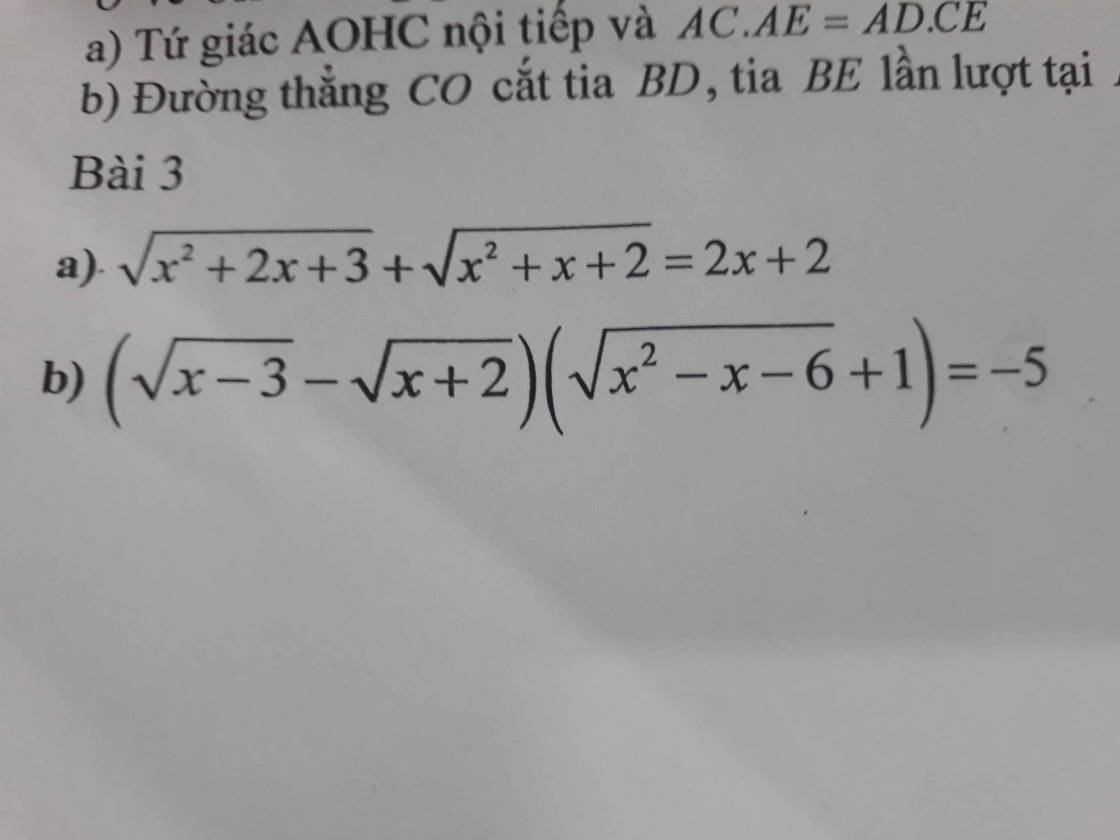Cho các số thực dương x,y,z. Tìm GTNN của biểu thức \(A=\dfrac{x}{y}+\sqrt{\dfrac{y}{z}}+\sqrt[3]{\dfrac{z}{x}}\).
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
Theo định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=2$
$x_1x_2=-6$
Khi đó:
$A=2x_1-x_1x_2+2x_2=2(x_1+x_2)-x_1x_2$
$=2.2-(-6)=4+6=10$

\(A=\dfrac{x^5+x^4+1}{x^3-1}-\dfrac{x^3-x-3}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^5+x^4+1-\left(x^3-x-3\right).\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2+4x+4}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{x-1}\)
Có \(2A=x^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{8}{x-1}=x^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^4-16\right)-\left(x^3-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x+2\right).\left(x^2+4\right)-\left(x-2\right).\left(x^2+2x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right).\left(x^3+x^2+2x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x^3+x^2+2x+4=0\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình (1) dùng máy tính được một nghiệm
x \(\approx-1,4\)

Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiệm $x_1,x_2$ thì $\Delta'=(m+1)^2-4m\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow (m-1)^2\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\neq 1$
Khi đó, áp dụng định lý Viet:
$x_1+x_2=2(m+1)$
$x_1x_2=4m$
Khi đó:
$(x_1+m)(x_2+m)=3m^2+12$
$\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2+m(x_1+x_2)+m^2=3m^2+12$
$\Leftrightarrow 4m+2m(m+1)+m^2=3m^2+12$
$\Leftrightarrow 3m^2+6m=3m^2+12$
$\Leftrightarrow 6m=12$
$\Leftrightarrow m=2$ (tm)

Lời giải:
Áp dụng BĐT AM-GM ta có:
$x^5+x^5+x^5+1+1\geq 5\sqrt[5]{x^{15}}=5x^3$
$y^5+y^5+y^5+1+1\geq 5\sqrt[5]{y^{15}}=5y^3$
$\Rightarrow 3(x^5+y^5)+4\geq 5(x^3+y^3)\geq 10$ (do $x^3+y^3\geq 2$)
$\Leftrightarrow x^5+y^5\geq 2$
Vậy $C_{\min}=2$. Giá trị này đạt tại $x=y=1$

a.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=a>0\\\sqrt{x^2+x+2}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a^2-b^2=x+1\)
Pt trở thành:
\(a+b=2\left(a^2-b^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a+b=\left(2a-2b\right)\left(a+b\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a-2b=1\) (do \(a+b>0\))
\(\Leftrightarrow2a=2b+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=2\sqrt{x^2+x+2}+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2+2x+3\right)=4\left(x^2+x+2\right)+1+4\sqrt{x^2+x+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+3=4\sqrt{x^2+x+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-\dfrac{3}{4}\\16\left(x^2+x+2\right)=\left(4x+3\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-\dfrac{3}{4}\\8x=23\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{23}{8}\)
b.
ĐKXĐ: \(x\ge3\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-3}=a\ge0\\\sqrt{x+2}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a^2-b^2=-5\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(\left(a-b\right)\left(ab+1\right)=a^2-b^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-b\right)\left(ab+1\right)=\left(a-b\right)\left(a+b\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\left(vô-nghiệm\right)\\ab+1=a+b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow ab-a-b+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-1\right)\left(b-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=1\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x-3}=1\\\sqrt{x+2}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)