Giải phương trình: \(\dfrac{1}{x^2}+\sqrt{x+2}=\dfrac{1}{x}+\sqrt{2x+1}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.




Phương pháp 1: nếu đây là dạng bài trong đề thi hsg thì đây là cách giải:
Công thức sử dụng: \(1^2+2^2+...+n^2=\dfrac{n\left(n+1\right)\left(2n+1\right)}{6}\)
Ta đặt: \(B=2^2+4^2+6^2+...+100^2\)
\(B=2^2\cdot\left(1^2+2^2+3^2+...+50^2\right)\) (có n = 50)
\(B=2^2\cdot\dfrac{50\cdot\left(50+1\right)\cdot\left(2\cdot50+1\right)}{6}\)
\(B=171700\)
Ta có: \(A=1^2+3^2+5^2+...+99^2\)
\(A+B=\left(1^2+3^2+5^2+...+99^2\right)+\left(2^2+4^2+6^2+...+100^2\right)\)
\(A+B=1^2+2^2+3^2+...+100^2\) (có n = 100)
\(A+B=\dfrac{100\cdot\left(100+1\right)\cdot\left(2\cdot100+1\right)}{6}\)
\(A+B=3383500\)
\(A=3383500-B=3383500-171700=166650\)
Phương pháp 2: Nếu đây là dạng bài thi hsg trên máy tính cầm tay
Rất đơn giản ta bấm như sau:
\(\sum\limits^{50}_{x=1}\left(2x-1\right)^2\)
Bấm phím "=" để cho ra kq

a.
Do M thuộc parabol \(\Rightarrow y_M=\dfrac{1}{2}x_M^2=\dfrac{1}{2}.1=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow M\left(1;\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\)
Do N thuộc parabol \(\Rightarrow y_N=\dfrac{1}{2}x_N^2=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(-3\right)^2=\dfrac{9}{2}\Rightarrow N\left(-3;\dfrac{9}{2}\right)\)
Gọi pt đường thẳng qua MN có dạng \(y=ax+b\)
Thay tọa độ M, N vào pt đường thẳng ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=\dfrac{1}{2}\\-3a+b=\dfrac{9}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-1\\b=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow y=-x+\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b.
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm (P) và (d):
\(\dfrac{1}{2}x^2=-x+m\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-2m=0\)
\(\Delta'=1+2m>0\Rightarrow m>-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1x_2=-2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(A;B\in\left(d\right)\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y_1=-x_1+m\\y_2=-x_2+m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Từ đó ta có:
\(Q=x_1x_2+y_1y_2-1=-2m+\left(-x_1+m\right)\left(-x_2+m\right)-1\)
\(=-2m+x_1x_2+m^2-m\left(x_1+x_2\right)-1\)
\(=-2m-2m+m^2+2m-1\)
\(=m^2-2m-1=\left(m-1\right)^2-2\ge-2\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi \(m=1\)

Nó chỉ là cái tên (giống như đặt tên tam giác là ABC, MNP gì đó tùy thích).
Góc alpha có số đo bất kì và góc beta sẽ có số đo bất kì nhưng khác với góc alpha.
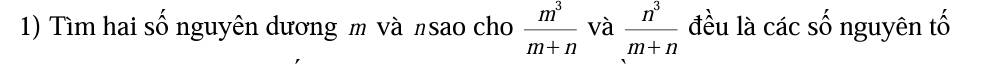
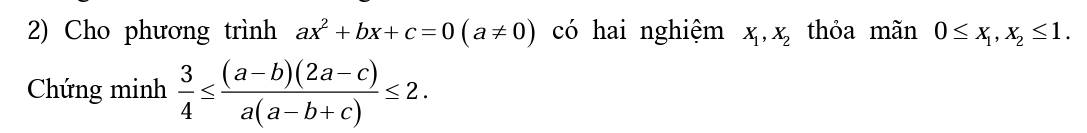
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{2};x\ne0\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2}-\dfrac{1}{x}=\sqrt{2x+1}-\sqrt{x+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{x-1}{x^2}=\dfrac{x-1}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\) (do \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\) luôn dương)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Đk: \(x\ge-\dfrac{1}{2},x\ne0\)
pt \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x^2}-\dfrac{1}{x}=\sqrt{2x+1}-\sqrt{x+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1-x}{x^2}=\dfrac{2x+1-\left(x+2\right)}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1-x}{x^2}=\dfrac{x-1}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\) (vì \(\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2x+1}+\sqrt{x+2}}+\dfrac{1}{x^2}>0\))
Vậy \(S=\left\{1\right\}\)