GIẢI PHƯƠNG TRÌNH X2-5X+6
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


â) thay m = 6 và phương trình ta đc
\(x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm khi: \(\Delta=25-4m\ge0\Rightarrow m\le\dfrac{25}{4}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Pt có 2 nghiệm dương khi \(m>0\)
\(x_1\sqrt{x_2}+x_2\sqrt{x_1}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2x_2+x_2^2x_1+2x_1x_2\sqrt{x_1x_2}=36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+2x_1x_2\sqrt{x_1x_2}=36\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5m+2m\sqrt{m}=36\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{m}=t>0\Rightarrow2t^3+5t^2-36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-2\right)\left(2t^2+9t+18\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t=2\Rightarrow\sqrt{m}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow m=4\)

x2 – 5x + 6 = 0
⇔ x2 – 2x – 3x + 6 = 0
(Tách để xuất hiện nhân tử chung)
⇔ (x2 – 2x) – (3x – 6) = 0
⇔ x(x – 2) – 3(x – 2) = 0
⇔(x – 3)(x – 2) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x – 2 = 0
+ x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3.
+ x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2.
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {2; 3}.

– x 2 + 5x – 6 = 0 ⇔ - x 2 + 2x + 3x – 6 = 0
⇔ - x(x – 2) + 3(x – 2) = 0 ⇔ (x – 2)(3 – x) = 0
⇔ x – 2 = 0 hoặc 3 – x = 0
x – 2 = 0 ⇔ x = 2
3 – x = 0 ⇔ x = 3
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm x = 2 hoặc x = 3.

Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{5}{3}\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2-1}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1-1}=\dfrac{x_1\left(x_1-1\right)+x_2\left(x_2-1\right)}{\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x_1^2+x_2^2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}=\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)}{x_1x_2-\left(x_1+x_2\right)+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)^2-2.\left(-2\right)-\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)}{-2-\left(-\dfrac{5}{3}\right)+1}=...\)

Giải thích các bước giải:
a.Với m=6→x2−5x+6=0→(x−2)(x−3)=0→x∈{2,3}m=6→x2−5x+6=0→(x−2)(x−3)=0→x∈{2,3}
b.Để phương trình có 2 nghiệm x1,x2x1,x2
→Δ=52−4m≥0→m≤254→Δ=52−4m≥0→m≤254
→{x1+x2=5x1x2=m→{x1+x2=5x1x2=m
Mà |x1−x2|=3→(x1−x2)2=9|x1−x2|=3→(x1−x2)2=9
→(x1+x2)2−4x1x2=9→(x1+x2)2−4x1x2=9
→52−4m=9→52−4m=9
→m=−4
a, khi m=6 thì pt\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-2x\right)-\left(3x-6\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-3\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b,Ta có:\(\Delta=\left(-5\right)^2-4.1.m=25-4m\)
để pt có 2 nghiệm x1, x2 phân biệt thì \(\Delta>0\) hay \(25-4m>0\Rightarrow m< \dfrac{25}{4}\)

\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+...+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}+\dfrac{1}{x+3}-\dfrac{1}{x+4}+...+\dfrac{1}{x+5}-\dfrac{1}{x+6}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>1/x+2-1/x+6=1/8
=>\(\dfrac{x+6-x-2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+6\right)}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>x^2+8x+12=32
=>x^2+8x-20=0
=>(x+10)(x-2)=0
=>x=-10 hoặc x=2

a: Thay m=6 vào pt, ta được:
\(x^2-5x+6=0\)
=>x=2 hoặc x=3
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-5\right)^2-4m=-4m+25\)
để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì -4m+25>=0
=>-4m>=-25
hay m<=25/4
Theo đề, ta có:
\(\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow25-4m=9\)
=>m=4
a, Thay m=6 vào pt ta có:
\(x^2-5x+6=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(\Delta\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(-5\right)^2-4.1.m\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{25}{4}\)
Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=5\\x_1x_2=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)^2=3\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2_1+x^2_2-2x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow5^2-4m=9\\ \Leftrightarrow25-4m=9\\ \Leftrightarrow m=4\left(tm\right)\)
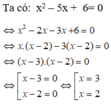

BẠN ƠI MÌNH MỚI HỌC LỚP BẢY
ta có x2-5x+6=x2-2x-3x+6=(x-2)(x-3)
=>x=2 hoặc x=3