x=3-x\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow B\left(1;2\right)\)
Vậy \(B\left(1;2\right)\) là giao 2 đths
c, PTHDGD: \(2x-1=-2x+3\Leftrightarrow x=1\Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow C\left(1;1\right)\)
Vậy \(C\left(1;1\right)\) là giao 2 đths
d, PTHDGD: \(x+2=3x-4\Leftrightarrow x=3\Leftrightarrow y=5\Leftrightarrow D\left(3;5\right)\)
Vậy \(D\left(3;5\right)\) là giao 2 đths

a: 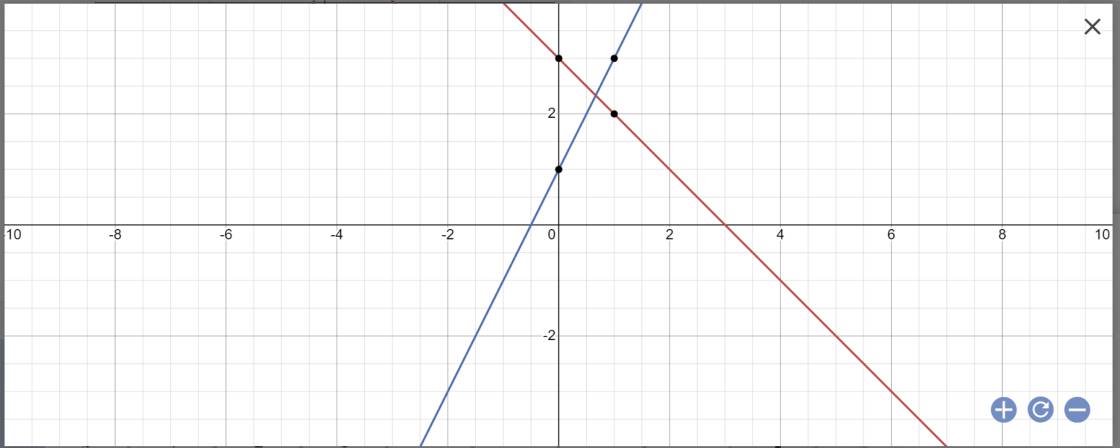
b: Tọa độ giao điểm là nghiệm của hệ phương trình sau:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=-x+3\\y=2x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x=2\\y=2x+1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\y=\dfrac{4}{3}+1=\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(3x+2=x-2\Leftrightarrow x=-2\Leftrightarrow y=-4\Leftrightarrow A\left(-2;-4\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-2;-4\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm

a: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{3}x+m+\dfrac{1}{3}=2x-6m+5\\y=\dfrac{1}{3}x+m+\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{5}{3}x=-7m+5\\y=\dfrac{1}{3}x+m+\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{21}{5}m-3\\y=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(\dfrac{21}{5}m-3\right)+m+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{7}{5}m-1+m+\dfrac{1}{3}=\dfrac{12}{5}m-\dfrac{2}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: Theo đề, ta có: \(\dfrac{12}{5}m-\dfrac{2}{3}=9\cdot\left(\dfrac{21}{5}m-3\right)^2\)
Đến đây bạn chỉ cần giải phương trình bậc hai ra thôi