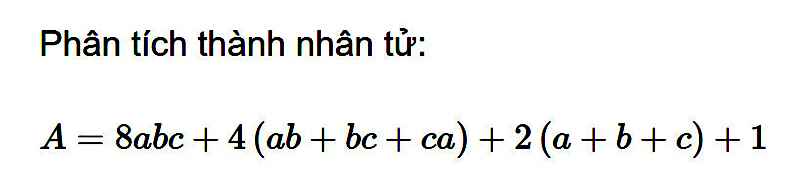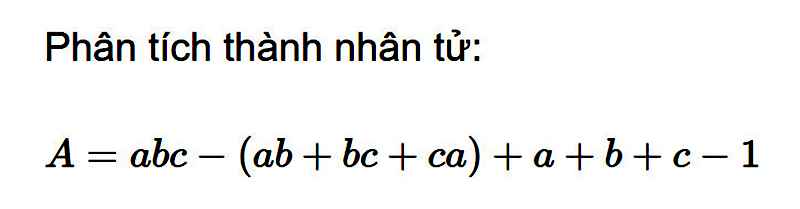Cho a,b,c ≥ 1. Chứng minh rằng: \(\dfrac{1}{1+a^3}+\dfrac{1}{1+b^3}+\dfrac{1}{1+c^3}\)≥\(\dfrac{3}{1+abc}\)
ai giúp mik câu này vs, mik đang cần gấp
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Vì \(\dfrac{1}{2}\ne2=\dfrac{2}{1}\)
nên hệ luôn có nghiệm duy nhất
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2y=m-1\\2x+y=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y=2m-2\\2x+y=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+4y-2x-y=2m-2-m+3\\x+2y=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3y=m+1\\x+2y=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{m+1}{3}\\x=m-1-2y=m-1-\dfrac{2}{3}\left(m+1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{m+1}{3}\\x=m-1-\dfrac{2}{3}m-\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{1}{3}m-\dfrac{5}{3}=\dfrac{m-5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
xy=-1
=>\(\dfrac{\left(m+1\right)\left(m-5\right)}{9}=-1\)
=>(m+1)(m-5)=-9
=>\(m^2-4m-5+9=0\)
=>\(m^2-4m+4=0\)
=>\(\left(m-2\right)^2=0\)
=>m-2=0
=>m=2(nhận)

\(x^3+ax+b⋮x^2+x-2\)
=>\(x^3+x^2-2x-x^2-x+2+\left(a+3\right)x+b-2⋮x^2+x-2\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+3=0\\b-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-3\\b=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: Để (d) song song với đường thẳng y=-x+2 thì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1=-1\\4\ne2\left(đúng\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>m-1=-1
=>m=0
b: Tọa độ giao điểm của hai đường thẳng y=2x+1 và y=x là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=x\\y=x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x=-1 và y=-1 vào (d), ta được:
\(\left(m-1\right)\cdot\left(-1\right)+4=-1\)
=>-(m-1)=-5
=>m-1=5
=>m=6(nhận)

a: \(\left(a+b\right)=5\)
=>\(\left(a+b\right)^2=5^2=25\)
=>\(a^2+b^2+2ab=25\)
=>\(a^2+b^2=25-2ab=25-2\cdot6=13\)
b: \(\left(a-b\right)^2=a^2+b^2-2ab=13-2\cdot6=1\)
=>\(a-b=\pm1\)
a; (a + b)2 - 2ab
= a2 + 2ab + b2 - 2ab
= a2 + b2 + (2ab - 2ab)
= a2 + b2 + 0
= a2 + b2
vậy a2 + b2 = (a + b)2 - 2ab (1)
Thay a + b = 5 và ab = 6 vào biểu thức (1) ta có:
a2 + b2 = 52 - 2.6 = 25 - 12 = 13
Vậy a2 + b2 = 13

Thay x = 1 và y = 2 vào 2x - y ta có:
\(2\cdot1-2=0\) (1)
THay x = 1 và y= 2 vào 3x - 2y = 11 có:
\(3\cdot1-2\cdot2=-1\) ≠ 11
=> Cặp số (1;2) không phải là nghiệm của hpt: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=0\\3x-2y=11\end{matrix}\right.\)

a; \(x^3\) + 3\(x^2\) + 3\(x\) + 1
= \(x^3\) + 3\(x^2\).1 + 3\(x\).12 + 13
= (\(x\) + 1)3
b; 27y3 - 9y2 + y - \(\dfrac{1}{27}\)
= (3y)3 - 3(3y)2.\(\dfrac{1}{3}\) + 3.(3y).(\(\dfrac{1}{3}\))2 - (\(\dfrac{1}{3}\))3
= (3y - \(\dfrac{1}{3}\))3

\(A=8abc+4\left(ab+bc+ca\right)+2\left(a+b+c\right)+1\\= 8abc+4ab+4bc+4ca+2a+2b+2c+1\\ =\left(8abc+4ab\right)+\left(4bc+2b\right)+\left(4ca+2a\right)+\left(2c+1\right)\\ =4ab\left(2c+1\right)+2b\left(2c+1\right)+2a\left(2c+1\right)+\left(2c+1\right)\\ =\left(2c+1\right)\left(4ab+2b+2a+1\right)\\ =\left(2c+1\right)\left[\left(4ab+2b\right)+\left(2a+1\right)\right]\\ =\left(2c+1\right)\left[2b\left(2a+1\right)+\left(2a+1\right)\right]\\ =\left(2c+1\right)\left(2a+1\right)\left(2b+1\right)\)

\(A=abc-\left(ab+bc+ca\right)+a+b+c-1\\ =abc-ab-bc-ca+a+b+c-1\\ =\left(abc-ab\right)+\left(-bc+b\right)+\left(-ca+a\right)+\left(c-a\right)\\ =ab\left(c-1\right)-b\left(c-1\right)-a\left(c-1\right)+\left(c-1\right)\\ =\left(ab-b-a+1\right)\left(c-1\right)\\ =\left[b\left(a-1\right)-\left(a-1\right)\right]\left(c-1\right)\\ =\left(a-1\right)\left(b-1\right)\left(c-1\right)\)