Một ô tô chayjqua quãng đường AB trong 3 giờ. Giờ đầu chạy được 2/5 quãng đường AB. Giờ thứ hai chạy được 2/5 quãng đường còn lại và thêm 4 km. Giờ thứ 3 chạy nốt 40 km cuối. Tính vận tốc trung bình của ô tô trên quãng đường AB
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


** Bổ sung điều kiện $x,y$ là số nguyên.
Lời giải:
$2x+xy+y=5$
$\Rightarrow (2x+xy)+y=5$
$\Rightarrow x(y+2)+(y+2)=7$
$\Rightarrow (x+1)(y+2)=7$
Do $x,y$ là số nguyên nên $x+1, y+2$ cũng là số nguyên. Mà $(x+1)(y+2)=7$ nên ta có các TH sau:
TH1: $x+1=1, y+2=7$
$\Rightarrow x=0; y=5$
TH2: $x+1=-1, y+2=-7$
$\Rightarrow x=-2; y=-9$
TH3: $x+1=7, y+2=1$
$\Rightarrow x=6; y=-1$
TH4: $x+1=-7, y+2=-1$
$\Rightarrow x=-8; y=-3$
Tìm \(x;y\) \(\in\) Z/ 2\(x+xy+y=5\)
Ta có: 2\(x+xy+y=5\)
⇒ \(x\)(2 + y) + y = 5
\(x\)(2 + y) = 5 - y
\(x\) = \(\dfrac{5-y}{2+y}\) (y ≠ - 2)
\(x\in\) Z ⇔ 5 - y ⋮ 2 + y
7 - 2 - y ⋮ 2 + y
7 - (2 + y) ⋮ 2 + y
7 ⋮ 2 + y
2 + y \(\in\) Ư(7) = {-7; -1; 1; 7}
Lập bảng ta có:
| 2+ y | -7 | -1 | 1 | 7 |
| y | -9 | -3 | -1 | 5 |
| \(x\) = \(\dfrac{5-y}{2+y}\) | -2 | -8 | 6 | 0 |
Theo bảng trên ta có các cặp số nguyên thỏa mãn đề bài là:
(\(x;y\)) = (-2; -9); (-8; -3); (6; -1); (0; 5)

Câu 4:
a: O nằm trên tia đối của tia AB
=>A nằm giữa O và B
=>OB=OA+AB
=>OB=4+6=10(cm)
M là trung điểm của OA
=>\(OM=MA=\dfrac{OA}{2}\)
N là trung điểm của OB
=>\(ON=NB=\dfrac{OB}{2}\)
Vì OA<OB
nên OM<ON
=>M nằm giữa O và N
=>OM+MN=ON
=>\(MN=ON-OM=\dfrac{OB}{2}-\dfrac{OA}{2}=\dfrac{10}{2}-\dfrac{4}{2}=5-2=3\left(cm\right)\)
b: \(MN=ON-OM=\dfrac{OB}{2}-\dfrac{OA}{2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(OB-OA\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AB\) không đổi khi O di chuyển trên tia đối của tia AB

b; 1 + \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) + ... + \(\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) = 1\(\dfrac{2023}{2025}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\).(1 + \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{6}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{10}\) + ... + \(\dfrac{2}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)) = \(\dfrac{4048}{2025}\).\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{1.2}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2.3}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{12}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{20}\) + ... + \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{2024}{2025}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{1.2}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2.3}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{3.4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{4.5}\) + ... + \(\dfrac{1}{x.\left(x+1\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{2024}{2025}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{1}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{3}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{5}\) + ... + \(\dfrac{1}{x}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{2024}{2025}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{1}\) - \(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{2024}{2025}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = 1 - \(\dfrac{2024}{2025}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x+1}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2025}\)
\(x+1\) = 2025
\(x\) = 2025 - 1
\(x=2024\)
Vậy \(x=2024\)

\(S=\dfrac{2}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}\times...\times\dfrac{4046}{4047}\)
\(S< \dfrac{3}{4}\times\dfrac{5}{6}\times...\times\dfrac{4047}{4048}\)
\(S^2< \dfrac{2}{3}\times\dfrac{4}{5}\times...\times\dfrac{4046}{4047}\times\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\times\dfrac{5}{6}\times...\times\dfrac{4047}{4048}\right)\)
\(S^2< \dfrac{2\times3\times4\times5\times...\times4046\times4047}{3\times4\times5\times6\times...\times4047\times4048}\)
\(S^2< \dfrac{2}{4048}\)
⇒ \(S^2< \dfrac{1}{2024}\)

\(C=\dfrac{4}{3\cdot5}+\dfrac{4}{5\cdot7}+\dots+\dfrac{4}{97\cdot99}\)
\(=2\cdot\left(\dfrac{2}{3\cdot5}+\dfrac{2}{5\cdot7}+\dots+\dfrac{2}{97\cdot99}\right)\)
\(=2\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{7}+\dots+\dfrac{1}{97}-\dfrac{1}{99}\right)\)
\(=2\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{99}\right)\)
\(=2\cdot\dfrac{32}{99}=\dfrac{64}{99}\)
\(D=\dfrac{18}{2\cdot5}+\dfrac{18}{5\cdot8}+\dots+\dfrac{18}{203\cdot206}\)
\(=6\cdot\left(\dfrac{3}{2\cdot5}+\dfrac{3}{5\cdot8}+\dots+\dfrac{3}{203\cdot206}\right)\)
\(=6\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{8}+\dots+\dfrac{1}{203}-\dfrac{1}{206}\right)\)
\(=6\cdot\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-\dfrac{1}{206}\right)\)
\(=6\cdot\dfrac{51}{103}=\dfrac{306}{103}\)
Khi đó: \(\dfrac{C}{D}=\dfrac{\dfrac{64}{99}}{\dfrac{306}{103}}=\dfrac{3296}{15147}\)


\(10A=\dfrac{10^{11}+10}{10^{11}+1}=1+\dfrac{9}{10^{11}+1}\)
\(10B=\dfrac{10^{10}+10}{10^{10}+1}=1+\dfrac{9}{10^{10}+1}\)
\(10^{11}+1>10^{10}+1\)
=>\(\dfrac{9}{10^{11}+1}< \dfrac{9}{10^{10}+1}\)
=>\(\dfrac{9}{10^{11}+1}+1< \dfrac{9}{10^{10}+1}+1\)
=>10A<10B
=>A<B
A = \(\dfrac{10^{10}+1}{10^{11}+1}\) < \(\dfrac{10^{10}+1+9}{10^{11}+1+9}\) = \(\dfrac{10^{10}+10}{10^{11}+10}\) = \(\dfrac{10.\left(10^9+1\right)}{10.\left(10^{10}+1\right)}\) = B
Vậy A < B

\(M=\dfrac{1}{1\cdot5}+\dfrac{1}{5\cdot9}+...+\dfrac{1}{n\left(n+4\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{4}{1\cdot5}+\dfrac{4}{5\cdot9}+...+\dfrac{4}{n\left(n+4\right)}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(1-\dfrac{1}{5}+\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{1}{9}+...+\dfrac{1}{n}-\dfrac{1}{n+4}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(1-\dfrac{1}{n+4}\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot\dfrac{n+4-1}{n+4}=\dfrac{n+3}{4\left(n+4\right)}\)
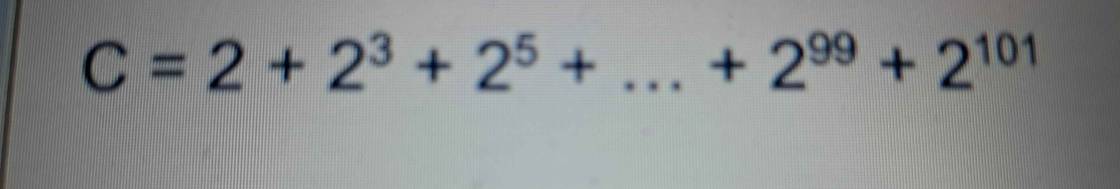

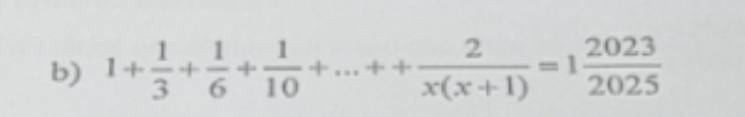
Lời giải:
Coi quãng đường $AB$ dài $x$ km. Sau khi chạy được 2/5 quãng đường đầu thì còn $x-\frac{2}{5}x=\frac{3}{5}x$ (km)
Vậy kể từ giờ thứ hai ô tô còn $\frac{3}{5}x$ km đường. Giờ thứ hai sau khi xe chạy được 2/5 quãng đường thì đi còn 3/5 quãng đường. 3/5 quãng đường này dài: $40+4=44$ (km)
Độ dài quãng đường ô tô đi kể từ giờ thứ hai (tức là $\frac{3}{5}x$) dài:
$44:\frac{3}{5}=73,3$ (km)
Độ dài quãng đường AB là:
$x=73,3:\frac{3}{5}=122$ (km)
Vận tốc trung bình: $122:3=40,7$ (km/h)