Câu 2.(1,5 điểm) Tìm x, biết:
a) 5x(x2 – 9) = 0. b) 3(x+3) - x2 - 3x =0. c) x2 – 9x – 10 = 0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(a,15x-5xy\\ =5x\left(3-y\right)\\ b,\left(x^2+1\right)^2-4x^2\\ =\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\\ c,x^2-10x-9y^2+25\\ =\left(x-5\right)^2-9y^2\\ =\left(x-9y-5\right)\left(x+9y-5\right)\)

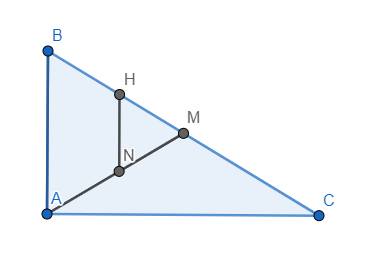
Ta có \(HN\perp AC\) và \(AB\perp AC\) nên AB//HN. Do đó tứ giác ABHN là hình thang (1)
Mặt khác, tam giác ABC vuông tại A có trung tuyến AM nên \(AM=\dfrac{1}{2}BC=BM\), suy ra tam giác MAB cân tại M hay \(\widehat{ABH}=\widehat{NAB}\) (2)
Từ (1) và (2), ta suy ra tứ giác ABHN là hình thang cân. (đpcm)

\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+9+y^2+10y+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2+\left(y+5\right)^2=0\) (1)
Do \(\left(2x-3\right)^2\ge0\) và \(\left(y+5\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x-3\right)=0\\y+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(2x^2-2xy-4x+y^2+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2xy+y^2+x^2-4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)^2+\left(x-2\right)^2=0\left(1\right)\)
mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-y\right)^2\ge0,\forall x;y\\\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0,\forall x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-y\right)^2=0\\\left(x-2\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=0\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)

4\(x^2\) + y2 - 12\(x\) + 10y + 34 = 0
(4\(x^2\) - 12\(x\) + 9) + (y2 + 10y + 25) = 0
(2\(x\) - 3)2 + (y + 5)2 = 0
(2\(x\) - 3)2 ≥ 0 ∀ \(x\); (y + 5)2 ≥ 0 ∀ y
(2\(x-3\))2 + (y + 5)2 = 0 ⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\y+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\) ⇔ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kl: (\(x;y\)) = ( \(\dfrac{3}{2}\); -5)

\(4x^2+y^2-12x+10y+34=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+9+y^2+10y+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2+\left(y+5\right)^2=0\left(1\right)\)
mà \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x-3\right)^2\ge0,\forall x\\\left(y+5\right)^2\ge0,\forall y\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(2x-3\right)^2=0\\\left(y+5\right)^2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\y+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(4x^2+y^2-12x+10y+34=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+9+y^2+10y+25=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-3\right)^2+\left(y+5\right)^2=0\left(1\right)\)
Ta thấy : \(\left(2x-3\right)^2;\left(y+5\right)^2\ge0\)
Nên để (1) thoả mãn :
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\y+5=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy........

\(5^{x+1}-5^x=100\cdot25^{29}\)
\(\Rightarrow5^x\left(5-1\right)=100\cdot\left(5^2\right)^{29}\)
\(\Rightarrow5^x\cdot4=100\cdot5^{58}\)
\(\Rightarrow5^x=\dfrac{100\cdot5^{58}}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow5^x=25\cdot5^{58}\)
\(\Rightarrow5^x=5^{60}\)
\(\Rightarrow x=60\)
\(5^{x+1}-5x=100.25^{29}\)
\(5.5^x-5^x=4.25.25^{29}\)
\(5^x.\left(5-1\right)4.25^{30}\)
\(4.5^x-4.\left(5^2\right)^{30}\)
\(5x=5^{60}\)
\(x=60\)

tham khảo nhé, phần nào thừa thì bạn có thể ko vt
Góc A = 3. góc D
góc A + góc D = 1800
Giải bài toán tổng tỉ trên ta được :
góc A = 180:(1+3).3=1350
góc B - góc C = 30
góc B + góc C = 1800
Giải bài toán tổng hiệu trên ta được :
Góc B = ( 180+30 ) :2 = 1050
Tổng : góc A + góc B = 1350+1050= 2040

A B E I C D H
Xét hình thang ABCD có
\(\widehat{C}=\widehat{D}=80^o\) => ABCD là hình thang cân => AD=BC
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{A}=180^o-\widehat{D}=180^o-80^o=100^o\) (Hai góc trong cùng phía)
Tương tự ta cũng có \(\widehat{B}=100^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{A}=\widehat{B}=100^o\)
Xét tg ABC và tg ABD có
AD=BC (cmt)
\(\widehat{A}=\widehat{B}\) (cmt)
AB chung
=> tg ABD = tg ABC (c.g.c) \(\Rightarrow\widehat{ADB}=\widehat{ACB}\)
Mà \(\widehat{ADB}+\widehat{BDC}=\widehat{ADC}=180^o=\widehat{BCD}=\widehat{ACB}+\widehat{ACD}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{BDC}=\widehat{ACD}=\left(180^o-\widehat{CID}\right):2=60^o\)
=> tg CID là tg đều => CD=CI (1)
Xét tg ABI có
\(\widehat{BAC}=\widehat{ACD}=60^o\) (góc so le trong)
\(\widehat{ABD}=\widehat{BDC}=60^o\) (góc so le trong)
\(\widehat{AIB}=\widehat{CID}=60^o\) (góc đối đỉnh)
=> tg ABI là tg đều
Ta có AE là phân giác \(\widehat{BAI}\) (gt)
=> AE là đường trung trực, đường cao của tg ABI (trong tg đều đường phân giác đồng thời là đường cao, đường trung trực)
Xét tg BIE có
AE đồng thời là đường cao và đường trung trực => tg BIE cân tại E
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{DBC}=\widehat{BIE}\) (góc ở đáy tg cân)
Ta có
\(\widehat{DBC}=\widehat{B}-\widehat{ABD}=100^o-60^o=40^o=\widehat{BIE}\)
=> \(\widehat{BEI}=180^o-\left(\widehat{DBC}+\widehat{BIE}\right)=180^o-\left(40^o+40^o\right)=100^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{IEC}=180^o-\widehat{BEI}=180^o-100^o=80^o\)
Ta có
\(\widehat{BIC}=180^o-\widehat{CID}=180^o-60^o=120^o\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{EIC}=\widehat{BIC}-\widehat{BIE}=120^o-40^o=80^o\)
Xét tg CIE có
\(\widehat{IEC}=\widehat{EIC}=80^o\) => tg CIE cân tại C => CE=CI (2)
Từ (1) và (2) => CE=CD
\(a,5x\left(x^2-9\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2=9\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ b,3\left(x+3\right)-x^2-3x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow3\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(3-x\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\ c,x^2-9x-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x-10x-10=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-10\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-10\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
a, 5\(x\)(\(x^2\) - 9) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x^2-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\) { -3; 0; 3}
b, 3.(\(x+3\)) - \(x^2\) - 3\(x\) = 0
3.(\(x+3\)) - \(x\).( \(x\) + 3) = 0
(\(x+3\))( 3 - \(x\)) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\){ -3; 3}
c, \(x^2\) - 9\(x\) - 10 = 0
\(x^2\) + \(x\) - 10\(x\) - 10 = 0
\(x.\left(x+1\right)\) - 10.( \(x-1\)) = 0
(\(x+1\))(\(x-10\)) = 0
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=0\\x-10=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(x\) \(\in\){ -1; 10}