Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đáp án B
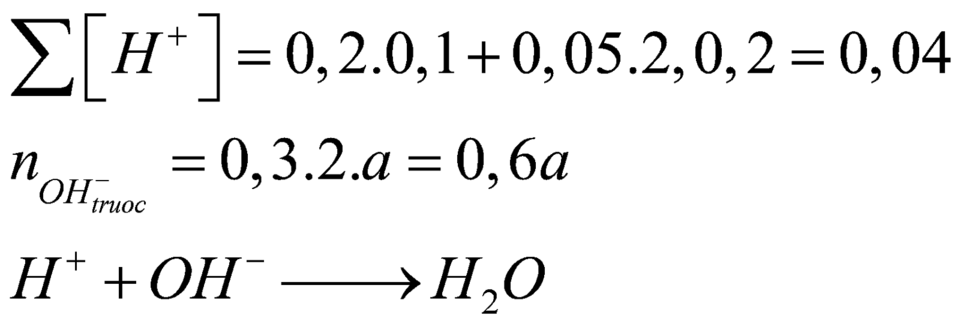
Mà sau phản ứng thu được dung dịch bazo có ph=13 (500ml)nên ta có
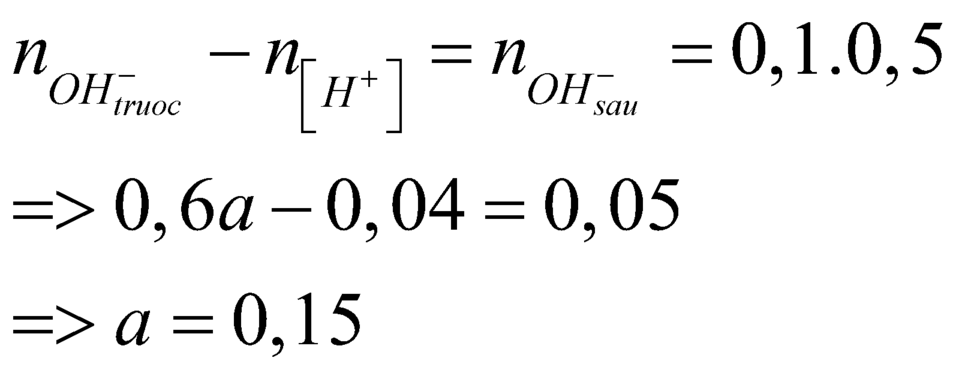
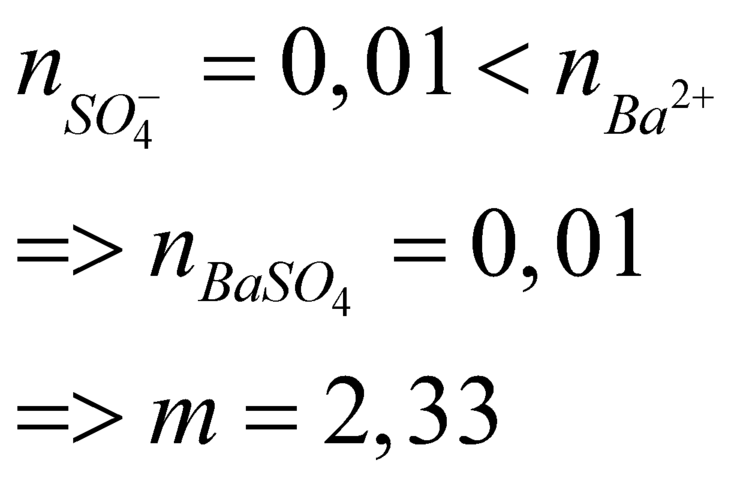

Đáp án B
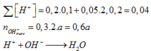
Mà sau phản ứng thu được dung dịch bazo có ph=13 (500ml)nên ta có
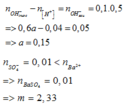

a, \(n_{HCl}=0,2.0,1=0,02\left(mol\right)=n_{H^+}=n_{Cl^-}\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=0,2.0,15=0,03\left(mol\right)=n_{SO_4^{2-}}\) \(\Rightarrow n_{H^+}=2n_{H_2SO_4}=0,06\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Sigma n_{H^+}=0,02+0,06=0,08\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,3.0,05=0,015\left(mol\right)=n_{Ba^{2+}}\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{OH^-}=2n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,03\left(mol\right)\)
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
0,03___0,03 (mol) ⇒ nH+ dư = 0,05 (mol)
\(Ba^{2+}+SO_4^{2-}\rightarrow BaSO_4\)
0,015___0,015______0,015 (mol) ⇒ nSO42- dư = 0,015 (mol)
⇒ m = mBaSO4 = 0,015.233 = 3,495 (g)
\(\left[Cl^-\right]=\dfrac{0,02}{0,2+0,3}=0,04\left(M\right)\)
\(\left[H^+\right]=\dfrac{0,05}{0,2+0,3}=0,1\left(M\right)\)
\(\left[SO_4^{2-}\right]=\dfrac{0,015}{0,2+0,3}=0,03\left(M\right)\)
b, pH = -log[H+] = 1

Đáp án : A
dd X : nH+ = 2nH2SO4 + nHCl = 0,02 mol
dd Y : nOH = nNaOH + 2nBa(OH)2 = 0,04 mol
=> Trong Y : nOH – nH+ = 0,02 mol = nOH- => COH = 0,1M => pH = 13


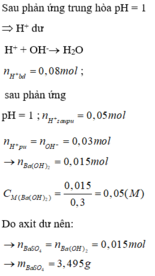
Ta có
\(\text{nHCl=0,2.0,1=0,02(mol)}\)
\(\text{nH2SO4=0,2.0,05=0,01(mol)}\)
2HCl+Ba(OH)2\(\rightarrow\)BaCl2+2H2O
H2SO4+Ba(OH)2\(\rightarrow\)BaSO4+2H2O
Ta có pH=13\(\rightarrow\)Ba(OH)2 dư
pH=13\(\rightarrow\)pOH=1\(\Rightarrow\)CM[OH-]=0,1(M)
\(\rightarrow\)CMBa(OH)2 dư=0,05(M)
\(\text{nBa(OH)2 dư=0,05.0,5=0,025(mol)}\)
\(\text{m=0,01.233=2,33(g)}\)
nBa(OH)2=0,025+0,02/2+0,01=0,045(mol)
\(\rightarrow\)a=\(\frac{0,045}{0,3}\)=0,15(M)