Cho hàm số \(y=\frac{1}{2}x^2\) có đồ thị (P).
a) Vẽ đồ thị (P) của hàm số.
b) Tìm tọa độ giao điểm của đồ thị (P) và đường thẳng d có phương trình y = x + 4.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Pt hoành độ giao điểm:
\(-x^2+2x+3=-2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2+\sqrt{6}\Rightarrow y=-3-2\sqrt{6}\\x=2-\sqrt{6}\Rightarrow y=-3+2\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm là: \(\left(2+\sqrt{6};-3-2\sqrt{6}\right)\)
Và \(\left(2-\sqrt{6};-3+2\sqrt{6}\right)\)
\(\left(P\right):y=-x^2+2x+3\\ \left(d\right):y=-2x+1\)
xét phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của (P) và (d)
\(-x^2+2x+3=-2x+1\)
\(< =>-x^2+4x+2=0\)
\(< =>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2+\sqrt{6}\\x=2-\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
thay vào (d) => \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2+\sqrt{6}=>y=-3-2\sqrt{6}\\x=2-\sqrt{6}=>y=-3+2\sqrt{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy ...

b: PTHĐGĐ là:
1/2x^2-x-4=0
=>x^2-2x-8=0
=>(x-4)(x+2)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-2
=>y=8 hoặc y=2
a: 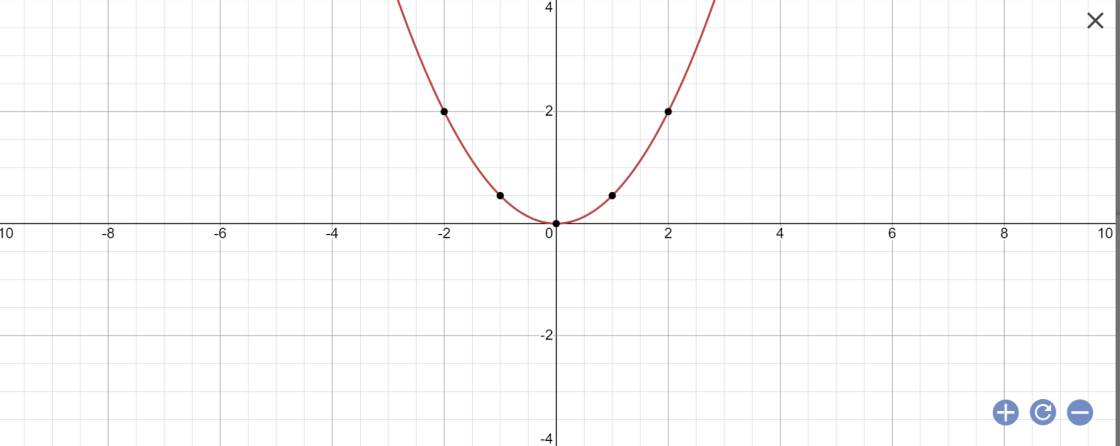

b. PTHĐGĐ của hai hàm số:
\(x+2=-2x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Thay x vào hs đầu tiên: \(y=-\dfrac{1}{3}+2=\dfrac{5}{3}\)
Tọa độ điểm \(A\left(-\dfrac{1}{3};\dfrac{5}{3}\right)\)
b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2=-2x+1\\y=x+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\y=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a) Đồ thị:
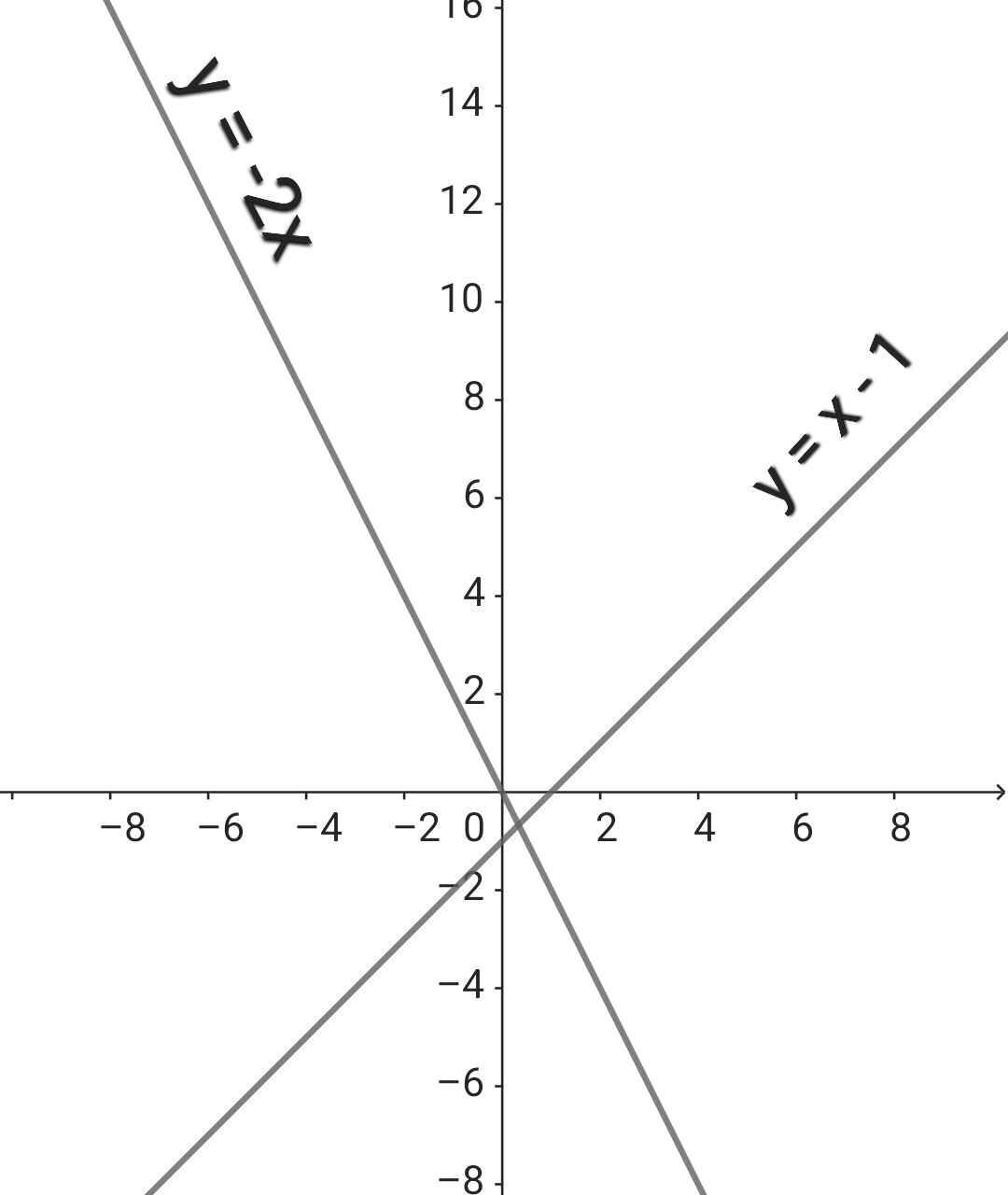
b) Gọi giao điểm của đồ thị của hàm số y = x - 1 với trục tung, với trục hoành lần lượt là 2 điểm B và C
Thay x = 0 vào hàm số y = x - 1 ta có:
y = 0 - 1 = - 1
⇒ B(0; -1)
Thay y = 0 vào hàm số y = x - 1 ta có:
x - 1 = 0
⇔ x = 1
⇒ C(1; 0)
c) Gọi (t): y = ax + b (a 0)
Do (t) // (d) nên a = -2
⇒ (t): y = -2x + b
Thay y = -3 vào (d') ta có:
x - 1 = -3
⇔ x = -3 + 1
⇔ x = -2
Thay x = -2; y = -3 vào (t) ta có:
-2.(-2) + b = -3
⇔ 4 + b = -3
⇔ b = -3 - 4
⇔ b = -7
Vậy (t): y = -2x - 7

\(b,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }x+2=-2x+1\Leftrightarrow3x=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{5}{3}\Leftrightarrow A\left(-\dfrac{1}{3};\dfrac{5}{3}\right)\\ c,\text{Gọi }y=ax+b\left(a\ne0\right)\text{ là đt cần tìm}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2;b\ne1\\-\dfrac{1}{3}a+b=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=\dfrac{7}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow y=2x+\dfrac{7}{3}\)
b: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}x^2-x-4=0\\y=x+4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x-8=0\\y=x+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-4\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\\y=x+4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(x,y\right)\in\left\{\left(4;8\right);\left(-2;2\right)\right\}\)