3x2+2x-1
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\left(-\dfrac{3x}{5y^2}\right).\left(-\dfrac{5y^2}{6x^3}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-3x.\left(-5y^2\right)}{5y^2.6x^3}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2x^2}\)

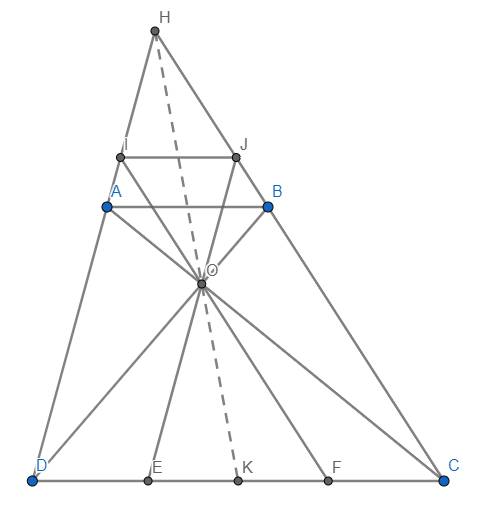
b) Theo Thales: \(\dfrac{DE}{DC}=\dfrac{AO}{AC};\dfrac{CF}{CD}=\dfrac{BO}{BD}\)
Theo câu a thì \(\dfrac{AO}{AC}=\dfrac{BO}{BD}\) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{DE}{DC}=\dfrac{CF}{CD}\Rightarrow DE=CF\) (đpcm)
c) Từ \(DE=CF\Rightarrow\dfrac{DE}{EF}=\dfrac{CF}{EF}\)
Mà theo Thales: \(\dfrac{DE}{EF}=\dfrac{IO}{OF};\dfrac{CF}{EF}=\dfrac{JO}{OE}\)
Do đó \(\dfrac{IO}{OF}=\dfrac{JO}{OE}\) \(\Rightarrow\) IJ//CD//AB
d) Dùng định lý Menelaus đảo nhé bạn. Ta có \(\dfrac{HA}{HD}=\dfrac{AB}{CD}=\dfrac{OA}{OC}\) nê \(\dfrac{HA}{AD}.\dfrac{OC}{OA}=1\). Do K là trung điểm EF mà \(DE=CF\) nên K cũng là trung điểm CD hay \(\dfrac{KD}{KC}=1\). Do đó \(\dfrac{HA}{AD}.\dfrac{KD}{KC}.\dfrac{OC}{OA}=1\). Theo định lý Menalaus đảo \(\Rightarrow\)H, O, K thẳng hàng (đpcm)


Biểu thức không có giá trị nhỏ nhất nhé. Bạn xem lại đã viết biểu thức đúng chưa nhỉ?


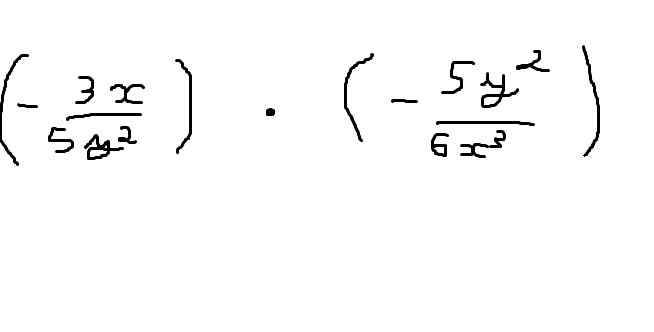
3x² + 2x - 1
= 3x² + 3x - x - 1
= (3x² + 3x) - (x + 1)
= 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1)
= (x + 1)(3x - 1)
3x² + 2x - 1
= 3x² + 3x - x - 1
= (3x² + 3x) - (x + 1)
= 3x(x + 1) - (x + 1)
= (x + 1)(3x - 1)