a. (2x - 5)2 + (4x - 10)(2 + x) + x2 + 4x + 4 = 0
b. ( 3 – x2 + 5x )( x2 – 5x + 3) = 9
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


A = - 3\(x\).(\(x-5\)) + 3(\(x^2\) - 4\(x\)) - 3\(x\) - 10
A = - 3\(x^2\) + 15\(x\) + 3\(x^2\) - 12\(x\) - 3\(x\) - 10
A = (- 3\(x^2\) + 3\(x^2\)) + (15\(x\) - 12\(x\) - 3\(x\)) - 10
A = 0 + (3\(x-3x\)) - 10
A = 0 - 10
A = - 10

a)
3 · x 2 + x 2 - 2 x 2 + x - 1 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt t = x 2 + x ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 3 t 2 – 2 t – 1 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2) : Có a = 3 ; b = -2 ; c = -1
⇒ a + b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm t 1 = 1 ; t 2 = c / a = - 1 / 3 .
+ Với t = 1 ⇒ x 2 + x = 1 ⇔ x 2 + x – 1 = 0 ( * )
Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -1 ⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 1 ) = 5 > 0
(*) có hai nghiệm
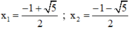
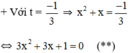
Có a = 3; b = 3; c = 1 ⇒ Δ = 3 2 – 4 . 3 . 1 = - 3 < 0
⇒ (**) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm 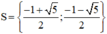
b)
x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 0 ⇔ x 2 − 4 x + 2 2 + x 2 − 4 x + 2 − 6 = 0 ( 1 )
Đặt x 2 – 4 x + 2 = t ,
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 + t – 6 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = 1; c = -6
⇒ Δ = 1 2 – 4 . 1 . ( - 6 ) = 25 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm
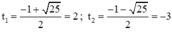
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = 2
⇔ x 2 – 4 x = 0
⇔ x(x – 4) = 0
⇔ x = 0 hoặc x = 4.
+ Với t = -3 ⇒ x 2 – 4 x + 2 = - 3
⇔ x2 – 4x + 5 = 0 (*)
Có a = 1; b = -4; c = 5 ⇒ Δ ’ = ( - 2 ) 2 – 1 . 5 = - 1 < 0
⇒ (*) vô nghiệm.
Vậy phương trình ban đầu có tập nghiệm S = {0; 4}.
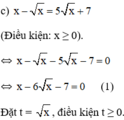
Khi đó (1) trở thành: t 2 – 6 t – 7 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -6; c = -7
⇒ a – b + c = 0
⇒ (2) có nghiệm t 1 = - 1 ; t 2 = - c / a = 7 .
Đối chiếu điều kiện chỉ có nghiệm t = 7 thỏa mãn.
+ Với t = 7 ⇒ √x = 7 ⇔ x = 49 (thỏa mãn).
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x = 49.
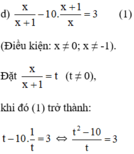
⇔ t 2 – 10 = 3 t ⇔ t 2 – 3 t – 10 = 0 ( 2 )
Giải (2): Có a = 1; b = -3; c = -10
⇒ Δ = ( - 3 ) 2 - 4 . 1 . ( - 10 ) = 49 > 0
⇒ (2) có hai nghiệm:
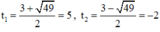
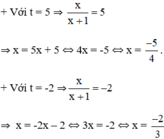
Cả hai nghiệm đều thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm 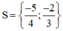

a) \(\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x-2=0\\4x+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};-\dfrac{5}{4}\right\}\)
b) \(\left(2,3x-6,9\right)\left(0,1x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2,3x-6,9=0\\0,1x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-20\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\left(4x+2\right)\left(x^2+1\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+1\ge1>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow4x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)
d) \(\left(2x+7\right)\left(x-5\right)\left(5x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+7=0\\x-5=0\\5x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\\x=5\\x=-\dfrac{1}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{7}{2};5;-\dfrac{1}{5}\right\}\)
e) \(\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)\left(x^2+2\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+2\ge2>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(2x+7\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\2x+7=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=-\dfrac{7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
f) \(\left(3x+2\right)\left(x^2-1\right)=\left(9x^2-4\right)\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(3x+2\right)\left(x+1\right)\right].\left(x-1-3x+2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2+5x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3x^2+3x+2x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[3x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)\right]\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\3x+2=0\\-2x+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-1;-\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{1}{2}\right\}\)

1) \(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x+3\right)\left(x^2-4x-6\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}x^3-2x^2-3x+3x^2-12x-18\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}x^3+x^2-15x-18\)
2) \(\left(6x^2-9x+15\right)\left(\dfrac{2}{3}x+1\right)\)
\(=4x^3+6x^2-6x^2-9x+10x+15\)
\(=4x^3+x+15\)
3) Ta có: \(\left(3x^2-x+5\right)\left(x^3+5x-1\right)\)
\(=3x^5+15x^2-3x^2-x^4-5x^2+x+5x^3+25x-5\)
\(=3x^5-x^4+5x^3+10x^2+26x-5\)
4) Ta có: \(\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\)
\(=x^3-2x^2-x+2\)

`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
`1.`
\(\left(-4xy\right)\cdot\left(2xy^2-3x^2y\right)\)
`=`\(\left(-4xy\right)\left(2xy^2\right)+\left(-4xy\right)\left(-3x^2y\right)\)
`=`\(-8\left(x\cdot x\right)\left(y\cdot y^2\right)+12\left(x\cdot x^2\right)\left(y\cdot y\right)\)
`=`\(-8x^2y^3+12x^3y^2\)
`2.`
\(\left(-5x\right)\left(3x^3+7x^2-x\right)\)
`=`\(\left(-5x\right)\left(3x^3\right)+\left(-5x\right)\left(7x^2\right)+\left(-5x\right)\left(-x\right)\)
`=`\(-15x^4-35x^3+5x^2\)
`3.`
\(\left(3x-2\right)\left(4x+5\right)-6x\left(2x-1\right)\)
`=`\(3x\left(4x+5\right)-2\left(4x+5\right)-12x^2+6x\)
`=`\(12x^2+15x-8x-10-12x^2+6x\)
`=`\(\left(12x^2-12x^2\right)+\left(15x-8x+6x\right)-10\)
`=`\(13x-10\)
`4.`
\(2x^2\left(x^2-7x+9\right)\)
`=`\(2x^2\cdot x^2+2x^2\cdot\left(-7x\right)+2x^2\cdot9\)
`=`\(2x^4-14x^3+18x^2\)
`5.`
\(\left(3x-5\right)\left(x^2-5x+7\right)\)
`=`\(3x\left(x^2-5x+7\right)-5\left(x^2-5x+7\right)\)
`=`\(3x^3-15x^2+21x-5x^2+25x-35\)
`=`\(3x^3-20x^2+46x-35\)

Bài 1:
a) (3x - 2)(4x + 5) = 0
<=> 3x - 2 = 0 hoặc 4x + 5 = 0
<=> 3x = 2 hoặc 4x = -5
<=> x = 2/3 hoặc x = -5/4
b) (2,3x - 6,9)(0,1x + 2) = 0
<=> 2,3x - 6,9 = 0 hoặc 0,1x + 2 = 0
<=> 2,3x = 6,9 hoặc 0,1x = -2
<=> x = 3 hoặc x = -20
c) (4x + 2)(x^2 + 1) = 0
<=> 4x + 2 = 0 hoặc x^2 + 1 # 0
<=> 4x = -2
<=> x = -2/4 = -1/2
d) (2x + 7)(x - 5)(5x + 1) = 0
<=> 2x + 7 = 0 hoặc x - 5 = 0 hoặc 5x + 1 = 0
<=> 2x = -7 hoặc x = 5 hoặc 5x = -1
<=> x = -7/2 hoặc x = 5 hoặc x = -1/5

Lời giải:
1.
$4x+9=0$
$4x=-9$
$x=\frac{-9}{4}$
2.
$-5x+6=0$
$-5x=-6$
$x=\frac{6}{5}$
3.
$x^2-1=0$
$x^2=1=1^2=(-1)^2$
$x=\pm 1$
4.
$x^2-9=0$
$x^2=9=3^2=(-3)^2$
$x=\pm 3$
5.
$x^2-x=0$
$x(x-1)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x-1=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=1$
6.
$x^2-2x=0$
$x(x-2)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x-2=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=2$
7.
$x^2-3x=0$
$x(x-3)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x-3=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=3$
8.
$3x^2-4x=0$
$x(3x-4)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $3x-4=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=\frac{4}{3}$
\(a,\Rightarrow\left(2x-5\right)^2+2\left(2x-5\right)\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)^2=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(2x-5+x+2\right)^2=0\\ \Rightarrow3x-3=0\\ \Rightarrow x=1\\ b,\Rightarrow9-\left(x^2-5x\right)^2=9\\ \Rightarrow x^2-5x=0\\ \Rightarrow x\left(x-5\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=5\end{matrix}\right.\)