Bài 2. Cho đường thẳng (d): y = (m – 1)x + m – 2.
a) Vẽ đường thẳng (d1) khi m = 3.
b) Viết phương trình đường thẳng (d2) song song với đường thẳng (d1) và thỏa mãn
khoảng cách từ gốc tọa độ O đến đường thẳng (d2) bằng 1.
c) Tìm tọa độ điểm cố định mà đường thẳng (d) luôn đi qua với mọi m. Xác định m để
đường thẳng (d) tạo với tia đối của các tia Ox và Oy một tam giác có diện tích nhỏ nhất.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: tọa độ giao điểm M là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=-x+2\\y=2x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

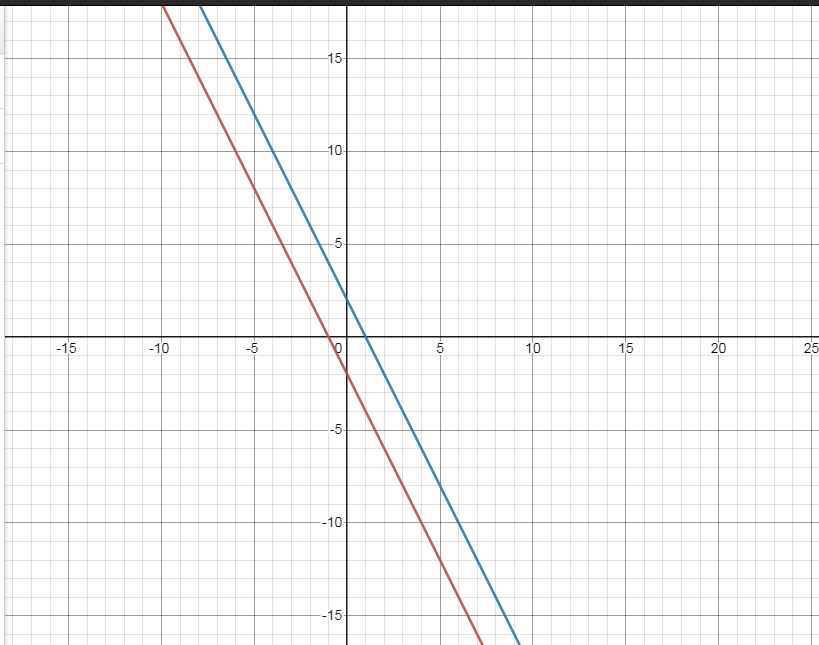
a) \(\left(d_1\right):y=-2x-2\)
\(\left(d_2\right):y=ax+b\)
\(\left(d_2\right)//d_1\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-2\\b\ne-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(d_2\right):y=-2x+b\)
\(M\left(2;-2\right)\in\left(d_2\right)\Leftrightarrow-2.2+b=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b=2\) \(\left(thỏa.đk.b\ne-2\right)\)
Vậy \(\left(d_2\right):y=-2x+2\)
b) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(d_1\right):y=-2x-2\\\left(d_2\right):y=-2x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\left(d_3\right):y=x+m\)
\(\left(d_1\right)\cap\left(d_3\right)=A\left(x;0\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x+m\\y=-2x-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}0=x+m\\0=-2x-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(d_3\right):y=x+1\)

BÀI 1
để d1 và d2 // thì: m-3=-1(1) ; m khác 3 (2)
ta có: (1) <=> m=2 (3)
từ (2) và (3) => để d1//d2 thì m = 2

a: Vì (d1)//y=2x-1 nên a=2
Vậy: (d1): y=2x+b
Thay x=0 và y=0 vào (d1), ta được:
b+0=0
hay b=0

b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x=x-1\\y=x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
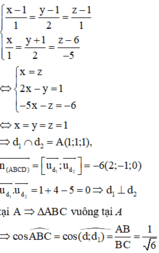
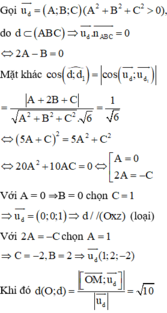
\(a,m=3\Leftrightarrow\left(d_1\right):y=2x+1\\ b,\text{Gọi PT cần tìm là }\left(d_2\right):y=ax+b\left(a\ne0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(d_2\right):y=2x+b\\ \text{PT giao }Ox:y=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{b}{2}\Leftrightarrow A\left(-\dfrac{b}{2};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=\left|\dfrac{b}{2}\right|\\ \text{PT giao }Oy:x=0\Leftrightarrow y=b\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;b\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=\left|b\right|\)
Gọi H là chân đường cao từ O tới \(\left(d_2\right)\Leftrightarrow OH=1\)
Áp dụng HTL: \(\dfrac{1}{OH^2}=\dfrac{1}{OA^2}+\dfrac{1}{OB^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{b^2}+\dfrac{1}{b^2}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{b^2}=1\Leftrightarrow b^2=5\Leftrightarrow b=\pm\sqrt{5}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(\left(d_2\right)\) có dạng \(\left(d_2\right):y=2x+\sqrt{5}\) hoặc \(\left(d_2\right):y=2x-\sqrt{5}\)
\(c,\text{Gọi điểm cần tìm là }A\left(x_0;y_0\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow y_0=mx_0-x_0+m-2\\ \Leftrightarrow m\left(x_0+1\right)-\left(x_0+y_0+2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0+1=0\\x_0+y_0+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_0=-1\\y_0=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow A\left(-1;-1\right)\\ \text{Vậy }A\left(-1;-1\right)\text{ là điểm cố định mà }\left(d\right)\text{ đi qua với mọi }m\)
\(\text{PT giao }Ox:y=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2-m}{m-1}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{2-m}{m-1};0\right)\Leftrightarrow OA=\left|\dfrac{m-2}{m-1}\right|\\ \text{PT giao }Oy:x=0\Leftrightarrow y=m-2\Leftrightarrow B\left(0;m-2\right)\Leftrightarrow OB=\left|m-2\right|\\ \text{Ta có }S_{OAB}=\dfrac{1}{2}OA\cdot OB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\left|\dfrac{m-2}{m-1}\right|\cdot\left|m-2\right|\\ \Leftrightarrow S_{OAB}=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left|m-1\right|}\)
Đặt \(S_{OAB}=t\)
Với \(m\ge1\Leftrightarrow t=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left(m-1\right)}\Leftrightarrow2mt-2t=m^2-4m+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m\left(2-t\right)+2t+4=0\)
PT có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(2-t\right)^2-\left(2t+4\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-6t\ge0\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-6\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t\le0\\t\ge6\end{matrix}\right.\left(1\right)\)
Với \(m< 1\Leftrightarrow t=\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left(1-m\right)}\Leftrightarrow2t-2mt=m^2-4m+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m\left(t-2\right)+4-2t=0\)
PT có nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(t-2\right)^2-\left(4-2t\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-2t\ge0\Leftrightarrow t\left(t-2\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t\le0\\t\ge2\end{matrix}\right.\left(2\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow t\ge6\)
Vậy \(\left(S_{OAB}\right)_{min}=6\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(m-2\right)^2}{2\left|m-1\right|}=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\left|m-1\right|=m^2-4m+4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}12\left(m-1\right)=m^2-4m+4\left(m\ge1\right)\\12\left(1-m\right)=m^2-4m+4\left(m< 1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m^2-16m+16=0\\m^2+8m-8=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=8\pm4\sqrt{3}\\m=-4\pm2\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)